Inversion Count for an array indicates – how far (or close) the array is from being sorted. If the array is already sorted, then the inversion count is 0,
but if the array is sorted in the reverse order, the inversion count is the maximum.
Formally speaking, two elements a[i] and a[j] form an inversion if a[i] > a[j] and i < j
Input: arr[] = {8, 4, 2, 1}
Output: 6
Explanation: Given array has six inversions:
(8, 4), (4, 2), (8, 2), (8, 1), (4, 1), (2, 1).
Input: arr[] = {3, 1, 2}
Output: 2
Explanation: Given array has two inversions:
(3, 1), (3, 2)
Recursive program to replace all occurrences of pi with 3.14 in a given string
Input : str = “pippppiiiipi”
Output : 3.14ppp3.14iii3.14
Input : str = “pip”
Output : 3.14p
Input : str = “xpix”
Output : x3.14x
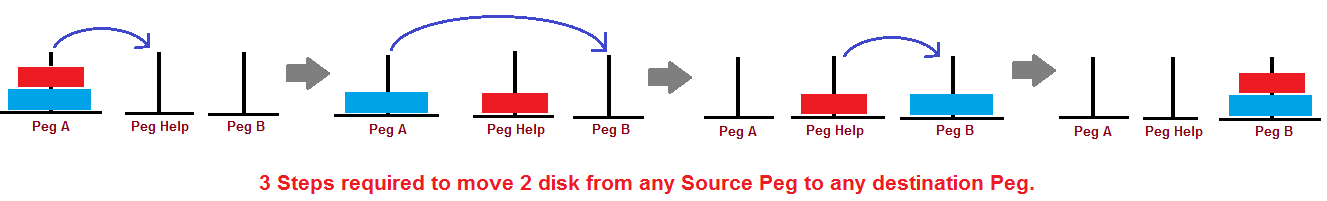
Tower of Hanoi is a mathematical game or puzzle involving three sticks and a number of different discs,
which can slip on any stick/rod. The paradox begins with discs embedded in the same object in a declining size(descending order),
the smallest at the top, thus almost showing a conical shape.
Here are three simple rules:
- Only one disk can be moved at a time.
- Each movement involves taking a disk above one of the stacks and placing it on top of another stack.
In other words, the disk can only be moved if it is the highest disk in the stack. - No larger disk can be placed on a smaller disk.
Input : 2
Output : Disk 1 moved from X to Y
Disk 2 moved from X to Z
Disk 1 moved from Y to Z
Explanation:
Taking the example for 2 disks :
Let rod 1 = 'X', rod 2 = 'Y', rod 3 = 'Z'.
Step 1 : Shift first disk from 'X' to 'Y'.
Step 2 : Shift second disk from 'X' to 'Z'.
Step 3 : Shift first disk from 'Y' to 'Z'.
The pattern here is :
Shift 'n-1' disks from 'X' to 'Y'.
Shift last disk (nth) from 'X' to 'Y'.
Shift 'n-1' disks from 'Y' to 'Z'.
START
Procedure Hanoi(disk, source, destination, auxillary)
IF disk == 1, THEN
move disk from source to destination
ELSE
Hanoi(disk - 1, source, auxillary, destination) // Step 1
move disk from source to destination // Step 2
Hanoi(disk - 1, auxillary, destination, source) // Step 3
END IF
END Procedure
STOP
- Time Complexity : O(n)
- Space Complexity : O(n)
- The Tower of Hanoi puzzle is sensitive to previous damage and malfunction. The level of complexity can be easily increased or decreased with additional discs.
- The Hanoi Tower cannot be used independently to understand and evaluate higher brain functions.
The least common multiple (LCM) of two integers is the smallest positive integer that is a multiple of both. The greatest common divisor (GCD) of two integers is the largest positive integer dividing both. The product of the two numbers is the product of the LCM and the GCD.
The process in which a function calls itself directly or indirectly is called recursion and the corresponding function is called as recursive function. Using recursive algorithm, certain problems can be solved quite easily. Examples of such problems are Towers of Hanoi (TOH), Inorder/Preorder/Postorder Tree Traversals, DFS of Graph, etc.
- Read two numbers a and b
- If(a is equal to 0) return b
- If(b is equal to 0) return a
- else return (b, a mod b)
- Read two numbrs a and b
- return (a x b) / GCD(a, b)
- Time Complexity:
O(n) - Space complexity:
O(n)
- The logic used by the program is simple to understand
- time complexity of this program is less compared to other methods for finding GCD and LCM
- As recursion uses stack, for large numbers, memory may become full due to stack full