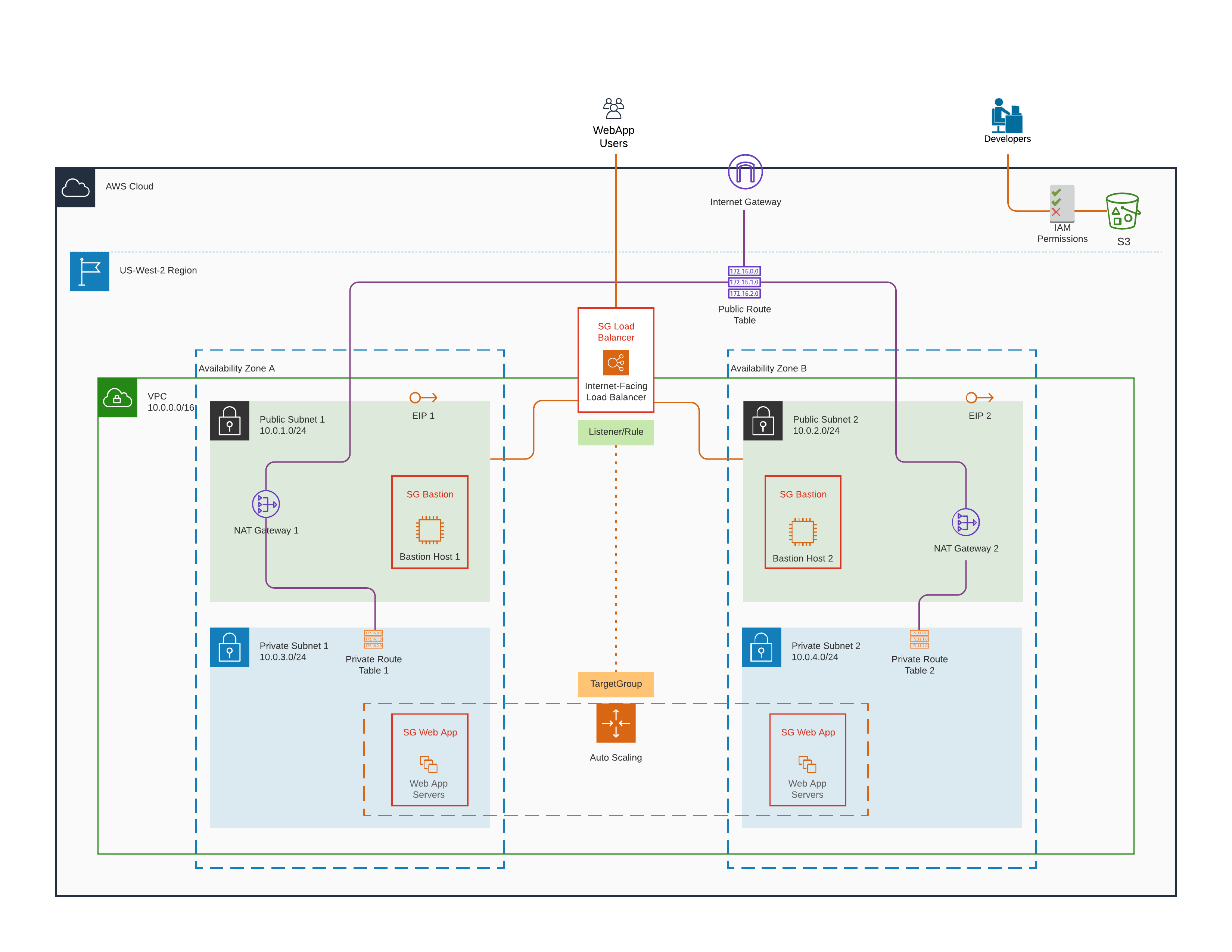
Infrastructure-as-code (IAC) that automates the process of creating a secured and high-availability environment and deploying an application (packaged and staged in AWS S3 Storage) into a dockerized Apache Web Server. The script contains all the configurations needed for a repeatable process so that the infrastructure can be discarded and recreated at will multiple times.
1. Load-balanced servers with auto-scaling capability across two availability zones within a single region.
2. Server/instance specification: 2vCPUs, 4GB RAM, 10GB disk space.
3. Linux Operating System using the Ubuntu distribution machine image.
4. Compute instances are secured in a private subnet and only accepts traffic originating from a bastion host and load-balancer both within a public subnet.
5. Each availability zone contain a bastion host to enable SSH to instances in each of the private subnets for debugging and troubleshooting.
6. Load-balancer, bastion host, and application servers have security groups defined with only needed ports opened.
7. Application servers have outbound internet access via NAT gateway for critical OS updates and patches.
8. Sample application code is packaged and stored in an S3 bucket with IAM permissions.
9. Application servers are configured with IAM instance profile to be able to access and download application code from AWS S3 bucket.
10. Application code is deployed in a dockerized apache web server for added security and isolation.
11. Health checks and thresholds are defined to aid in system availability detection. Metrics are collected, aggregated, and monitored via AWS CloudWatch.
12. Entire environment is fully virtualized in a cloud platform that can be taken down and brought back up within a short period of time. The process of creating and starting all the services, spinning up instances are automated via scripts in this repo.
Steps from #2 to #6 below are manual tasks for now but will be scripted in the next release.
1. AWS account - Make sure you have an AWS account created and most importantly for Amazon, billing information setup :)
2. aws cli is installed and configured. To test, run the aws commands below.
aws --version
or
aws s3 ls
3. Create an S3 storage in your AWS account and upload the sample code udacity.zip. Take note of the name you assigned to your S3 storage.
4. Apply the Bucket Policy below. Replace the text <REPLACE ME> from the policy below with the name of the S3 storage created in the previous step.
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Id": "Policy1564815775429",
"Statement": [
{
"Sid": "Stmt1564815768845",
"Effect": "Allow",
"Principal": {
"Service": "ec2.amazonaws.com"
},
"Action": "s3:ListBucket",
"Resource": "arn:aws:s3:::<REPLACE ME>"
}
]
}5. Edit the servers-params.json file and update/replace the value of S3CodeRepo with the full S3 path and file name of udacity.zip. See AWS S3 console.
6. Create a Key Pair in AWS EC2 and take note of the name assigned to the key pair. Alternatively, upload the sample PEM file included in this repo.
7. Edit the servers-params.json file and update/replace the value of KeyPairName with the key pair name created in the previous step.
1. Clone the git repository
2. There are two components to standing up our environment in AWS: infra and servers. Infrastructure are the VPCs, gateways, subnets, and routing. Servers are the compute resources, load-balancers, and auto-scaling.
Infrastructure must be setup first. Run the command below with an arbitrary stack name e.g. 'infra'
./aws_cu <stack name> infra-config.yml infra-params.json
Once infrastructure has been completed (by checking AWS CloudFormation for stack status), run the command below and assigning another arbitrary stack name e.g. 'servers'
./aws_cu <stack name> servers-config.yml servers-params.json
aws_cuis a custom shell script and wrapper aroundaws cloudformationcli commands. It includes template validation, checks if stack already exist, and if it does, performs anupdate-stackotherwisecreate-stack.
3. Check status of the stacks. This may take a while since each of the compute instances is setting up docker, downloading the code, and deploying this to a dockerized Apache server. Once complete and to test the environment is setup, navigate to EC2 Dashboard - Load Balancers and copy the DNS name to your browser.
Udacity Cloud DevOps Nanodegree Program