| comments | difficulty | edit_url | tags | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
true |
困难 |
|
设计一个内存文件系统,模拟以下功能:
实现文件系统类:
FileSystem()初始化系统对象List<String> ls(String path)- 如果
path是一个文件路径,则返回一个仅包含该文件名称的列表。 - 如果
path是一个目录路径,则返回该目录中文件和 目录名 的列表。
- 如果
答案应该 按字典顺序 排列。
void mkdir(String path)根据给定的路径创建一个新目录。给定的目录路径不存在。如果路径中的中间目录不存在,您也应该创建它们。void addContentToFile(String filePath, String content)- 如果
filePath不存在,则创建包含给定内容content的文件。 - 如果
filePath已经存在,将给定的内容content附加到原始内容。
- 如果
String readContentFromFile(String filePath)返回filePath下的文件内容。
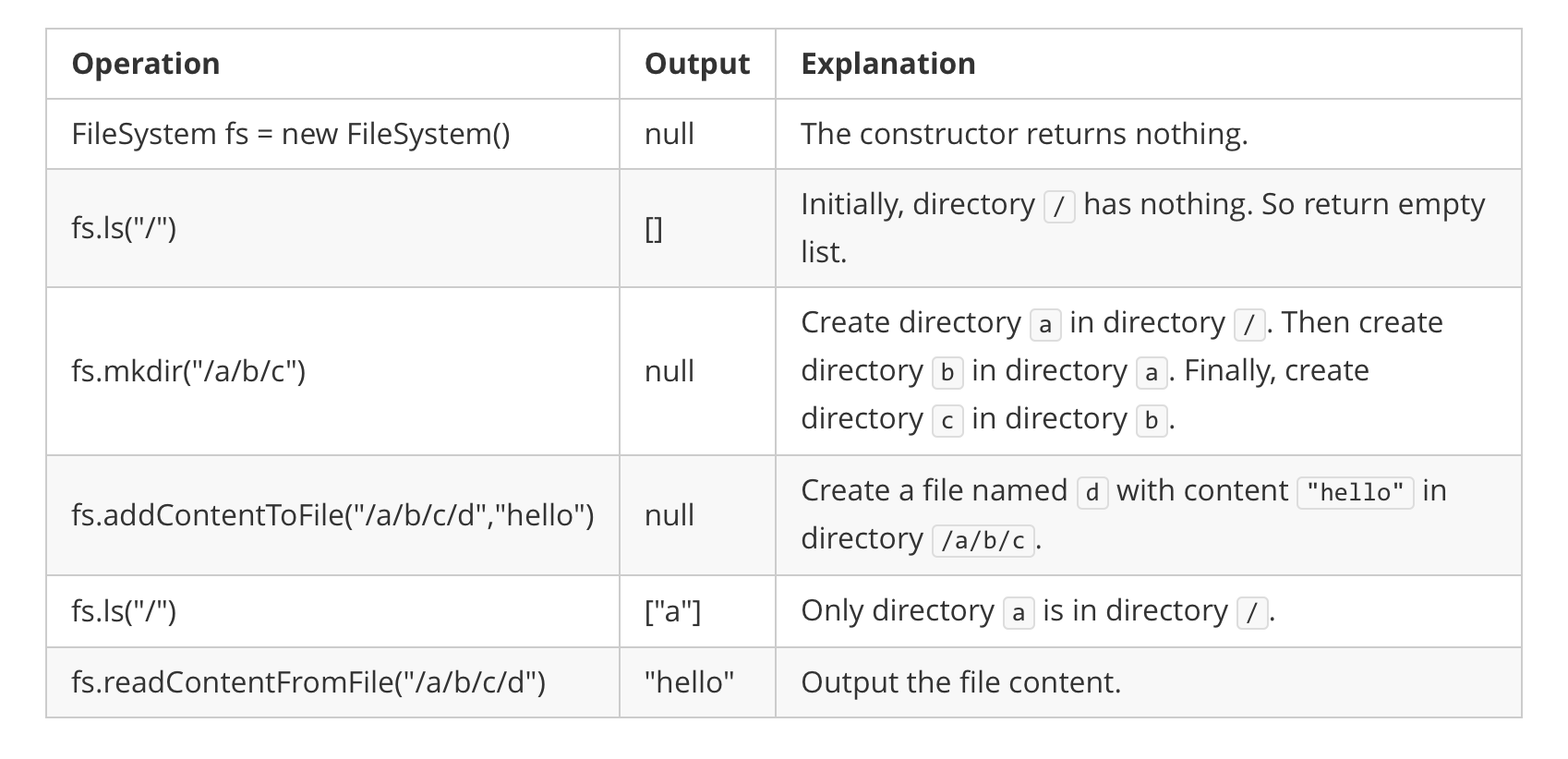
示例 1:
输入:
["FileSystem","ls","mkdir","addContentToFile","ls","readContentFromFile"]
[[],["/"],["/a/b/c"],["/a/b/c/d","hello"],["/"],["/a/b/c/d"]]
输出:
[null,[],null,null,["a"],"hello"]
解释:
FileSystem fileSystem = new FileSystem();
fileSystem.ls("/"); // 返回 []
fileSystem.mkdir("/a/b/c");
fileSystem.addContentToFile("/a/b/c/d", "hello");
fileSystem.ls("/"); // 返回 ["a"]
fileSystem.readContentFromFile("/a/b/c/d"); // 返回 "hello"
注意:
1 <= path.length, filePath.length <= 100path和filePath都是绝对路径,除非是根目录‘/’自身,其他路径都是以‘/’开头且 不 以‘/’结束。- 你可以假定所有操作的参数都是有效的,即用户不会获取不存在文件的内容,或者获取不存在文件夹和文件的列表。
- 你可以假定所有文件夹名字和文件名字都只包含小写字母,且同一文件夹下不会有相同名字的文件夹或文件。
- 你可以假定
addContentToFile中的文件的父目录都存在。 1 <= content.length <= 50ls,mkdir,addContentToFile, andreadContentFromFile最多被调用300次
哈希表实现前缀树。
class Trie:
def __init__(self):
self.name = None
self.isFile = False
self.content = []
self.children = {}
def insert(self, path, isFile):
node = self
ps = path.split('/')
for p in ps[1:]:
if p not in node.children:
node.children[p] = Trie()
node = node.children[p]
node.isFile = isFile
if isFile:
node.name = ps[-1]
return node
def search(self, path):
node = self
if path == '/':
return node
ps = path.split('/')
for p in ps[1:]:
if p not in node.children:
return None
node = node.children[p]
return node
class FileSystem:
def __init__(self):
self.root = Trie()
def ls(self, path: str) -> List[str]:
node = self.root.search(path)
if node is None:
return []
if node.isFile:
return [node.name]
return sorted(node.children.keys())
def mkdir(self, path: str) -> None:
self.root.insert(path, False)
def addContentToFile(self, filePath: str, content: str) -> None:
node = self.root.insert(filePath, True)
node.content.append(content)
def readContentFromFile(self, filePath: str) -> str:
node = self.root.search(filePath)
return ''.join(node.content)
# Your FileSystem object will be instantiated and called as such:
# obj = FileSystem()
# param_1 = obj.ls(path)
# obj.mkdir(path)
# obj.addContentToFile(filePath,content)
# param_4 = obj.readContentFromFile(filePath)class Trie {
String name;
boolean isFile;
StringBuilder content = new StringBuilder();
Map<String, Trie> children = new HashMap<>();
Trie insert(String path, boolean isFile) {
Trie node = this;
String[] ps = path.split("/");
for (int i = 1; i < ps.length; ++i) {
String p = ps[i];
if (!node.children.containsKey(p)) {
node.children.put(p, new Trie());
}
node = node.children.get(p);
}
node.isFile = isFile;
if (isFile) {
node.name = ps[ps.length - 1];
}
return node;
}
Trie search(String path) {
Trie node = this;
String[] ps = path.split("/");
for (int i = 1; i < ps.length; ++i) {
String p = ps[i];
if (!node.children.containsKey(p)) {
return null;
}
node = node.children.get(p);
}
return node;
}
}
class FileSystem {
private Trie root = new Trie();
public FileSystem() {
}
public List<String> ls(String path) {
List<String> ans = new ArrayList<>();
Trie node = root.search(path);
if (node == null) {
return ans;
}
if (node.isFile) {
ans.add(node.name);
return ans;
}
for (String v : node.children.keySet()) {
ans.add(v);
}
Collections.sort(ans);
return ans;
}
public void mkdir(String path) {
root.insert(path, false);
}
public void addContentToFile(String filePath, String content) {
Trie node = root.insert(filePath, true);
node.content.append(content);
}
public String readContentFromFile(String filePath) {
Trie node = root.search(filePath);
return node.content.toString();
}
}
/**
* Your FileSystem object will be instantiated and called as such:
* FileSystem obj = new FileSystem();
* List<String> param_1 = obj.ls(path);
* obj.mkdir(path);
* obj.addContentToFile(filePath,content);
* String param_4 = obj.readContentFromFile(filePath);
*/type Trie struct {
name string
isFile bool
content strings.Builder
children map[string]*Trie
}
func newTrie() *Trie {
m := map[string]*Trie{}
return &Trie{children: m}
}
func (this *Trie) insert(path string, isFile bool) *Trie {
node := this
ps := strings.Split(path, "/")
for _, p := range ps[1:] {
if _, ok := node.children[p]; !ok {
node.children[p] = newTrie()
}
node, _ = node.children[p]
}
node.isFile = isFile
if isFile {
node.name = ps[len(ps)-1]
}
return node
}
func (this *Trie) search(path string) *Trie {
if path == "/" {
return this
}
node := this
ps := strings.Split(path, "/")
for _, p := range ps[1:] {
if _, ok := node.children[p]; !ok {
return nil
}
node, _ = node.children[p]
}
return node
}
type FileSystem struct {
root *Trie
}
func Constructor() FileSystem {
root := newTrie()
return FileSystem{root}
}
func (this *FileSystem) Ls(path string) []string {
var ans []string
node := this.root.search(path)
if node == nil {
return ans
}
if node.isFile {
ans = append(ans, node.name)
return ans
}
for v := range node.children {
ans = append(ans, v)
}
sort.Strings(ans)
return ans
}
func (this *FileSystem) Mkdir(path string) {
this.root.insert(path, false)
}
func (this *FileSystem) AddContentToFile(filePath string, content string) {
node := this.root.insert(filePath, true)
node.content.WriteString(content)
}
func (this *FileSystem) ReadContentFromFile(filePath string) string {
node := this.root.search(filePath)
return node.content.String()
}
/**
* Your FileSystem object will be instantiated and called as such:
* obj := Constructor();
* param_1 := obj.Ls(path);
* obj.Mkdir(path);
* obj.AddContentToFile(filePath,content);
* param_4 := obj.ReadContentFromFile(filePath);
*/