| comments | difficulty | edit_url | rating | source | tags | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
true |
中等 |
1836 |
第 70 场双周赛 Q3 |
|
给你一个下标从 0 开始的二维整数数组 grid ,它的大小为 m x n ,表示一个商店中物品的分布图。数组中的整数含义为:
0表示无法穿越的一堵墙。1表示可以自由通过的一个空格子。- 所有其他正整数表示该格子内的一样物品的价格。你可以自由经过这些格子。
从一个格子走到上下左右相邻格子花费 1 步。
同时给你一个整数数组 pricing 和 start ,其中 pricing = [low, high] 且 start = [row, col] ,表示你开始位置为 (row, col) ,同时你只对物品价格在 闭区间 [low, high] 之内的物品感兴趣。同时给你一个整数 k 。
你想知道给定范围 内 且 排名最高 的 k 件物品的 位置 。排名按照优先级从高到低的以下规则制定:
- 距离:定义为从
start到一件物品的最短路径需要的步数(较近 距离的排名更高)。 - 价格:较低 价格的物品有更高优先级,但只考虑在给定范围之内的价格。
- 行坐标:较小 行坐标的有更高优先级。
- 列坐标:较小 列坐标的有更高优先级。
请你返回给定价格内排名最高的 k 件物品的坐标,将它们按照排名排序后返回。如果给定价格内少于 k 件物品,那么请将它们的坐标 全部 返回。
示例 1:
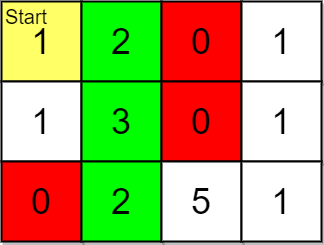
输入:grid = [[1,2,0,1],[1,3,0,1],[0,2,5,1]], pricing = [2,5], start = [0,0], k = 3 输出:[[0,1],[1,1],[2,1]] 解释:起点为 (0,0) 。 价格范围为 [2,5] ,我们可以选择的物品坐标为 (0,1),(1,1),(2,1) 和 (2,2) 。 这些物品的排名为: - (0,1) 距离为 1 - (1,1) 距离为 2 - (2,1) 距离为 3 - (2,2) 距离为 4 所以,给定价格范围内排名最高的 3 件物品的坐标为 (0,1),(1,1) 和 (2,1) 。
示例 2:
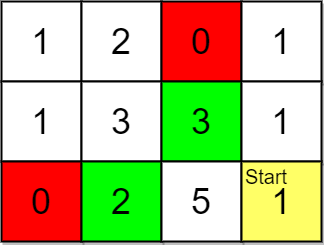
输入:grid = [[1,2,0,1],[1,3,3,1],[0,2,5,1]], pricing = [2,3], start = [2,3], k = 2 输出:[[2,1],[1,2]] 解释:起点为 (2,3) 。 价格范围为 [2,3] ,我们可以选择的物品坐标为 (0,1),(1,1),(1,2) 和 (2,1) 。 这些物品的排名为: - (2,1) 距离为 2 ,价格为 2 - (1,2) 距离为 2 ,价格为 3 - (1,1) 距离为 3 - (0,1) 距离为 4 所以,给定价格范围内排名最高的 2 件物品的坐标为 (2,1) 和 (1,2) 。
示例 3:
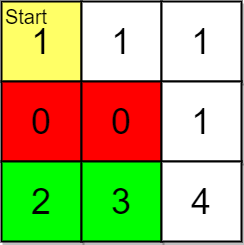
输入:grid = [[1,1,1],[0,0,1],[2,3,4]], pricing = [2,3], start = [0,0], k = 3 输出:[[2,1],[2,0]] 解释:起点为 (0,0) 。 价格范围为 [2,3] ,我们可以选择的物品坐标为 (2,0) 和 (2,1) 。 这些物品的排名为: - (2,1) 距离为 5 - (2,0) 距离为 6 所以,给定价格范围内排名最高的 2 件物品的坐标为 (2,1) 和 (2,0) 。 注意,k = 3 但给定价格范围内只有 2 件物品。
提示:
m == grid.lengthn == grid[i].length1 <= m, n <= 1051 <= m * n <= 1050 <= grid[i][j] <= 105pricing.length == 22 <= low <= high <= 105start.length == 20 <= row <= m - 10 <= col <= n - 1grid[row][col] > 01 <= k <= m * n
我们可以从
最后对
时间复杂度
class Solution:
def highestRankedKItems(
self, grid: List[List[int]], pricing: List[int], start: List[int], k: int
) -> List[List[int]]:
m, n = len(grid), len(grid[0])
row, col = start
low, high = pricing
q = deque([(row, col)])
pq = []
if low <= grid[row][col] <= high:
pq.append((0, grid[row][col], row, col))
grid[row][col] = 0
dirs = (-1, 0, 1, 0, -1)
step = 0
while q:
step += 1
for _ in range(len(q)):
x, y = q.popleft()
for a, b in pairwise(dirs):
nx, ny = x + a, y + b
if 0 <= nx < m and 0 <= ny < n and grid[nx][ny] > 0:
if low <= grid[nx][ny] <= high:
pq.append((step, grid[nx][ny], nx, ny))
grid[nx][ny] = 0
q.append((nx, ny))
pq.sort()
return [list(x[2:]) for x in pq[:k]]class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> highestRankedKItems(
int[][] grid, int[] pricing, int[] start, int k) {
int m = grid.length;
int n = grid[0].length;
int row = start[0], col = start[1];
int low = pricing[0], high = pricing[1];
Deque<int[]> q = new ArrayDeque<>();
q.offer(new int[] {row, col});
List<int[]> pq = new ArrayList<>();
if (low <= grid[row][col] && grid[row][col] <= high) {
pq.add(new int[] {0, grid[row][col], row, col});
}
grid[row][col] = 0;
final int[] dirs = {-1, 0, 1, 0, -1};
for (int step = 1; !q.isEmpty(); ++step) {
for (int size = q.size(); size > 0; --size) {
int[] curr = q.poll();
int x = curr[0], y = curr[1];
for (int j = 0; j < 4; j++) {
int nx = x + dirs[j];
int ny = y + dirs[j + 1];
if (0 <= nx && nx < m && 0 <= ny && ny < n && grid[nx][ny] > 0) {
if (low <= grid[nx][ny] && grid[nx][ny] <= high) {
pq.add(new int[] {step, grid[nx][ny], nx, ny});
}
grid[nx][ny] = 0;
q.offer(new int[] {nx, ny});
}
}
}
}
pq.sort((a, b) -> {
if (a[0] != b[0]) return Integer.compare(a[0], b[0]);
if (a[1] != b[1]) return Integer.compare(a[1], b[1]);
if (a[2] != b[2]) return Integer.compare(a[2], b[2]);
return Integer.compare(a[3], b[3]);
});
List<List<Integer>> ans = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < Math.min(k, pq.size()); i++) {
ans.add(List.of(pq.get(i)[2], pq.get(i)[3]));
}
return ans;
}
}class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> highestRankedKItems(vector<vector<int>>& grid, vector<int>& pricing, vector<int>& start, int k) {
int m = grid.size(), n = grid[0].size();
int row = start[0], col = start[1];
int low = pricing[0], high = pricing[1];
queue<pair<int, int>> q;
q.push({row, col});
vector<tuple<int, int, int, int>> pq;
if (low <= grid[row][col] && grid[row][col] <= high) {
pq.push_back({0, grid[row][col], row, col});
}
grid[row][col] = 0;
vector<int> dirs = {-1, 0, 1, 0, -1};
for (int step = 1; q.size(); ++step) {
int sz = q.size();
for (int i = 0; i < sz; ++i) {
auto [x, y] = q.front();
q.pop();
for (int j = 0; j < 4; ++j) {
int nx = x + dirs[j];
int ny = y + dirs[j + 1];
if (0 <= nx && nx < m && 0 <= ny && ny < n && grid[nx][ny] > 0) {
if (low <= grid[nx][ny] && grid[nx][ny] <= high) {
pq.push_back({step, grid[nx][ny], nx, ny});
}
grid[nx][ny] = 0;
q.push({nx, ny});
}
}
}
}
sort(pq.begin(), pq.end());
vector<vector<int>> ans;
for (int i = 0; i < min(k, (int) pq.size()); ++i) {
ans.push_back({get<2>(pq[i]), get<3>(pq[i])});
}
return ans;
}
};func highestRankedKItems(grid [][]int, pricing []int, start []int, k int) (ans [][]int) {
m, n := len(grid), len(grid[0])
row, col := start[0], start[1]
low, high := pricing[0], pricing[1]
q := [][2]int{{row, col}}
pq := [][]int{}
if low <= grid[row][col] && grid[row][col] <= high {
pq = append(pq, []int{0, grid[row][col], row, col})
}
grid[row][col] = 0
dirs := [5]int{-1, 0, 1, 0, -1}
for step := 1; len(q) > 0; step++ {
for sz := len(q); sz > 0; sz-- {
x, y := q[0][0], q[0][1]
q = q[1:]
for j := 0; j < 4; j++ {
nx, ny := x+dirs[j], y+dirs[j+1]
if nx >= 0 && nx < m && ny >= 0 && ny < n && grid[nx][ny] > 0 {
if low <= grid[nx][ny] && grid[nx][ny] <= high {
pq = append(pq, []int{step, grid[nx][ny], nx, ny})
}
grid[nx][ny] = 0
q = append(q, [2]int{nx, ny})
}
}
}
}
sort.Slice(pq, func(i, j int) bool {
a, b := pq[i], pq[j]
if a[0] != b[0] {
return a[0] < b[0]
}
if a[1] != b[1] {
return a[1] < b[1]
}
if a[2] != b[2] {
return a[2] < b[2]
}
return a[3] < b[3]
})
for i := 0; i < len(pq) && i < k; i++ {
ans = append(ans, pq[i][2:])
}
return
}function highestRankedKItems(
grid: number[][],
pricing: number[],
start: number[],
k: number,
): number[][] {
const [m, n] = [grid.length, grid[0].length];
const [row, col] = start;
const [low, high] = pricing;
let q: [number, number][] = [[row, col]];
const pq: [number, number, number, number][] = [];
if (low <= grid[row][col] && grid[row][col] <= high) {
pq.push([0, grid[row][col], row, col]);
}
grid[row][col] = 0;
const dirs = [-1, 0, 1, 0, -1];
for (let step = 1; q.length > 0; ++step) {
const nq: [number, number][] = [];
for (const [x, y] of q) {
for (let j = 0; j < 4; j++) {
const nx = x + dirs[j];
const ny = y + dirs[j + 1];
if (nx >= 0 && nx < m && ny >= 0 && ny < n && grid[nx][ny] > 0) {
if (low <= grid[nx][ny] && grid[nx][ny] <= high) {
pq.push([step, grid[nx][ny], nx, ny]);
}
grid[nx][ny] = 0;
nq.push([nx, ny]);
}
}
}
q = nq;
}
pq.sort((a, b) => {
if (a[0] !== b[0]) return a[0] - b[0];
if (a[1] !== b[1]) return a[1] - b[1];
if (a[2] !== b[2]) return a[2] - b[2];
return a[3] - b[3];
});
const ans: number[][] = [];
for (let i = 0; i < Math.min(k, pq.length); i++) {
ans.push([pq[i][2], pq[i][3]]);
}
return ans;
}