|
| 1 | +# ArgoCD |
| 2 | + |
| 3 | +Source: <https://argo-cd.readthedocs.io/en/stable/> |
| 4 | + |
| 5 | +Table of contents: |
| 6 | +- [ArgoCD](#argocd) |
| 7 | + - [1. Overview](#1-overview) |
| 8 | + - [2. Architecture:](#2-architecture) |
| 9 | + - [3. Core concepts](#3-core-concepts) |
| 10 | + |
| 11 | +## 1. Overview |
| 12 | + |
| 13 | +- Argo CD is a declarative, GitOps continuous delivery tool for Kubernetes. |
| 14 | +- Argo CD follows the **GitOps** pattern of using Git repositories as the source of truth for defining the desired application state. Kubernetes manifests can be specified in several ways: |
| 15 | + - kustomize applications |
| 16 | + - helm charts |
| 17 | + - jsonnet files |
| 18 | + - Plain directory of YAML/json manifests |
| 19 | + - Any custom config management tool configured as a config management plugin |
| 20 | +- ArgoCD automates the deployment of the desired application states in the specified target environments. Application deployments can track updates to branches, tags, or be pinned to a specific version of manifests at a Git commit. |
| 21 | + |
| 22 | + |
| 23 | + |
| 24 | +## 2. Architecture: |
| 25 | + |
| 26 | +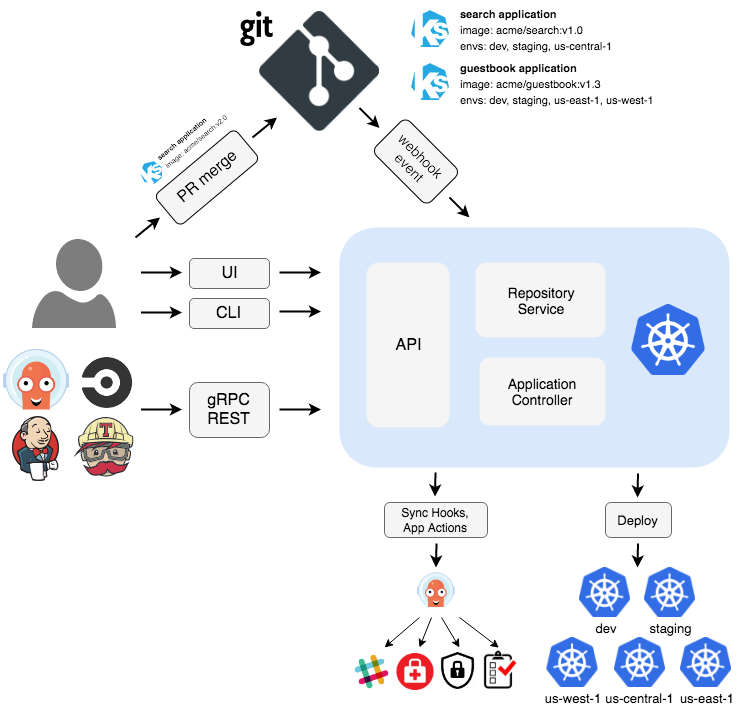 |
| 27 | + |
| 28 | +- ArgoCD is implemented as a Kubernetes controller which continously monitors running applications and compares the current, live state against the desired target state. |
| 29 | +- A deployed application whose live state deviates from the target state is considered `OutofSync`. |
| 30 | +- Any modifications made to the desired target state in the Git repo can be automatically applied and reflected in the specified target environments. |
| 31 | +- Components: |
| 32 | + - API Server: A gRPC/REST server which exposes the API consumed by the Web UI, CLI, and CI/CD systems. |
| 33 | + - Repository Server: An internal service which maintains a local cache of the Git repository holding the application manifests. It is responsible for generating and returning the Kubernetes mainfests. |
| 34 | + - Application controller: a Kubernetes controller which continously monitors running applications and compares the current, live state against the desired target state (as specified in the repo). It detects `OutOfSync` application state and optionally takes corrective action. It is responsible for invoking any user-defined hooks for lifecycle events. |
| 35 | + |
| 36 | +## 3. Core concepts |
| 37 | + |
| 38 | +- Application A group of Kubernetes resources as defined by a manifest. This is a Custom Resource Definition (CRD). |
| 39 | +- Application source type Which Tool is used to build the application. |
| 40 | +- Target state The desired state of an application, as represented by files in a Git repository. |
| 41 | +- Live state The live state of that application. What pods etc are deployed. |
| 42 | +- Sync status Whether or not the live state matches the target state. Is the deployed application the same as Git says it should be? |
| 43 | +- Sync The process of making an application move to its target state. E.g. by applying changes to a Kubernetes cluster. |
| 44 | +- Sync operation status Whether or not a sync succeeded. |
| 45 | +- Refresh Compare the latest code in Git with the live state. Figure out what is different. |
| 46 | +- Health The health of the application, is it running correctly? Can it serve requests? |
| 47 | +- Tool A tool to create manifests from a directory of files. E.g. Kustomize. See Application Source Type. |
| 48 | +- Configuration management tool See Tool. |
| 49 | +- Configuration management plugin A custom tool. |
0 commit comments