|
1 | 1 | # pystardog |
2 | 2 | [](https://badge.fury.io/py/pystardog) |
3 | 3 |
|
4 | | -a Python wrapper for communicating with the Stardog HTTP server. |
5 | | - |
6 | | -**Docs**: [http://pystardog.readthedocs.io](http://pystardog.readthedocs.io) |
| 4 | +Python client for Stardog servers and Stardog Cloud. |
7 | 5 |
|
8 | 6 | **Requirements**: Python 3.9+ |
9 | 7 |
|
10 | | -## What is it? |
11 | | - |
12 | | -This library wraps all the functionality of a client for the Stardog |
13 | | -Knowledge Graph, and provides access to a full set of functions such |
14 | | -as executing SPARQL queries and many administrative tasks. |
15 | | - |
16 | | -The implementation uses the HTTP protocol, since most of Stardog |
17 | | -functionality is available using this protocol. For more information, |
18 | | -see [HTTP |
19 | | -Programming](https://docs.stardog.com/developing/http-api) |
20 | | -in Stardog's documentation. |
| 8 | +## Quick Start |
21 | 9 |
|
22 | | -## Installation |
23 | | - |
24 | | -pystardog is on [PyPI](https://pypi.org/project/pystardog/). To install: |
| 10 | +Install from PyPI: |
25 | 11 |
|
26 | 12 | ```shell |
27 | 13 | pip install pystardog |
28 | 14 | ``` |
29 | 15 |
|
30 | | -## Quick Example |
31 | | - |
32 | | -```python |
33 | | -import stardog |
34 | | - |
35 | | -conn_details = { |
36 | | - 'endpoint': 'http://localhost:5820', |
37 | | - 'username': 'admin', |
38 | | - 'password': 'admin' |
39 | | -} |
40 | | - |
41 | | -with stardog.Admin(**conn_details) as admin: |
42 | | - db = admin.new_database('db') |
43 | | - |
44 | | - with stardog.Connection('db', **conn_details) as conn: |
45 | | - conn.begin() |
46 | | - conn.add(stardog.content.File('./test/data/example.ttl')) |
47 | | - conn.commit() |
48 | | - results = conn.select('select * { ?a ?p ?o }') |
49 | | - |
50 | | - db.drop() |
51 | | -``` |
52 | | - |
53 | | -## Interactive Tutorial |
54 | | - |
55 | | -There is a Jupyter notebook and instructions in the [`notebooks`](./notebooks) |
56 | | -directory of this repository. |
57 | | - |
58 | | -## Documentation |
59 | | - |
60 | | -Documentation is available at [http://pystardog.readthedocs.io](http://pystardog.readthedocs.io) |
61 | | - |
62 | | -### Build the Docs Locally |
63 | | - |
64 | | -The docs can be built locally using [Sphinx](https://www.sphinx-doc.org/en/master/): |
65 | | - |
66 | | - ```shell |
67 | | - pip install -e ".[docs]" |
68 | | - cd docs |
69 | | - make html |
70 | | - ``` |
71 | | - |
72 | | -#### Autodoc Type Hints |
73 | | - |
74 | | -The docs use [`sphinx-autodoc-typehints`](https://github.com/tox-dev/sphinx-autodoc-typehints) which allows you to omit types when documenting argument/returns types of functions. For example: |
75 | | - |
76 | | -The following function: |
77 | | - |
78 | | -```python |
79 | | -def database(self, name: str) -> "Database": |
80 | | - """Retrieves an object representing a database. |
81 | | -
|
82 | | - :param name: The database name |
83 | | -
|
84 | | - :return: the database |
85 | | - """ |
86 | | - return Database(name, self.client) |
87 | | -``` |
88 | | - |
89 | | -will yield the following documentation after Sphinx processes it: |
90 | | - |
91 | | -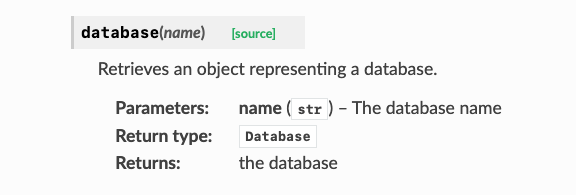 |
92 | | - |
93 | | -> **Note** |
94 | | -> Only arguments that have an existing `:param:` directive in the docstring get their |
95 | | -> respective `:type:` directives added. The `:rtype:` directive is added if and only if no existing `:rtype:` is found. |
96 | | -> See the [docs](https://github.com/tox-dev/sphinx-autodoc-typehints) for additional information on how the extension works. |
97 | | -
|
98 | | -#### Auto Build |
99 | | - |
100 | | -Docs can be rebuilt automatically when saving a Python file by utilizing [`sphinx-autobuild`](https://github.com/executablebooks/sphinx-autobuild) |
| 16 | +For Stardog Cloud functionality: |
101 | 17 |
|
102 | 18 | ```shell |
103 | | -pip install -e ".[docs]" |
104 | | -cd docs |
105 | | -make livehtml |
| 19 | +pip install pystardog[cloud] |
106 | 20 | ``` |
107 | 21 |
|
108 | | -This should make the docs available at [http://localhost:8000](http://localhost:8000). |
109 | | - |
110 | | -Example output after running `make livehtml`: |
111 | | - |
112 | | -```text |
113 | | -❯ make livehtml |
114 | | -sphinx-autobuild "." "_build" --watch ../stardog/ |
115 | | -[sphinx-autobuild] > sphinx-build /Users/frodo/projects/pystardog/docs /Users/frodo/projects/pystardog/docs/_build |
116 | | -Running Sphinx v6.2.1 |
117 | | -loading pickled environment... done |
118 | | -building [mo]: targets for 0 po files that are out of date |
119 | | -writing output... |
120 | | -building [html]: targets for 0 source files that are out of date |
121 | | -updating environment: 0 added, 0 changed, 0 removed |
122 | | -reading sources... |
123 | | -looking for now-outdated files... none found |
124 | | -no targets are out of date. |
125 | | -build succeeded. |
126 | | -
|
127 | | -The HTML pages are in _build. |
128 | | -[I 230710 15:26:18 server:335] Serving on http://127.0.0.1:8000 |
129 | | -[I 230710 15:26:18 handlers:62] Start watching changes |
130 | | -[I 230710 15:26:18 handlers:64] Start detecting changes |
131 | | -``` |
132 | | - |
133 | | -## Contributing and Development |
134 | | - |
135 | | -Contrbutions are always welcome to pystardog. |
136 | | - |
137 | | -To make a contribution: |
138 | | - |
139 | | -1. Create a new branch off of `main`. There is no set naming convention for branches but try and keep it descriptive. |
140 | | - |
141 | | - ```bash |
142 | | - git checkout -b feature/add-support-for-X |
143 | | - ``` |
144 | | - |
145 | | -2. Make your changes. If you are making substantive changes to pystardog, tests should be added to ensure your changes are working as expected. See [Running Tests](#running-tests) for additional information |
146 | | -about running tests. |
147 | | - |
148 | | -3. Format your code. All Python code should be formatted using [Black](https://pypi.org/project/black/). See [Formatting Your Code](#formatting-your-code) for additional information. |
149 | | - |
150 | | -4. Commit and push your code. Similar to branch names, there is no set structure for commit messages but try and keep your commit messages succinct and on topic. |
151 | | - |
152 | | - ```bash |
153 | | - git commit -am "feat: adds support for feature X" |
154 | | - git push origin feature/add-support-for-x |
155 | | - ``` |
156 | | - |
157 | | -5. Create a pull request against `main`. All CircleCI checks should be passing in order to merge your PR. CircleCI will run tests against all supported versions of Python, single node and cluster tests for pystardog, as well as do some static analysis of the code. |
158 | | - |
159 | | -### Running Tests |
160 | | - |
161 | | -#### Requirements: |
162 | | - |
163 | | -- [Docker](https://docs.docker.com/) |
164 | | -- [Docker Compose](https://docs.docker.com/compose/) |
165 | | -- Valid Stardog License |
166 | | - |
167 | | -To run the tests locally, a valid Stardog license is required and placed at `dockerfiles/stardog-license-key.bin`. |
168 | | - |
169 | | -1. Bring a stardog instance using docker-compose. For testing about 90% of the pystardog features, just a single node is sufficient, |
170 | | -although we also provide a cluster set up for further testing. |
171 | | - |
172 | | - ```shell |
173 | | - # Bring a single node instance plus a bunch of Virtual Graphs for testing (Recommended). |
174 | | - docker-compose -f docker-compose.single-node.yml up -d |
175 | | -
|
176 | | - # A cluster setup is also provided, if cluster only features are to be implemented and tested. |
177 | | - docker-compose -f docker-compose.cluster.yml up -d |
178 | | - ``` |
179 | | - |
180 | | -2. Install the package in development mode with dependencies: |
181 | | - |
182 | | - ```shell |
183 | | - # Create a virtual environment and activate it |
184 | | - python -m venv venv |
185 | | - source venv/bin/activate |
186 | | -
|
187 | | - # Install in development mode with dev dependencies |
188 | | - pip install -e ".[dev]" |
189 | | - ``` |
190 | | - |
191 | | -3. Run the test suite: |
192 | | - |
193 | | - ```shell |
194 | | - # Run the basic test suite (covers most of the pystardog functionalities) |
195 | | - pytest test/test_admin_basic.py test/test_connection.py test/test_utils.py -s |
196 | | - ``` |
197 | | - |
198 | | - > **Note** |
199 | | - > Tests can be targeted against a specific Stardog endpoint by specifying an `--endpoint` option to `pytest`. Please note, that the tests will make modifications |
200 | | - > to the Stardog instance like deleting users, roles, databases, etc. By default, the `--endpoint` is set to `http://localhost:5820`, |
201 | | - > which is where the Dockerized Stardog (defined in the Docker compose files) is configured to be available at. |
202 | | - > |
203 | | - > ```bash |
204 | | - > pytest test/test_connection.py -k test_queries -s --endpoint https://my-other-stardog:5820 |
205 | | - > ``` |
206 | | - |
207 | | -### Formatting your code |
208 | | - |
209 | | -To format all the Python code: |
210 | | - |
211 | | - ```shell |
212 | | - # Create and activate virtual environment |
213 | | - python -m venv venv |
214 | | - source venv/bin/activate |
215 | | - pip install -e ".[dev]" |
216 | | -
|
217 | | - # run black formatter |
218 | | - black . |
219 | | - ``` |
220 | | - |
221 | | -### Running Tests with Tox |
222 | | - |
223 | | -To run tests across multiple Python versions: |
224 | | - |
225 | | -```shell |
226 | | -# Run tests for all supported Python versions |
227 | | -tox |
228 | | -
|
229 | | -# Run tests for a specific Python version |
230 | | -tox -e py312 |
| 22 | +## Documentation |
231 | 23 |
|
232 | | -# Run cluster-specific tests |
233 | | -tox -e cluster |
| 24 | +**Full documentation**: [http://pystardog.readthedocs.io](http://pystardog.readthedocs.io) |
234 | 25 |
|
235 | | -# Run single-node-specific tests |
236 | | -tox -e single_node |
237 | | -``` |
| 26 | +- [**Getting Started**](http://pystardog.readthedocs.io/en/latest/getting-started.html) - Installation, examples, and basic usage |
| 27 | +- [**API Reference**](http://pystardog.readthedocs.io/en/latest/source/stardog.html) - Complete API documentation |
| 28 | +- [**Contributing**](http://pystardog.readthedocs.io/en/latest/contributing.html) - Development setup, testing, and contribution guidelines |
238 | 29 |
|
239 | | -### Building and Publishing |
| 30 | +## Interactive Tutorial |
240 | 31 |
|
241 | | -To build and publish the package to PyPI: |
| 32 | +There is a Jupyter notebook and instructions in the [`notebooks`](./notebooks) directory of this repository. |
242 | 33 |
|
243 | | -```shell |
244 | | -# Install build dependencies |
245 | | -pip install -e ".[build]" |
| 34 | +## Voicebox Demo |
246 | 35 |
|
247 | | -# Build the package |
248 | | -python -m build |
| 36 | +Interactive example showing natural language queries with Stardog Cloud's Voicebox ([`examples/voicebox_example.py`](examples/voicebox_example.py)): |
249 | 37 |
|
250 | | -# Upload to PyPI (requires authentication) |
251 | | -twine upload dist/* |
252 | | -``` |
| 38 | + |
253 | 39 |
|
0 commit comments