The Simple SSH Honeypot Server is a low-interaction SSH server built for cybersecurity practitioners and enthusiasts who want to observe and analyze SSH traffic safely. It uses Python and the Twisted (Conch) framework to simulate an SSH service and log authentication attempts and protocol metadata without providing a real shell.
In addition to credential logging, this version captures SSH version exchange, key-exchange (KEXINIT) negotiation details, and raw inbound byte snapshots to help identify unusual client behavior and potential zero-day probing patterns.
- Low-Interaction Honeypot: Emulates an SSH server without offering a usable shell/session.
- Customizable Configuration: Adjust bind host, port, and displayed SSH banner/version string via CLI.
- Expanded Protocol Telemetry:
- Connection events (source/destination, connection ID)
- SSH version exchange (local/remote version strings)
- KEXINIT parsing (KEX, host key algorithms, ciphers, MACs, compression)
- Credential & Auth Visibility:
- Logs password attempts (username/password)
- Logs non-password USERAUTH requests
- Logs publickey attempts (algorithm, fingerprint, signature presence, key blob prefix)
- Raw Byte Logging for Anomaly Detection:
- Records a limited number of early inbound payloads per connection
- Includes SHA-256, hex prefix, base64 prefix, printable ratio, and NUL/high-bit indicators
- Multi Host-Key Support:
- Auto-generates and serves RSA by default
- Adds ECDSA (nistp256) and Ed25519 when available (depends on installed
cryptography)
- Python 3.x
- Twisted (
twisted, includes Conch) - Cryptography (
cryptography)
git clone https://github.com/0xNslabs/ssh-honeypot.git
cd ssh-honeypot
pip install twisted cryptographyStart the server with optional parameters for host, port, and version string. By default, it binds to 0.0.0.0 on port 2222.
python3 ssh.py --host 0.0.0.0 --port 2222 --version "SSH-2.0-OpenSSH_7.4"Notes:
- If you bind to port 22, you will typically need elevated privileges:
sudo python3 ssh.py --host 0.0.0.0 --port 22 --version "SSH-2.0-OpenSSH_8.9p1"
All SSH interactions are logged to ssh_honeypot.log.
Typical logged event types include:
NEW_CONNECTION: initial TCP connection metadataVERSION_EXCHANGE: local and remote SSH identification stringsKEXINIT: negotiated algorithm lists (KEX/ciphers/MACs/compression/etc.)Login attempt - Username: ..., Password: ...: password auth attemptsUSERAUTH_REQUEST: method reconnaissance (e.g.,publickey,none, etc.)RAW_IN: early inbound raw byte snapshots (truncated + hashed)
To reduce log volume and avoid dumping excessive data:
- Raw inbound logging is limited to a small number of early events per connection
- Each raw event is truncated to a bounded size (prefix only)
The server will create host keys in the script directory if they do not exist:
id_rsa/id_rsa.pub(RSA)ssh_host_ecdsa_key/.pub(ECDSA P-256, when supported)ssh_host_ed25519_key/.pub(Ed25519, when supported)
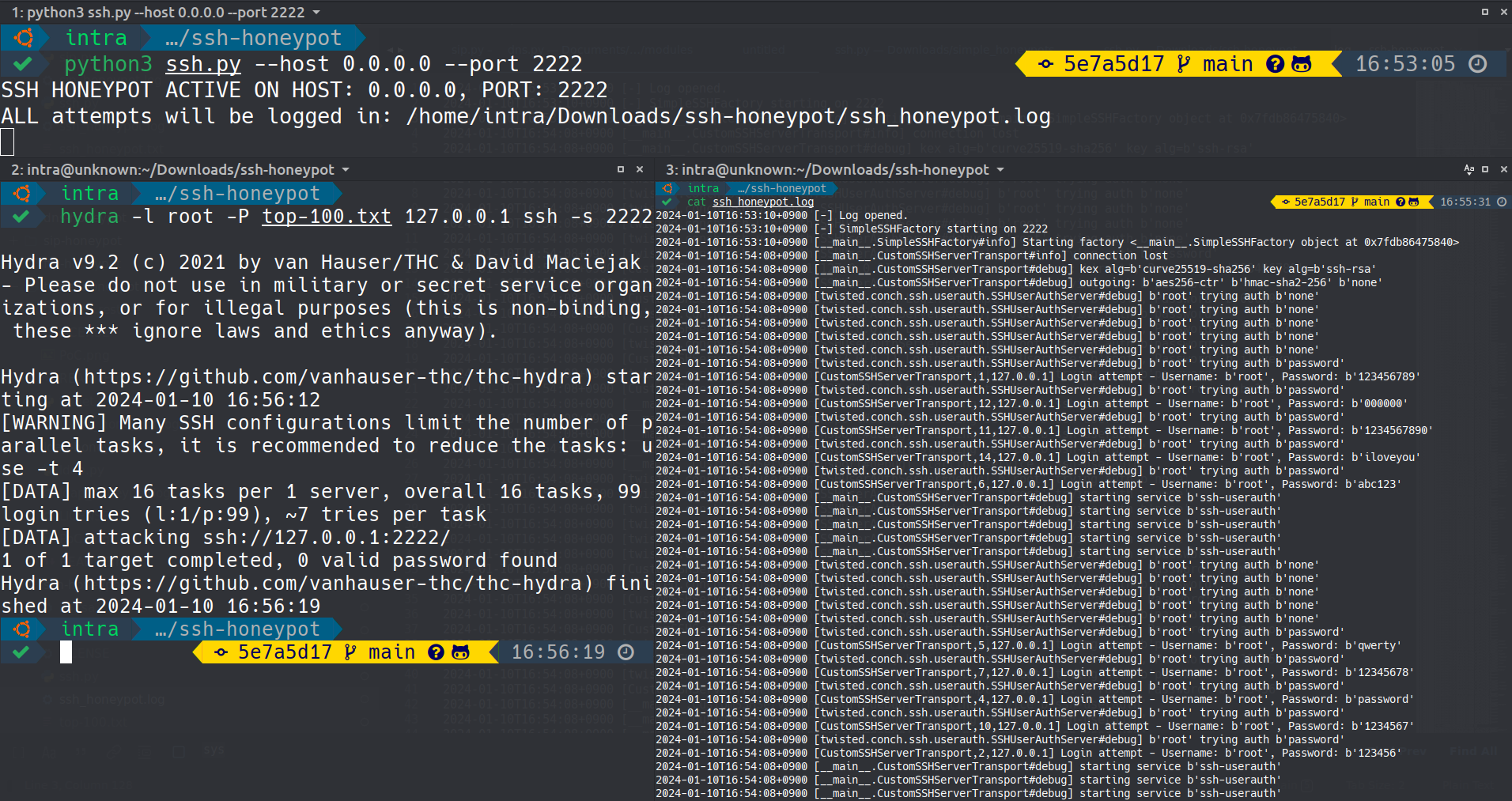 This image displays the honeypot capturing real-time SSH login attempts and protocol activity.
This image displays the honeypot capturing real-time SSH login attempts and protocol activity.
Check out the other honeypot services for monitoring various network protocols:
- DNS Honeypot - Monitors DNS interactions.
- FTP Honeypot - Simulates an FTP server.
- LDAP Honeypot - Mimics an LDAP server.
- HTTP Honeypot - Monitors HTTP interactions.
- HTTPS Honeypot - Monitors HTTPS interactions.
- MongoDB Honeypot - Simulates a MongoDB database server.
- NTP Honeypot - Monitors Network Time Protocol interactions.
- PostgreSQL Honeypot - Simulates a PostgreSQL database server.
- SIP Honeypot - Monitors SIP (Session Initiation Protocol) interactions.
- SSH Honeypot - Emulates an SSH server.
- TELNET Honeypot - Simulates a TELNET server.
- Caution: Deploy in controlled environments. Treat logs as sensitive: they may contain credential attempts and client key material prefixes.
- Compliance: Ensure all deployments comply with local and international legal standards, including consent and logging requirements.
This project is released under the MIT License. For more details, see the LICENSE file.