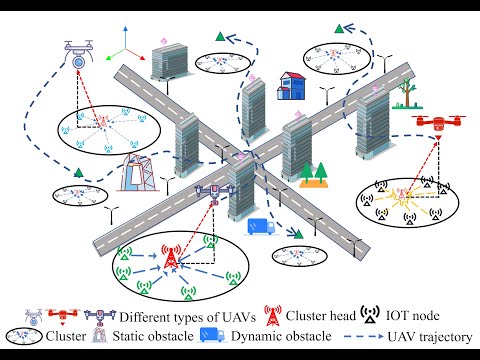
This repository accompanies our research paper "Energy-Efficient Path Planning and Task Allocation for Multi-UAV Aided IoT Cluster-Based Data Collection". The work presents a novel approach to optimize energy efficiency in multi-UAV systems for IoT data collection scenarios.
Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs) are increasingly becoming an integral part of Internet of Things (IoT) ecosystems, particularly for data collection in hard-to-reach areas. However, the limited battery capacity of UAVs poses significant challenges for extended missions. Our research addresses this limitation by developing energy-efficient strategies for both task allocation and path planning in multi-UAV systems.
-
A two-phase optimization framework for multi-UAV systems:
- Phase 1: Centralized task allocation and hovering point selection
- Phase 2: Distributed path planning and trajectory optimization
-
Novel algorithms for:
- Cluster-based IoT device grouping
- Optimal UAV-to-cluster assignment
- Energy-efficient hovering point determination
- Minimum-energy trajectory generation
-
Comprehensive energy consumption model that accounts for:
- Propulsion energy during flight
- Hovering energy during data collection
- Communication energy for data transmission
Our approach begins with a centralized process that:
- Groups IoT devices into logical clusters based on spatial proximity
- Assigns each cluster to the most suitable UAV
- Determines optimal hovering points for data collection within each cluster
Once tasks are allocated, each UAV independently:
- Plans an energy-efficient path connecting its assigned hovering points
- Optimizes trajectory parameters using MINCO (Minimum Control Effort) algorithm
- Executes the optimized trajectory while considering kinodynamic constraints
The simulation process is demonstrated in our YouTube video, which illustrates:
- The assignment of clusters to individual UAVs
- Selection of hovering points for data collection
- Generation of optimized flight trajectories
- Multi-UAV coordination during mission execution
While the video does not visualize the actual data collection during hovering (due to visualization constraints), these processes are fully incorporated into the energy consumption calculations and system performance metrics.
The EEPTA-MultiUAV framework has potential applications in:
- Smart city monitoring
- Agricultural surveillance
- Disaster response
- Environmental monitoring
- Industrial inspection
- Border patrol and security
Comming soon...
If you find this research useful, please consider citing our paper:
@article{EEPTA-MultiUAV,
title={Energy-Efficient Path Planning and Task Allocation for Multi-UAV Aided IoT Cluster-Based Data Collection},
author={[Guodong Zhao, Jingjing Wang, Zhijun Meng, Zichen Wang, Hang Fu and Chunxiao Jiang.]},
year={2025}
}
For further information or inquiries, please contact:
- Guodong Zhao
- zhaoguodong00@buaa.edu.cn
- SIC Lab, Beihang University
Note: This repository serves as a companion to our published research and contains documentation about our methodology. For detailed implementation or access to simulation code, please contact the us directly.