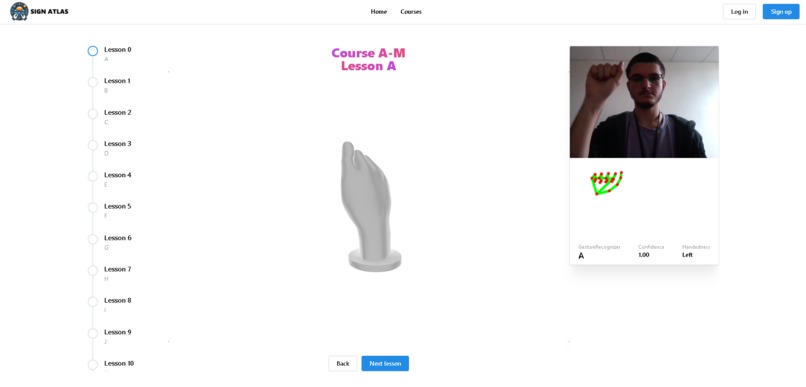
An interactive web platform for learning American Sign Language (ASL) using real-time gesture recognition, 3D hand models, and gamified quizzes.
DEVPOST - MariHacks 7.0 First place - advanced
Learning American Sign Language can be a challenging endeavor, often hampered by a lack of immediate, interactive feedback. Traditional methods like static images or videos can make it difficult to understand the complex, three-dimensional nature of hand signs.
Sign Atlas was built to solve this problem. It's an immersive, browser-based learning platform that makes acquiring ASL skills more accessible and engaging. By leveraging modern web technologies, it provides learners with real-time gesture recognition from their webcam, interactive 3D models to inspect signs from any angle, and a structured, gamified curriculum to test their knowledge. This project aims to bridge the gap between learning and practicing, creating a seamless and effective educational experience.
- 🤘 Real-Time Gesture Recognition: Utilizes a custom-trained machine learning model via MediaPipe to translate ASL signs from a live webcam feed directly in the browser.
- 🎓 Structured Learning Modules: Offers courses that break down the ASL alphabet into manageable lessons (e.g., A-M, N-Z).
- 🧠 Gamified Quizzes: Interactive tests that challenge users to sign the correct letter, providing instant visual feedback on their accuracy.
- 🧊 Interactive 3D Visualizations: Renders a 3D model for each ASL letter, allowing users to rotate, pan, and zoom to understand the precise hand shape from any perspective.
- 🌐 Fully Client-Side: The entire application, including the ML model inference, runs in the web browser, ensuring privacy and a fast, responsive user experience with no server-side dependency for the core features.
The project is built with a modern, full-stack JavaScript and Python toolchain:
| Category | Technologies |
|---|---|
| Frontend | Next.js, React, TypeScript, Mantine UI |
| 3D Graphics | React Three Fiber, Three.js |
| ML Inference | MediaPipe Tasks for Vision (GestureRecognizer) |
| ML Model Training | Python, TensorFlow, MediaPipe Model Maker, OpenCV |
| Deployment | Vercel |
The application has two primary components: the offline model training pipeline and the online Next.js application.
- Model Training (Offline): A set of Python scripts (
collect_imgs.py,create_dataset.py) are used to gather image data and train a custom gesture recognition model using the MediaPipe Model Maker library. This process outputs a lightweight.taskfile optimized for on-device inference. - Next.js Application (Online): The frontend is a server-rendered React application. The trained
.taskmodel is loaded directly into the browser. MediaPipe'sGestureRecognizerthen uses this model to perform real-time inference on the user's webcam stream. This client-side approach minimizes latency and removes the need for a dedicated ML backend server.
To get a local copy up and running, follow these simple steps.
Ensure you have Node.js and npm (or yarn) installed on your machine.
- npm
npm install npm@latest -g
- Clone the repository:
git clone https://github.com/ParsaJafarian/sign-atlas.git
- Navigate to the project directory:
cd sign-atlas - Install NPM packages:
npm install
- Run the development server:
npm run dev
- Open http://localhost:3000 in your browser to see the application.
Note: The Python scripts in the ASLTranslatorModel/ directory are for retraining the model and are not required to run the web application.
Once the application is running, you can:
- Navigate to the Courses page to start a learning module.
- Follow the lessons, using the 3D hand models to guide you.
- Use the integrated ASL Translator camera view to practice making the signs.
- Take a Practice quiz to test your knowledge with real-time feedback.
This project presented several interesting technical challenges that were crucial to its success.
-
Challenge: Achieving Real-Time, In-Browser Gesture Recognition
- Problem: Performing machine learning inference on a live video stream can be computationally expensive. Doing this in the browser without significant latency or freezing the UI is a major challenge.
- Solution: I chose to use MediaPipe's
GestureRecognizertask with its efficient WebAssembly (WASM) backend. The custom-trained TensorFlow Lite model (.taskfile) is loaded on the client-side, eliminating server round-trips for predictions. To stabilize the output and prevent flickering, the prediction logic incorporates a confidence threshold and a debouncing mechanism that confirms a gesture only after it's been detected consistently across several frames. - What I Learned: This taught me the fundamentals of client-side ML, the trade-offs between server-side and on-device inference, and how to optimize for performance in real-time browser applications.
-
Challenge: Integrating Interactive 3D Models into a Web UI
- Problem: Static 2D images of ASL signs can be ambiguous. To provide a clear learning aid, users needed the ability to inspect the hand shapes from any angle.
- Solution: I integrated React Three Fiber to render
.gltf3D models within the React component tree. I created a reusable<ASL3DHand />component that dynamically loads the correct model based on the current lesson. Camera controls were added to allow users to intuitively rotate, pan, and zoom the model. - What I Learned: This was an excellent opportunity to dive into 3D rendering in a declarative React environment. I learned how to manage 3D assets, set up lighting and cameras, and bridge the gap between a standard web UI and an interactive 3D scene to create a more engaging and effective user experience.
While the current version is fully functional, here are some features I'd like to add to enhance the platform:
- User Authentication & Progress Tracking: Implement a full backend with a database to allow users to sign up, log in, and save their progress across courses and quizzes.
- Expanded Vocabulary: Train the ML model to recognize full words and common phrases, moving beyond the alphabet.
- Dockerize Training Pipeline: Containerize the Python model training environment with Docker to ensure perfect reproducibility for anyone wanting to retrain or fine-tune the model.
- Gamification Features: Introduce a points system, achievements, and a leaderboard to further motivate users and encourage consistent practice.
Distributed under the MIT License. See LICENSE for more information.