QueryGPT-ADK is an open-source, multi-agent system for natural language to SQL query generation and explanation. It leverages LLMs and vector search to help users convert natural language questions into SQL queries, explain them, and validate them, making database analytics accessible to everyone.
QueryGPT-ADK in action:
- Enter a natural language question (e.g., "Show me the top 5 medicines by usage")
- Authenticate via registration/login
- See the generated SQL, explanation, and results
- Handles rate limiting, account lockout, and error responses
➡️ Watch the demo video below to see QueryGPT-ADK in action:
➡️ See Usage Examples below for API calls and more!
-
Natural Language to SQL: Converts user questions into SQL queries using LLM-based agents.
-
Multi-Agent Architecture: Modular agents for query formation, explanation, table/column selection, and validation.
-
Automatic Schema Extraction & Table Description:
- New agent (
sql_table_describer_agent) for extracting and describing SQL table schemas, including sub-agents for table-level tasks. - Includes a script to auto-generate JSON documentation of all tables, views, and enums from your database (
generate_tables_json.py).
- New agent (
-
Robust SQL Query Validation: Ensures only valid SELECT statements are executed, supporting both MySQL and PostgreSQL.
-
Vector Search Integration: Uses Qdrant for semantic search over sample queries and table schemas.
-
Validation: Ensures only valid SELECT queries are generated and executed.
-
Production-Ready Security:
- Redis-backed rate limiting (per-IP, distributed)
- Account lockout after repeated failed logins (also Redis-backed)
- JWT authentication, password hashing, and best-practice error handling
-
Extensible & Modular:
- Models organized in
models/, infra ininfra/, and all middlewares inmiddleware/ - Easy to add new agents, tools, or infrastructure
- Models organized in
-
Next.js UI:
- Built with Next.js and TypeScript
- Provides a user-friendly interface for entering queries and viewing generated SQL and results
- Interactive UI for entering and submitting natural language queries to various databases.
-
LLM Provider Flexibility: Supports Gemini (default), Ollama, OpenAI, or any LLM provider by configuring environment variables in
.env. See.env.examplefor details. -
Sample Data: Includes sample queries and table schemas for demonstration and testing.
- Database schema changes are managed using Alembic migrations. See
alembic/for migration scripts. - Code is formatted and linted using
ruff. Runmake lintandmake formatto check and auto-fix code style.
- Added
sql_table_describer_agentfor automated SQL table schema extraction and description. - Introduced
backend/scripts/generate_tables_json.pyfor generating up-to-date JSON documentation of all database tables, views, and enums. - Enhanced SQL query validation tools to support both MySQL and PostgreSQL, with improved error handling.
- Updated configuration and helper utilities for multi-database and LLM support.
- PostgreSQL Support: Added support for PostgreSQL alongside MySQL for query validation.
- SQL Validation Improvements: Cleaned up JSON formatting and simplified SQL syntax validation in query formation prompts.
- Requirements Update: Specified
psycopg2package version as 2.9.10 inrequirements.txt. - Model/Migration Cleanup: Removed
LLMCredentialmodel and related migrations.
- Python 3.9+
- Qdrant vector database
- Redis (for rate limiting and account lockout)
- Next.js (for UI)
- TypeScript (for UI)
- (Optional) Gemini, Ollama, OpenAI, or any other LLM API (configurable via
.env)
- Clone the repository:
git clone https://github.com/Shrijeeth/QueryGPT-ADK.git
cd QueryGPT-ADK- Install dependencies (Backend):
cd backend
python -m pip install -r requirements.txt- Set up environment variables (Backend):
cd backend
cp .env.example .envEdit .env and set your database and Redis URLs as needed. Example:
POSTGRES_DB_URL=postgresql+asyncpg://user:password@localhost:5432/querygpt
REDIS_URL=redis://localhost:6379/1
- Generate up-to-date table and enum documentation (Backend):
cd backend
python -m scripts.generate_tables_jsonThis command will connect to your configured database and auto-generate the latest tables, views, and enums documentation in backend/scripts/data/tables.json. Before running this command, make sure your database is up and running and the connection string in .env is correct for validation database. You also need LLM provider and API key for this command to work. Set SYNTHETIC_DATA_LLM_MODEL and SYNTHETIC_DATA_LLM_API_KEY in .env for this to work.
- Set up environment variables (Frontend):
cd frontend
cp .env.example .envEdit .env and set your API base URL as needed. Example:
NEXT_PUBLIC_API_BASE_URL=http://localhost:8000
- Set up the Frontend (Next.js UI):
cd frontend
npm install
npm run build
npm run devThis will start the frontend at http://localhost:3000.
- Clear Qdrant database (Optional):
cd backend
python scripts/clear_vector_db.py- Load db data into Qdrant:
cd backend
python scripts/add_table_schemas.py
python scripts/add_sample_queries_qdrant.py- (Optional) Use Your Own Data:
To use QueryGPT-ADK with your own data, replace the provided sample_queries.json and tables.json files in the backend/scripts/data/ directory with your own files. Make sure your files follow the same structure as the samples. Then, rerun the data loading scripts:
python scripts/add_table_schemas.py
python scripts/add_sample_queries_qdrant.py-
sample_queries.json
-
Contains a list of example queries for your database.
-
Each entry should have a
description,query, andtype. -
Example:
{ "data": [ { "description": "Check current stock balance", "query": "SELECT * FROM stock_balance", "type": "SAMPLE_QUERY" }, { "description": "Monthly purchase summary", "query": "SELECT ...", "type": "SAMPLE_QUERY" } ] }
-
-
tables.json
-
Contains a list of tables (or views) and their schemas.
-
Each entry should have a
name,description,schema, andtype(usuallyTABLE). -
Example:
{ "data": [ { "name": "medicines", "description": "Stores information about each medicine.", "schema": "CREATE TABLE medicines (id SERIAL PRIMARY KEY, name VARCHAR(255) NOT NULL, ...);", "type": "TABLE" }, { "name": "stock_credit", "description": "When stock is added (purchase or restock).", "schema": "CREATE TABLE stock_credit (id SERIAL PRIMARY KEY, ...);", "type": "TABLE" } ] }
-
Ensure your files follow the above structure for successful data loading and agent operation.
The application is designed to be integrated into a Google ADK, FastAPI, or Streamlit app (frontend coming soon). You can interact with the agents programmatically or extend the project for your use case.
- The
/queryendpoint requires a Bearer token for authentication. Obtain a token from/tokenusing username/password (seefake_users_dbinauth.pyfor default credentials).
Example: Obtain Token and Query (using curl)
# Get access token
curl -X POST "http://localhost:8000/token" -d "username=testuser&password=secret"
# Use the returned access_token for authenticated query
curl -X POST "http://localhost:8000/query" -H "Authorization: Bearer <access_token>" -H "Content-Type: application/json" -d '{"query": "Show me the top 5 medicines by usage"}'curl -X POST "http://localhost:8000/register" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{"username": "alice", "password": "secret123", "email": "[email protected]", "full_name": "Alice Smith"}'curl -X POST "http://localhost:8000/token" \
-H "Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded" \
-d "username=alice&password=secret123"
# Response: {"access_token": "<JWT>", "token_type": "bearer"}curl -X POST "http://localhost:8000/query" \
-H "Authorization: Bearer <JWT>" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{"query": "Show me the top 5 medicines by usage"}'-
Rate Limit Exceeded:
{"detail": "Too Many Requests"} -
Account Lockout:
{"detail": "Account locked due to too many failed login attempts. Try again in 299 seconds."} -
Unauthorized:
{"detail": "Incorrect username or password"}
- Visit http://localhost:8000/docs for Swagger UI (auto-generated, try endpoints in browser)
-
Generate a new migration after model changes:
cd backend alembic revision --autogenerate -m "describe_change" alembic upgrade head
-
Lint and format code:
make lint make format
- Make sure Redis and your database are running and accessible (see
.envfor connection strings). - For distributed deployments, Redis ensures rate limiting and lockout work across all app instances.
- Add new endpoints, agents, or tools in
backend/as needed. Seemiddleware/andinfra/for scalable patterns.
-
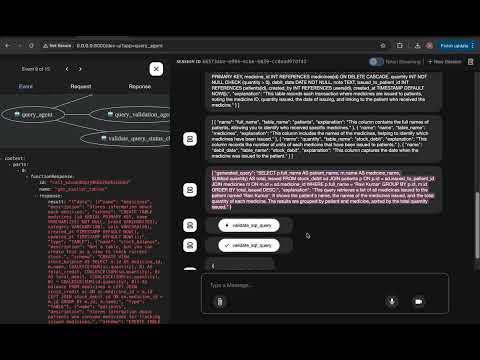
Launch the ADK Web UI
From the parent directory of your agent project (e.g. QueryGPT-ADK/):
cd backend adk web agents- Open the URL provided in the terminal (usually http://localhost:8000 or http://127.0.0.1:8000) in your browser.
- In the top-left corner, select your agent (e.g., query_agent) from the dropdown.
- Chat with your agent using the textbox, inspect function calls, and view responses.
-
Run your Agent from the CLI
You can run your agent directly in the terminal:
cd backend adk run agents/query_agentUse
Ctrl+Cto exit the agent from the terminal. -
Start a Local API Server
To expose your agent as a FastAPI server for local development and integration:
cd backend adk api_server agentsThis will start a FastAPI server (by default on port 8000), allowing you to send HTTP requests to your agent.
-
Programmatic Interaction in Python
You can also invoke your agent programmatically:
from agents.query_agent.agent import root_agent response = root_agent.run(user_input="Show me the top 5 medicines by usage") print(response)
query_agent: Delegates tasks to sub-agents for query formation, explanation, table, and column selection.query_explanation_agent: Finds and explains similar queries related to the user input.table_agent: Identifies relevant tables based on the user input.column_selection_agent: Selects appropriate columns for the query.query_formation_agent: Generates SQL queries based on the user input and available tables and columns.query_validation_agent: Validates the generated SQL queries for correctness and safety.
get_similar_queries_tool: Retrieves similar queries from the Qdrant database based on the user input.get_similar_tables_tool: Retrieves similar tables from the Qdrant database based on the user input.validate_sql_query_tool: Validates the generated SQL query.
- Build a modern Next.js web app for natural-language-to-SQL interactions. (Completed)
- Provide a user-friendly interface for entering queries and viewing generated SQL and results. (Completed)
- Display results in interactive, filterable tables. (To Do)
- Add authentication, query history, and user profile management. (In Progress)
- Integrate responsive design and accessibility best practices. (To Do)
- Enable seamless communication with the FastAPI backend via REST API. (Completed)
- Develop REST API endpoints for query submission, execution, and validation. (Completed)
- Implement CORS, rate limiting, and token-based authentication. (Completed)
- Establish database connectivity and connection pooling. (Completed)
- Provide interactive OpenAPI documentation via Swagger UI. (Completed)
- Write unit and integration tests for API endpoints. (To Do)
- Add support for BYOK (Bring Your Own Key/Model) to allow users to plug in their preferred LLM provider (e.g., OpenAI, Gemini, Ollama, Azure, local models, etc.).
- Provide a configuration interface for selecting and managing model providers.
- Ensure compatibility with multiple model APIs and authentication mechanisms.
- Add documentation and examples for integrating new model providers.
- Build a flexible importer to support connecting and importing schemas from various custom databases (e.g., PostgreSQL, SQLite, Oracle, etc.).
- Provide a UI and/or CLI for users to add new database connections.
- Auto-detect and map table schemas and relationships from imported databases.
- Validate and test queries on imported/custom databases.
- Add support for connecting to and importing from various vector databases (e.g., Pinecone, Weaviate, Milvus, Chroma, etc.).
- Provide configuration and interface for users to add/manage vector DB connections.
- Enable schema and collection import for semantic search and retrieval.
- Ensure integration of custom vector DBs with agentic workflow and query tools.
- Add support for generating synthetic data for a given database.
- Provide a UI and/or CLI for users to generate synthetic data for their own database.
- Create an agent that can generate synthetic data queries for a given database.
- Add scripts to generate synthetic data and fetch schema for a given database.
- Write test cases for agentic workflow (end-to-end and agent interaction tests).
Contributions are welcome! The agent system is modular. New agents and tools can be added by following the existing pattern in backend/agents/. Please open issues or submit pull requests for bug fixes, new features, or improvements.
- Fork the repository.
- Create your feature branch (git checkout -b feature/your-feature).
- Commit your changes (git commit -am 'Add new feature').
- Push to the branch (git push origin feature/your-feature).
- Open a Pull Request.
This project is licensed under the MIT License. See the LICENSE file for details.