OpenTSLM: Time-Series Language Models for Reasoning over Multivariate Medical Text- and Time-Series Data
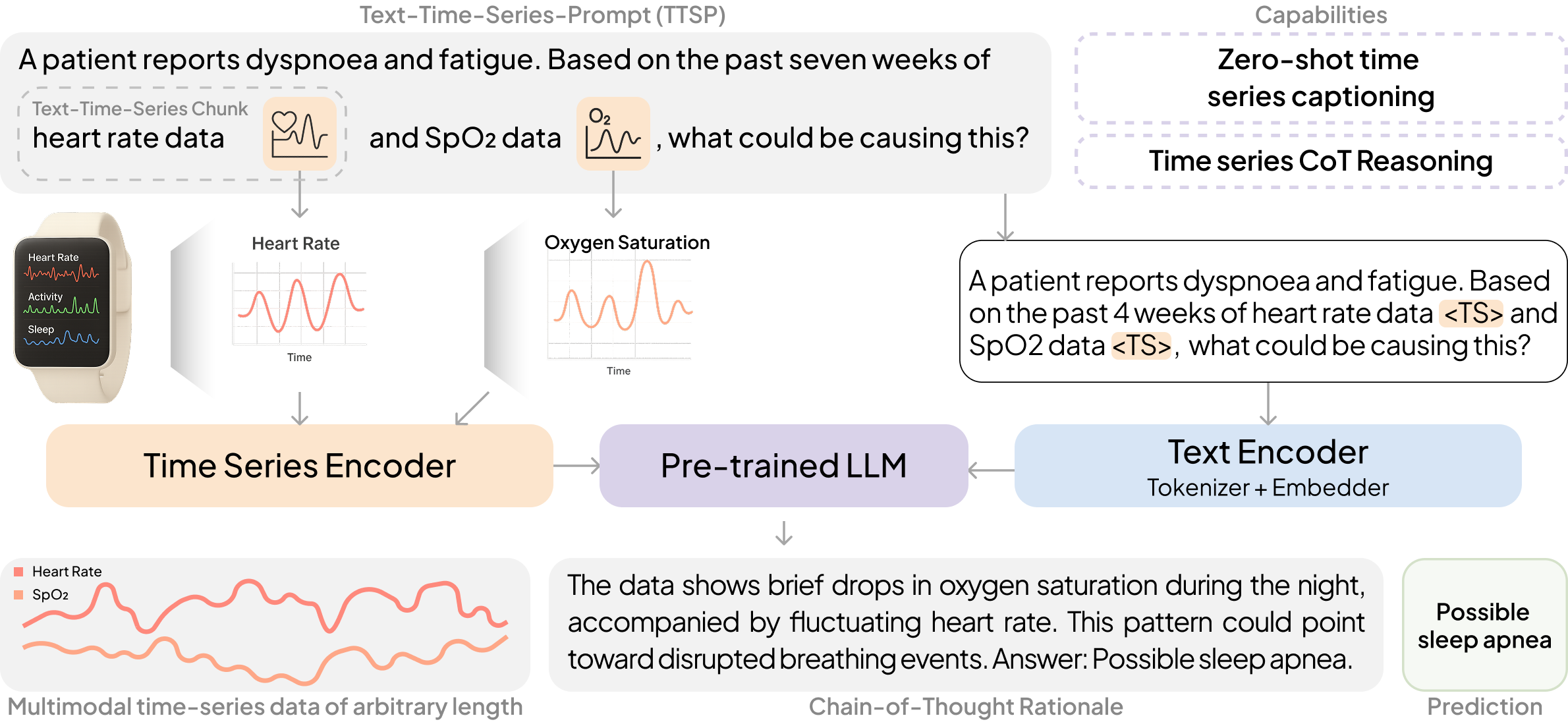
Large Language Models (LLMs) have emerged as powerful tools for interpreting multimodal data (e.g., images, audio, text), often surpassing specialized models. In medicine, they hold particular promise for synthesizing large volumes of clinical information into actionable insights and patient-facing digital health applications. Yet, a major limitation remains their inability to handle time series data. To overcome this gap, we present OpenTSLM, a family of Time Series Language Models (TSLMs) created by integrating time series as a native modality to pretrained Large Language Models, enabling natural-language prompting and reasoning over multiple time series of any length [...] 🔗 Read the full paper
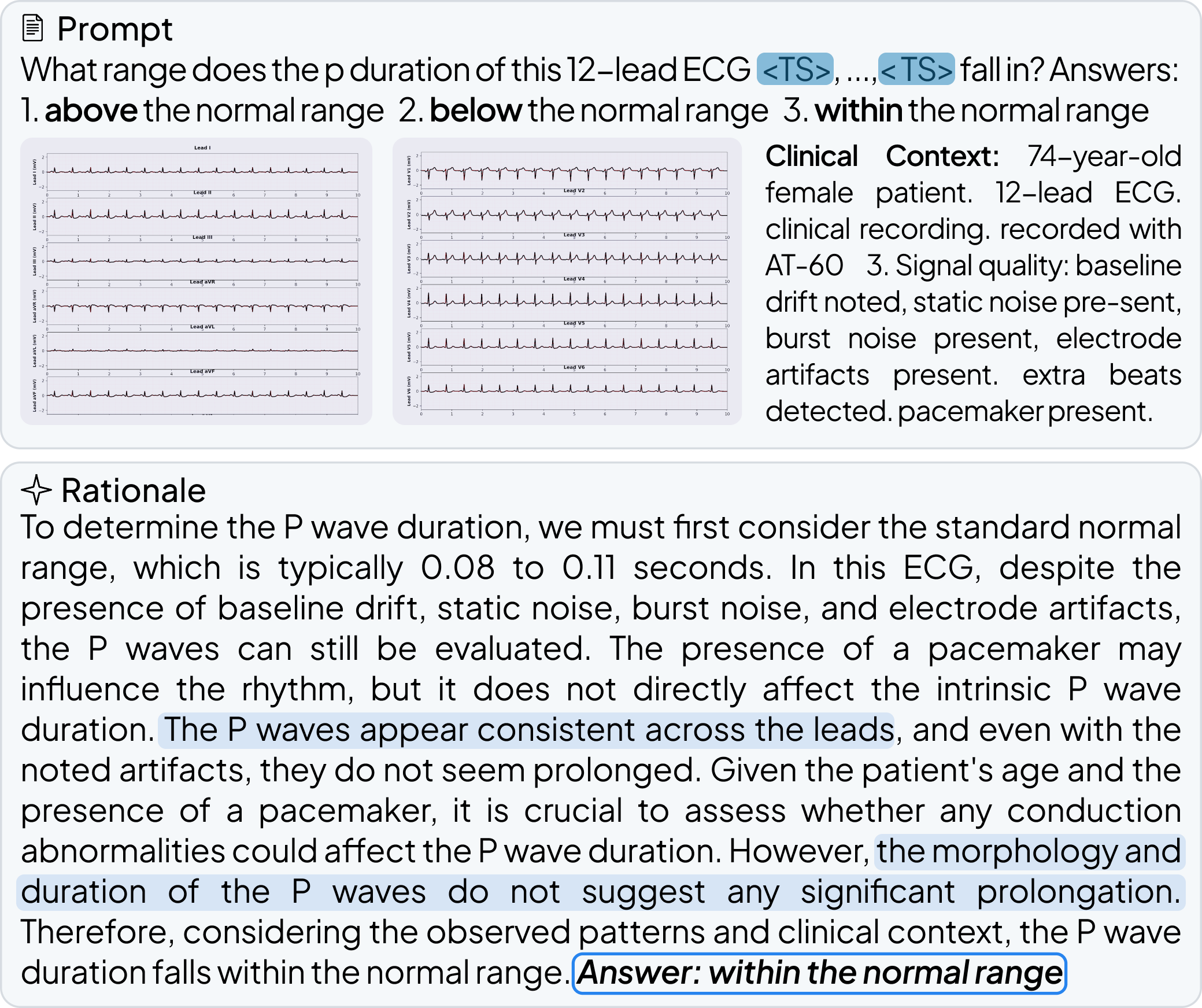
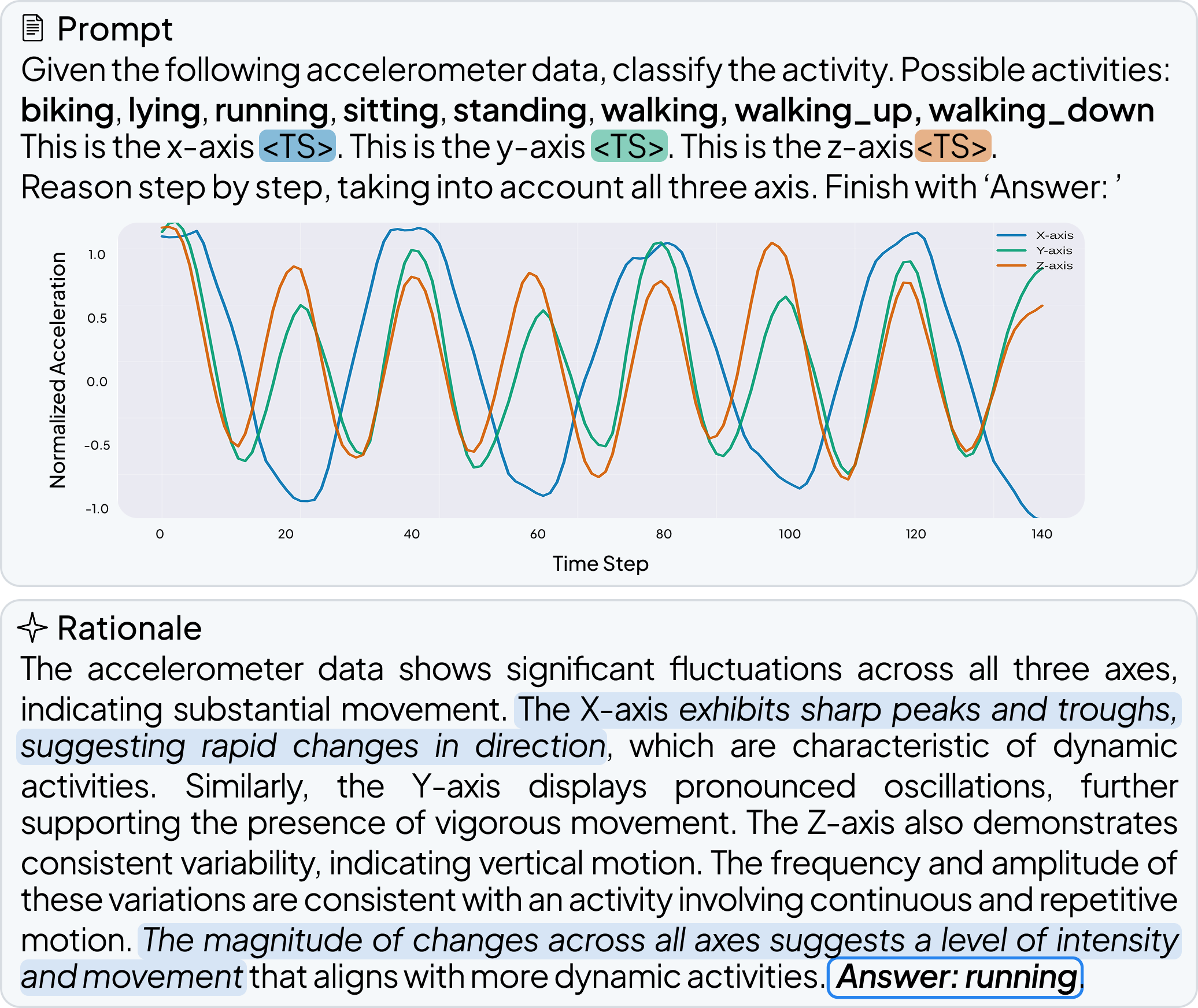
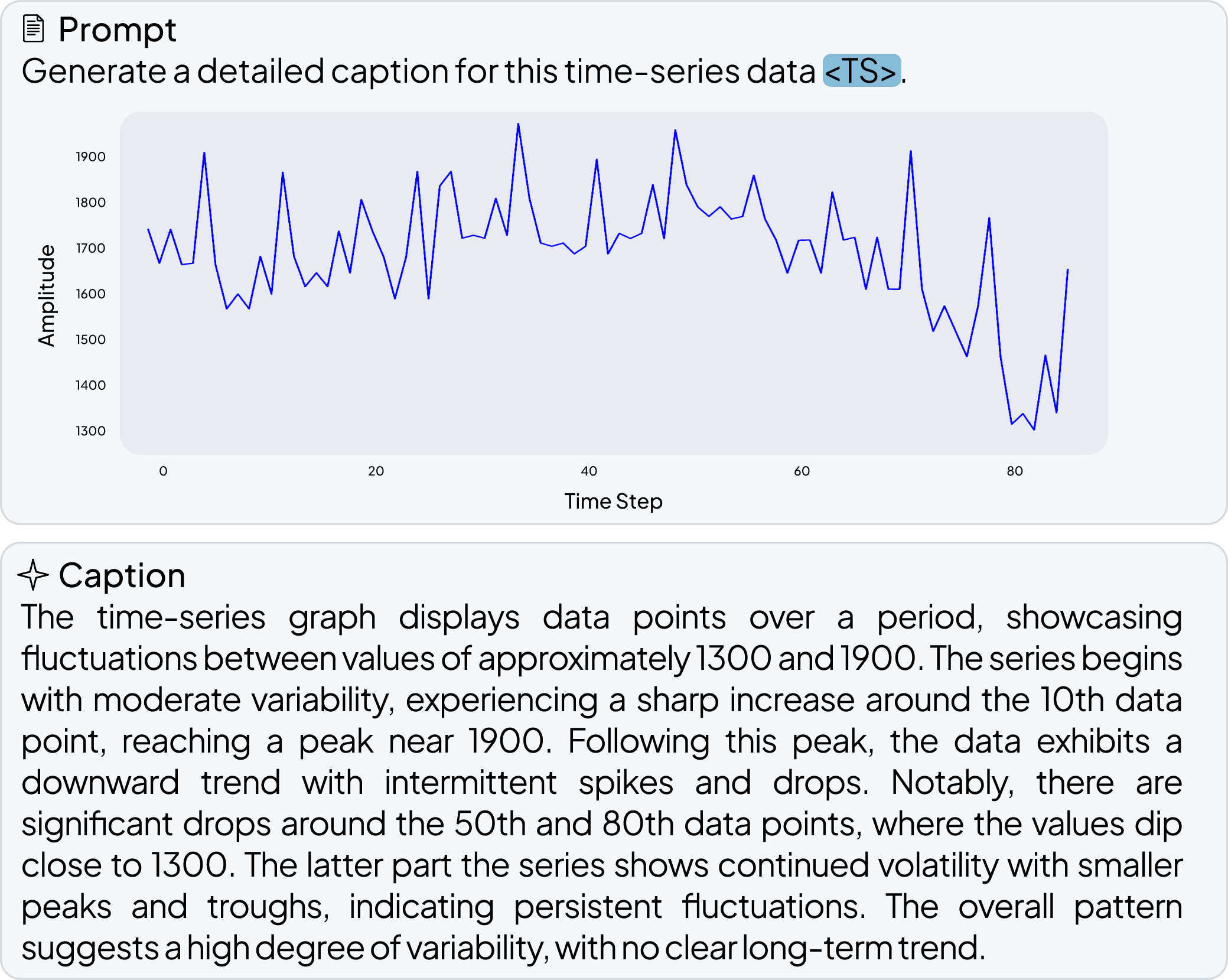
OpenTSLM models can reason over multiple time series of any length at once, generating findings, captions, and rationales in natural language. We tested these models across a wide range of tasks spanning Human Activity Recognition (HAR) from 3-axis acceleration data, sleep staging from EEG readings, 12-lead ECG question answering, and time series captioning. Some examples are shown below, more are available in the paper.
pip install opentslmOpenTSLM is designed to work with Llama and Gemma models, with Llama 3.2 1B as the default. These models are stored in Hugging Face repositories which may require access permissions. Follow these steps to gain access and download:
-
Request Access (for Llama models)
Visit the Llama model repository (e.g., https://huggingface.co/meta-llama/Llama-3.2-1B) or Gemma models repository (https://huggingface.co/google/gemma-3-270m) and request access from Meta. -
Authenticate with Hugging Face
Log in to your Hugging Face account and configure the CLI:huggingface-cli login
-
Create an API Token
- Go to your Hugging Face settings: https://huggingface.co/settings/tokens
- Generate a new token with
readscope. - Copy the token for CLI login.
OpenTSLM has been tested and works with the following models:
Llama Models:
- meta-llama/Llama-3.2-1B (default)
- meta-llama/Llama-3.2-3B
Gemma Models:
- google/gemma-3-270m
- google/gemma-3-1b-pt
Other variants may work but have not been extensively tested.
A factory class called OpenTSLM for easily loading pre-trained models from Hugging Face Hub. The load_pretrained method automatically detects the model type and returns the appropriate model instance.
There are demo scripts available which use the following minimal code. If you want to create your own applications, create a new file in this repo folder and use the following code as start:
from opentslm import OpenTSLM
from opentslm.time_series_datasets.TSQADataset import TSQADataset
from opentslm.time_series_datasets.util import extend_time_series_to_match_patch_size_and_aggregate
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader
from opentslm.model_config import PATCH_SIZE
REPO_ID = "OpenTSLM/llama-3.2-1b-tsqa-sp"
# Use CPU or CUDA for inference. MPS does NOT work for pretrained HF checkpoints.
model = OpenTSLM.load_pretrained(REPO_ID, device="cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
test_dataset = TSQADataset("test", EOS_TOKEN=model.get_eos_token())
test_loader = DataLoader(
test_dataset,
shuffle=False,
batch_size=1,
collate_fn=lambda batch: extend_time_series_to_match_patch_size_and_aggregate(
batch, patch_size=PATCH_SIZE
),
)
for i, batch in enumerate(test_loader):
predictions = model.generate(batch, max_new_tokens=200)
for sample, pred in zip(batch, predictions):
print("Question:", sample.get("pre_prompt", "N/A"))
print("Answer:", sample.get("answer", "N/A"))
print("Output:", pred)
if i >= 4:
breakTo run the demos and use finetuning scripts clone the repository and set up all dependencies. We recommend using uv to set up the environment, but you can also use pip:
git clone https://github.com/StanfordBDHG/OpenTSLM.git
# uv environment management (recommended). Installs uv if it does not exist and creates the virtual environment
command uv > /dev/null || curl -LsSf https://astral.sh/uv/install.sh | sh
uv sync --all-groups
source .venv/bin/activate
# or alternatively install via pip:
pip install -r requirements.txt
We provide ready-to-use demo scripts in the demo/huggingface/ directory that demonstrate how to load pretrained models from HuggingFace Hub and run inference on the evaluation sets for each task:
01_test_hf_tsqa.py- Test TSQA (Time Series Question Answering) models02_test_hf_m4.py- Test M4 (Time Series Captioning) models03_test_hf_har_cot.py- Test HAR CoT (Human Activity Recognition Chain-of-Thought) models04_test_hf_sleep_cot.py- Test Sleep CoT (Sleep Stage Classification) models05_test_hf_ecg_qa_cot.py- Test ECG QA CoT (ECG Question Answering) models
Each script:
- Downloads the model checkpoint from HuggingFace Hub automatically (change repo id as neededs)
- Loads the corresponding test dataset
- Runs inference on the evaluation set
- Prints model outputs with sample information
Note: The scripts above use the OpenTSLM-SP models except for ECG-QA, as they require less VRAM and should run on most hardware. Change the model checkpoints as needed in each file.
Usage:
# Run any of the demo scripts
python demo/huggingface/01_test_hf_tsqa.py
python demo/huggingface/02_test_hf_m4.py
python demo/huggingface/03_test_hf_har_cot.py
python demo/huggingface/04_test_hf_sleep_cot.py
python demo/huggingface/05_test_hf_ecg_qa_cot.pyCustomizing the model:
Edit the REPO_ID variable at the top of each script to test different model variants. For example:
# In 01_test_hf_tsqa.py
REPO_ID = "OpenTSLM/llama-3.2-1b-tsqa-sp" # Soft Prompt model
# or
REPO_ID = "OpenTSLM/llama-3.2-1b-tsqa-flamingo" # Flamingo modelAvailable models on HuggingFace:
All pretrained models are available under the OpenTSLM organization on HuggingFace Hub. Model names follow the pattern:
OpenTSLM/{base_model}-{dataset}-{model_type}base_model:llama-3.2-1b,llama-3.2-3b,gemma-3-1b-pt,gemma-3-270mdataset:tsqa,m4,har,sleep,ecgmodel_type:sp(Soft Prompt) orflamingo(Flamingo)
Example: OpenTSLM/llama-3.2-1b-ecg-flamingo
OpenTSLM uses curriculum learning with progressive training stages:
- Stage 1 (MCQ): Multiple choice questions on time series data (TSQA dataset)
- Stage 2 (Captioning): Generate detailed captions for time series (M4 dataset)
- Stage 3 (CoT): Chain-of-thought reasoning on human activity recognition (HAR dataset)
- Stage 4 (Sleep CoT): Chain-of-thought reasoning on sleep stage classification (SleepEDF dataset)
- Stage 5 (ECG CoT): Chain-of-thought reasoning on ECG question answering (ECG QA dataset)
⚠️ MPS/CUDA Compatibility Warning:If you are using Apple's MPS (Metal Performance Shaders) backend (e.g., on Mac with Apple Silicon), you may encounter issues with training or inference. Checkpoints trained with CUDA (NVIDIA GPUs) may not yield good results or may not be fully compatible when loaded and run on MPS. For best results, use the same device type (CUDA or MPS) for both training and inference. CUDA is preferred in general.
# Run full curriculum with OpenTSLMFlamingo
python curriculum_learning.py --model OpenTSLMSP
# Run full curriculum with OpenTSLMSP
python curriculum_learning.py --model OpenTSLMFlamingo
# Run specific stages
python curriculum_learning.py --model OpenTSLMFlamingo --stages stage1_mcq
python curriculum_learning.py --model OpenTSLMFlamingo --stages stage2_captioning
python curriculum_learning.py --model OpenTSLMFlamingo --stages stage3_cot
python curriculum_learning.py --model OpenTSLMFlamingo --stages stage4_sleep_cot
python curriculum_learning.py --model OpenTSLMFlamingo --stages stage5_ecg_cot
# Run multiple stages
python curriculum_learning.py --model OpenTSLMFlamingo --stages stage1_mcq stage2_captioning stage3_cot
# Specify device
python curriculum_learning.py --model OpenTSLMFlamingo --device cuda
# Use different models
python curriculum_learning.py --model OpenTSLMFlamingo --llm_id meta-llama/Llama-3.2-1B
python curriculum_learning.py --model OpenTSLMFlamingo --llm_id google/gemma-3-270m
# Run only evaluation
python curriculum_learning.py --model OpenTSLMFlamingo --eval_only--model: Model type (OpenTSLMSPorOpenTSLMFlamingo)--stages: Stages to run (any combination of:stage1_mcq,stage2_captioning,stage3_cot,stage4_sleep_cot,stage5_ecg_cot)--device: Device to use (cuda,mps,cpu)--eval_only: Run evaluation only (requires an existing checkpoint for the stage)--llm_id: Model ID (default:meta-llama/Llama-3.2-1B, supports Llama and Gemma models)--batch_size: Batch size for training--gradient_checkpointing: Enable gradient checkpointing for memory efficiency--verbose: Enable verbose logging
Helper scripts for analysis, testing, and batch processing are available in the scripts/ directory:
Shell Scripts:
run_all_memory.sh- Run comprehensive memory usage analysis across all stagesrun_all_memory_missing.sh- Run memory analysis for missing stages only
Python Scripts:
create_doctor_eval_dataset.py- Create evaluation dataset for doctor assessmentsget_memory_use.py- Analyze and report memory usage across stagesplot_memory_usage.py- Visualize memory usage patternsplot_memory_simulation.py- Simulate and plot memory requirementsplot_memory_simulation_per_length.py- Analyze memory usage by sequence lengthhf_test.py- Test HuggingFace model loading and inference
These scripts can be customized by editing the parameters directly or by passing command-line arguments.
- Repository IDs ending with
-spwill load and returnOpenTSLMSPmodels - Repository IDs ending with
-flamingowill load and returnOpenTSLMFlamingomodels
During training, the script creates a structured results directory:
results/
├── {llm_id}/
│ ├── OpenTSLMSP/
│ │ ├── stage1_mcq/
│ │ │ ├── checkpoints/
│ │ │ │ ├── best_model.pt
│ │ │ │ └── loss_history.txt
│ │ │ └── results/
│ │ │ ├── test_predictions.jsonl
│ │ │ └── metrics.json
│ │ ├── stage2_captioning/
│ │ │ ├── checkpoints/
│ │ │ │ ├── best_model.pt
│ │ │ │ └── loss_history.txt
│ │ │ └── results/
│ │ │ ├── test_predictions.jsonl
│ │ │ └── metrics.json
│ │ ├── stage3_cot/
│ │ │ ├── checkpoints/
│ │ │ │ ├── best_model.pt
│ │ │ │ └── loss_history.txt
│ │ │ └── results/
│ │ │ ├── test_predictions.jsonl
│ │ │ └── metrics.json
│ │ ├── stage4_sleep_cot/
│ │ │ ├── checkpoints/
│ │ │ │ ├── best_model.pt
│ │ │ │ └── loss_history.txt
│ │ │ └── results/
│ │ │ ├── test_predictions.jsonl
│ │ │ └── metrics.json
│ │ ├── stage5_ecg_cot/
│ │ │ ├── checkpoints/
│ │ │ │ ├── best_model.pt
│ │ │ │ └── loss_history.txt
│ │ │ └── results/
│ │ │ ├── test_predictions.jsonl
│ │ │ └── metrics.json
│ │ └── curriculum_results.json
│ └── OpenTSLMFlamingo/
│ ├── stage1_mcq/
│ ├── stage2_captioning/
│ ├── stage3_cot/
│ ├── stage4_sleep_cot/
│ ├── stage5_ecg_cot/
│ └── curriculum_results.json
Each stage automatically loads the best model from the previous stage, ensuring proper curriculum progression. Results are organized by model ID (sanitized), then by model type and stage. The {llm_id} directory name is derived from the --llm_id parameter (e.g., meta-llama/Llama-3.2-1B becomes Llama3_2_1B, google/gemma-3-1b-pt becomes gemma_3_1b_pt).
This work was made possible through the collaborative efforts of an interdisciplinary team of researchers from computer science, medicine, and engineering. Thank you to all of the Co-authors of the TSLM publication:
- Patrick Langer (Stanford University, ETH Zurich, ETH Agentic Systems Lab)
- Thomas Kaar (Stanford University, TUM, ETH Agentic Systems Lab)
- Max Rosenblattl (Stanford University, TUM, ETH Agentic Systems Lab)
- Maxwell A. Xu (Google Research, University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign)
- Winnie Chow (Stanford University)
- Martin Maritsch (Amazon)
- Robert Jakob (ETH Zurich, ETH Agentic Systems Lab)
- Aradhana Verma (Stanford University)
- Brian Han (Stanford University)
- Daniel Seung Kim (University of Washington)
- Henry Chubb (Stanford University)
- Scott Ceresnak (Stanford University)
- Aydin Zahedivash (Stanford University)
- Alexander Tarlochan Singh Sandhu (Stanford University)
- Fatima Rodriguez (Stanford University)
- Daniel McDuff (Google Research, University of Washington)
- Elgar Fleisch (ETH Zurich, University of St. Gallen)
- Oliver Aalami (Stanford University)
- Filipe Barata (ETH Zurich)
- Paul Schmiedmayer (Stanford University)
Contributions to this project are welcome. Please make sure to read the contribution guidelines and the contributor covenant code of conduct first.
You can find a list of all current contributors at CONTRIBUTORS.md.
Are you a student interested in advancing the frontiers of time-series language models and digital health research? We welcome students to get involved in our research projects!
Visit our Student Research Opportunities page to learn more about current projects and how you can contribute to cutting-edge research at the intersection of AI and healthcare.
For researchers and project partners interested in collaboration opportunities, please reach out to us at [email protected].
This project is licensed under the MIT License.
OpenTSLM uses REUSE specification to ensure consistent and machine-readable licensing across the repository.
To add or update license headers, run:
reuse annotate --recursive \
--copyright "Stanford University, ETH Zurich, and the project authors (see CONTRIBUTORS.md)" \
--copyright "This source file is part of the OpenTSLM open-source project." \
--license MIT \
--skip-unrecognized \
.