Team: Team 1
Overview • Repository • Datasets • Approach • Results • Conclusion • Contact
- Adithya Shetty
- Aibek Akhmetkazy
- Altair Toleugazinov
- Daniyal Asif
- Sergey Smetankin
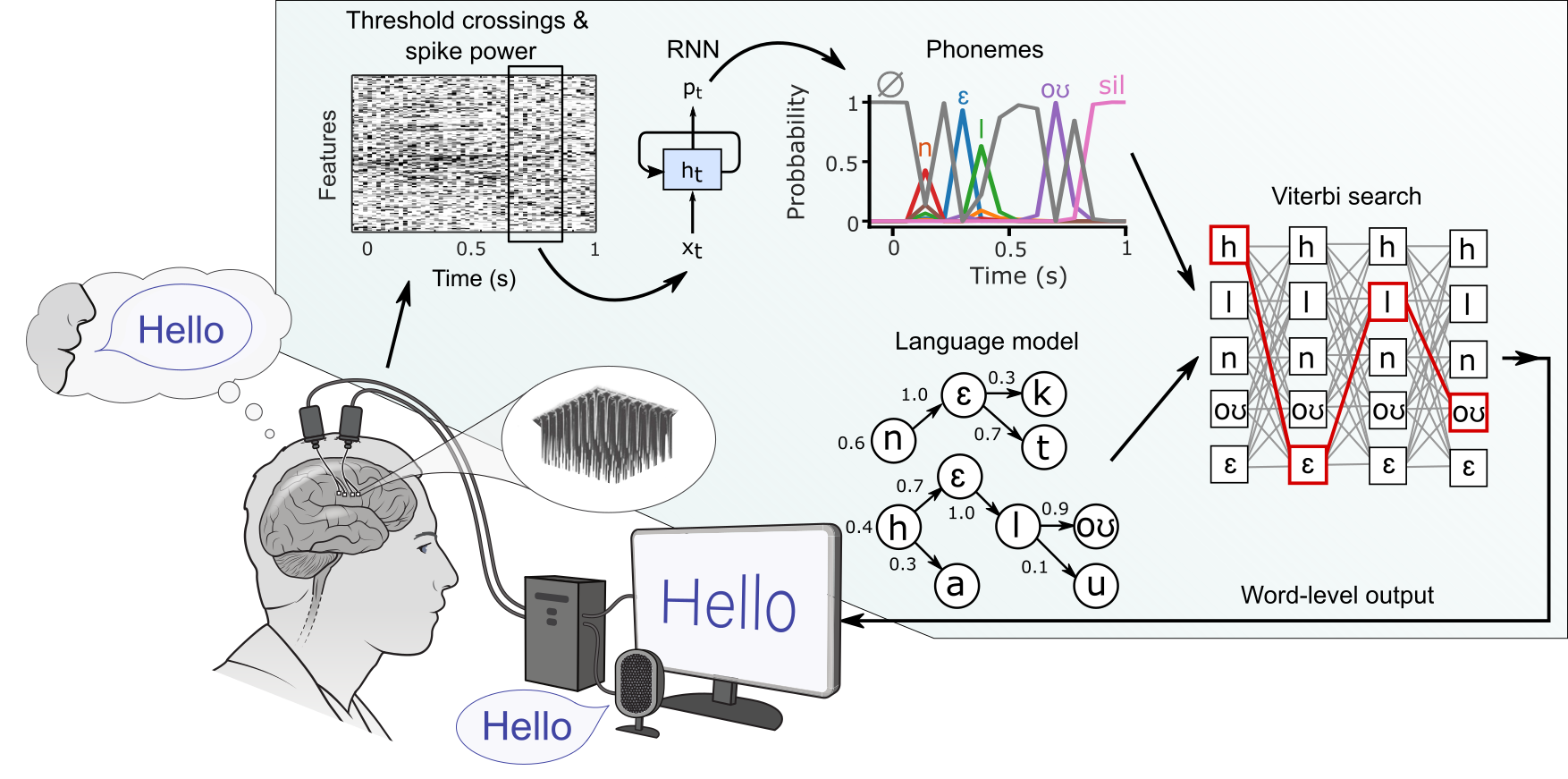
Our project is part of the "Brain-to-Text Benchmark '24" hosted on Eval.ai, which challenges teams to develop a system capable of translating human neural activity into text using deep learning. This involves decoding EEG data to convert it into sentences.
approach1: Folder for the first approach using specific neural decoding strategies.approach2: Folder for the second approach with alternate decoding strategies.approach3: Folder for the third approach, integrating complex models.baseline: Folder to run the Baseline model for comparison.requirements.txt: List of Python dependencies for reproducing the analysis.
To set up the environment and run the code, please follow these steps:
- Clone the repository:
git clone https://github.com/your-repo-url - Install dependencies:
pip install -r requirements.txt - Navigate to the approach folder:
cd approach1(or any other approach) - Run the notebook:
jupyter notebook
We utilize a dataset from neurobiological experiments where neural activity was recorded with microelectrode arrays. The data consist of 12,100 spoken sentences and include features like threshold crossings and spike band power, which are crucial for developing our decoding models.
- sentenceText: Text of each sentence.
- spikePow: Time series of spike power neural features.
- tx1, tx2, tx3, tx4: Time series of threshold crossing neural features with different thresholds.
Our project includes three main approaches to decoding neural signals:
-
Approach 1: Involves preprocessing for data normalization, feature extraction by combining
tx1andspikePow, phoneme decoding using a G2p model, and a SpeechBCIModel for generating phoneme probabilities, followed by a language model for text generation. -
Approach 2: Starts with data segmentation and normalization, utilizes
tx1andspikePowfor feature extraction, employs a G2p model for phoneme decoding, and uses a convolutional and LSTM network for neural decoding, with an n-gram language model to enhance text coherence. -
Approach 3: Features block-wise normalization, concatenates
tx1andspikePowfor input features, uses a Seq2Seq model with attention mechanisms for phoneme-to-text conversion, and includes a GRU-based encoder and decoder for final text prediction.
The following table compares the Word Error Rate (%) across different approaches:
| Approach | Word Error Rate (%) |
|---|---|
| SOTA | 8.93 |
| Approach 1 | 13.65 |
| Approach 2 | 14.78 |
| Approach 3 | 15.23 |
| Baseline | 15.43 |
Our project demonstrates significant advances in the ability to decode speech from neural signals, pushing the boundaries of what's possible in brain-computer interfacing technology.
For more details, you can reach out to us:
- Adithya Shetty: [email protected]
- Aibek Akhmetkazy: [email protected]
- Altair Toleugazinov: [email protected]
- Daniyal Asif: [email protected]
- Sergey Smetankin: [email protected]