Releases: atellaluca/ImportSpy
ImportSpy v0.4.1
Fixes
- Added validation for environment secrets in
SystemValidator.
In the previous version, validation stopped at regular environment variables and did not check for the presence or match of secrets. - Introduced new error codes (
SCOPE_SECRETS,KEY_SYSTEM_1) to improve handling and reporting of missing secrets. - Improved exception handling when expected secrets are absent.
Details
- Implemented
_secrets_validatorto ensure that:- All secrets from the source environment are present in the target environment.
- Missing secrets are properly reported in the error bundle.
- Minor cleanup in tests, removing unused fixtures.
v0.4.0 – Context-aware validation & structured violations
What's new
-
Environment-aware import contracts
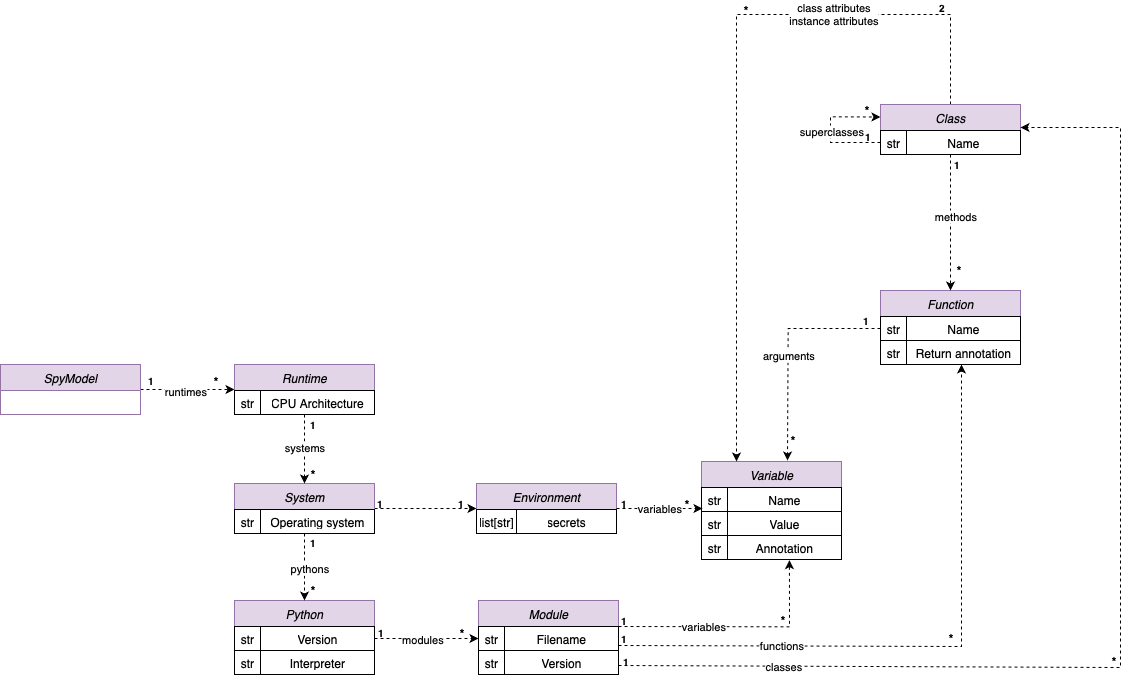
Added support for theenvironmentkey in.ymlcontracts. You can now specify:variables: a list of expected runtime environment variables using the newVariabletype.secrets: a list of required secret names (without exposing content).
This enables safe, declarative enforcement of runtime conditions without leaking sensitive data.
-
Structured import errors
Import failures are now context-aware. The newViolationSystemintroduces a structured error model that includes the reason, scope, and expected vs actual values—making debugging and tooling integration easier. -
SpyModel simplification
The internal representation ofSpyModelhas been cleaned up and optimized for better maintainability and future extensibility. -
Documentation overhaul
All documentation has been migrated from Sphinx to MkDocs. The new docs are faster to navigate and easier to contribute to.
Fixes and improvements
- Updated internal validation logic to support environment-based conditions.
- Added test coverage for new
environmentandViolationSystemfeatures. - Security patches applied to all dependencies.
Breaking changes
-
Environment variable schema
Previously defined as a raw dictionary, environment variables must now be defined using the newVariabletype under theenvironmentsection.environment: variables: - name: MY_ENV_VAR required: true secrets: - API_TOKEN
Release v0.3.2
This release introduces a key structural update to the Variable model, improving clarity, validation, and YAML contract expressiveness. It also includes a full rewrite of the README.rst for better readability and consistency with the updated architecture.
What's Changed
Variable model refactor
- Replaced the previous dictionary-style variable declaration with a list of
Variableobjects. - Each variable now includes:
name: variable identifiervalue: literal value (int, str, float, bool, None)annotation: optional type annotation, validated at runtime
- Introduced
Variable.from_variable_info()for metadata transformation. - Type annotations are validated against a defined list of supported types.
YAML contract structure update
- Contracts must now define
variablesas a list of structured objects. - Example:
variables:
- name: engine
value: docker
annotation: strImportSpy v0.3.0 — YAML Contracts & CLI Validation
🎉 Highlights
- YAML contract support → Say goodbye to hardcoded
SpyModel. - Dual validation modes:
- ✅ Embedded (runtime enforcement)
- ✅ External CLI (for CI/CD, scripting, or pipelines)
- Powerful new CLI using Typer
- New architecture for reflection, validation, and error messaging
✨ What’s New
✅ YAML-based Contract System
- Modules now validated against external
.ymldefinitions - Define required:
- Classes, methods, attributes
- Runtime (Python version, OS, arch, environment variables)
- Deployment-specific logic
🔧 CLI Integration
importspy -s contracts.yml mymodule.pyImportSpy 0.2.0 - Advanced Execution Compliance & Security
Tag: 0.2.0
Release Type: Minor
Previous Version: 0.1.12
Date: March 4, 2025
🔥 What’s New in ImportSpy 0.2.0?
This milestone release significantly enhances runtime compliance, security, and execution validation for modular and distributed Python applications.
With full execution context verification, enhanced import-time security, and performance optimizations, ImportSpy now offers an even more robust validation system.
- 🔍 Prevent execution failures before they happen
- 🛡️ Ensure all imported modules conform to execution rules
- ❌ Block misconfigured environments from running your code
- 🔬 Provide deep introspection of execution security
📌 Documentation Update: The documentation has been rewritten & expanded with structured beginner & advanced guides, architectural deep dives, and API enhancements.
📖 Explore the full docs → ImportSpy Documentation
🚀 Key Enhancements in ImportSpy 0.2.0
1️⃣ Comprehensive Validation of Imported Modules in Execution Context
✅ Full execution context validation → Modules are now validated at the moment of import, ensuring they match predefined execution rules.
✅ Cross-layer verification → Imported modules are checked against:
- System architecture (
x86_64,ARM64, etc.) - Operating system compatibility (
Linux,Windows,macOS) - Python interpreter version & implementation (
CPython,PyPy) - Dependency versions to prevent silent upgrades that may introduce conflicts.
- Required environment variables before execution begins.
✅ Blocking mechanism → Non-compliant modules are prevented from execution, ensuring stability and preventing runtime failures.
2️⃣ Strengthened Compliance for Modular and Plugin-Based Architectures
✅ Enforced import-time validation → Dynamically loaded modules must now adhere to predefined structures.
✅ Signature verification → Ensures expected functions, classes, and attributes exist within imported modules.
✅ Microservices and plugin support → Modules imported into microservices must match expected API specifications.
✅ Distributed consistency checks → Detects inconsistencies across multiple instances of the same module in a distributed environment.
3️⃣ Advanced Environment and Dependency Validation
✅ Execution environment compliance → Every import is validated within its execution context to prevent misconfigurations.
✅ Package integrity verification → ImportSpy detects modified dependencies, ensuring installed packages have not been altered post-installation.
✅ Version stability enforcement → Prevents silent dependency upgrades that could introduce unexpected behavior.
4️⃣ Improved Runtime Security and System Hardening
✅ Security-first execution enforcement → Ensures modules meet security requirements before execution.
✅ Environment variable enforcement → Modules relying on specific configurations must pass validation before being imported.
✅ Unauthorized import prevention → Blocks altered, untrusted, or modified modules from executing, reducing security vulnerabilities.
5️⃣ Codebase Refactoring and Performance Optimization
✅ Optimized validation logic → Reduced execution overhead for faster import-time checks.
✅ Refactored internal structure → Improved code maintainability and extendability.
✅ Granular logging and error handling → Provides clearer compliance failure reports for developers.
6️⃣ Enhanced Documentation and Developer Usability
✅ Complete API Reference Update → Reflects the new validation mechanisms.
✅ Improved onboarding guides & examples → Easier integration into software architectures.
✅ Streamlined documentation → Clearer explanations with a focus on real-world compliance scenarios.
📖 Explore the new docs → ImportSpy Docs
📦 Upgrade to ImportSpy 0.2.0
To install or upgrade to the latest version:
pip install --upgrade importspyImportSpy 0.1.12: Dependency Upgrades
Changelog:
-
Dependency Updates:
- Pydantic: Updated from
2.10.3to2.10.4.- Includes bug fixes and compatibility improvements. Notable changes:
- Resolved an
AttributeErrorwhen using data classes withdefer_build=True. - Fixed URL compatibility issues between versions
2.9.2and2.10.X.
- Resolved an
- Details: GitHub Issues
- Includes bug fixes and compatibility improvements. Notable changes:
- Jinja2: Updated from
3.1.4to3.1.5.- Introduced critical security fixes and minor bug resolutions to enhance stability.
- Details: New Releases
- Pytest: Updated from
8.3.3to8.3.4.- General improvements and bug fixes for the Python testing framework.
- Sphinx-rtd-theme: Updated from
3.0.1to3.0.2.- Minor updates to improve the style and functionality of Sphinx-generated documentation.
- Pydantic: Updated from
-
Why Upgrade?
This release ensures a more stable, secure, and feature-rich environment. Dependency updates address known issues and provide important improvements.
For further details, see the links provided for specific dependency updates.
ImportSpy 0.1.11: Enhanced Validation and Error Clarity
Release Notes for ImportSpy 0.1.11
What's New in Version 0.1.11
Enhancements
-
Improved Error Messages for Validation:
- Enhanced error messages for class methods, attributes, and superclass mismatches to provide clearer, more actionable feedback during validation.
- Added specific error messages for missing and mismatched functions, classes, attributes, and environment variables.
-
Modular Validation Refactoring:
- Refactored the
is_subsetfunction for better modularity:- Introduced helper functions
list_compareanddict_compareto simplify validation logic and improve code readability.
- Introduced helper functions
- Refactored the
How to Upgrade
Update to the latest version using pip:
pip install --upgrade importspyImportSpy 0.1.10 - Feature Enhancements and Improvements 🚀
What's New in Version 0.1.10
🔥 New Features:
- Environment Variable Support:
- You can now define
env_varsas a dictionary inSpyModel, enabling validation of required environment variables and their values. - Example:
env_vars: dict = { "CI": "true", "DATA_PATH": "/data/" }
- You can now define
🔧 Improvements:
- Enhanced Variables Validation:
- Variables are now represented as a dictionary in
SpyModel(variables: dict), allowing developers to validate both the names and the expected values of module-level variables. - Example:
variables: dict = { "default_timeout": "30", "max_connections": "100" }
- Variables are now represented as a dictionary in
nameField in Classes Now Mandatory:- The
namefield inClassModelis now required, ensuring clarity and consistency in class validation.
- The
How to Update:
- Update your package:
pip install --upgrade importspy
Proactive Validation Enhancements and CI Integration
What's New in Version 0.1.9
- Proactive Validation Enhancements: Enhanced the
is_subsetfunction to raise descriptiveValueErrorsfor each validation failure, improving the clarity and maintainability of error handling. - Documentation Updates: Updated all documentation to reflect changes in code and added examples on how to handle new validation exceptions.
Continuous Integration Improvements
- Python Package Testing Workflow: Introduced a new GitHub Actions workflow to automate the testing process, ensuring that each push or pull request to the 'main' branch triggers a series of actions that validate the codebase across different environments and Python versions.
- Setup steps for Python environment and dependencies using Poetry.
- Code linting with flake8 to enforce coding standards and identify issues early.
- Automated tests with pytest to verify that new changes do not break existing functionalities.
- Documentation build using Sphinx to keep the project documentation up to date.
Documentation and README Updates
- Enhanced Documentation: Updated the documentation and README files to better reflect the current functionalities and how to implement the module within other projects.
- Workflow Integration: Detailed the inclusion of a new GitHub Actions workflow that automates testing across multiple Python versions (3.9, 3.10, 3.11, 3.12) to ensure compatibility and reliability.
- Example Code Added: New example codes and usage scenarios have been added to the documentation to assist users in understanding how to use the validation features effectively.
Other Improvements
- Simplified File Path Extraction: Refactored string handling to ensure compatibility with Python versions 3.9 to 3.11, making the codebase more future-proof.
Improvements
- Improved error message clarity in the validation process.
We encourage all users to update to this latest version to benefit from these improvements.
v0.1.8
This release introduces the following changes:
Features:
- Added support for class and instance attributes in SpyModel and ClassModel.
- Implemented
extract_variablesto retrieve variables from modules. - Enhanced
extract_classesto extract class attributes, instance attributes, methods, and superclasses.
Documentation:
- Updated
README.rstto reflect the new validation capabilities, including examples of variable, class, and instance attribute validation.
Version:
- Version bump to
0.1.8.