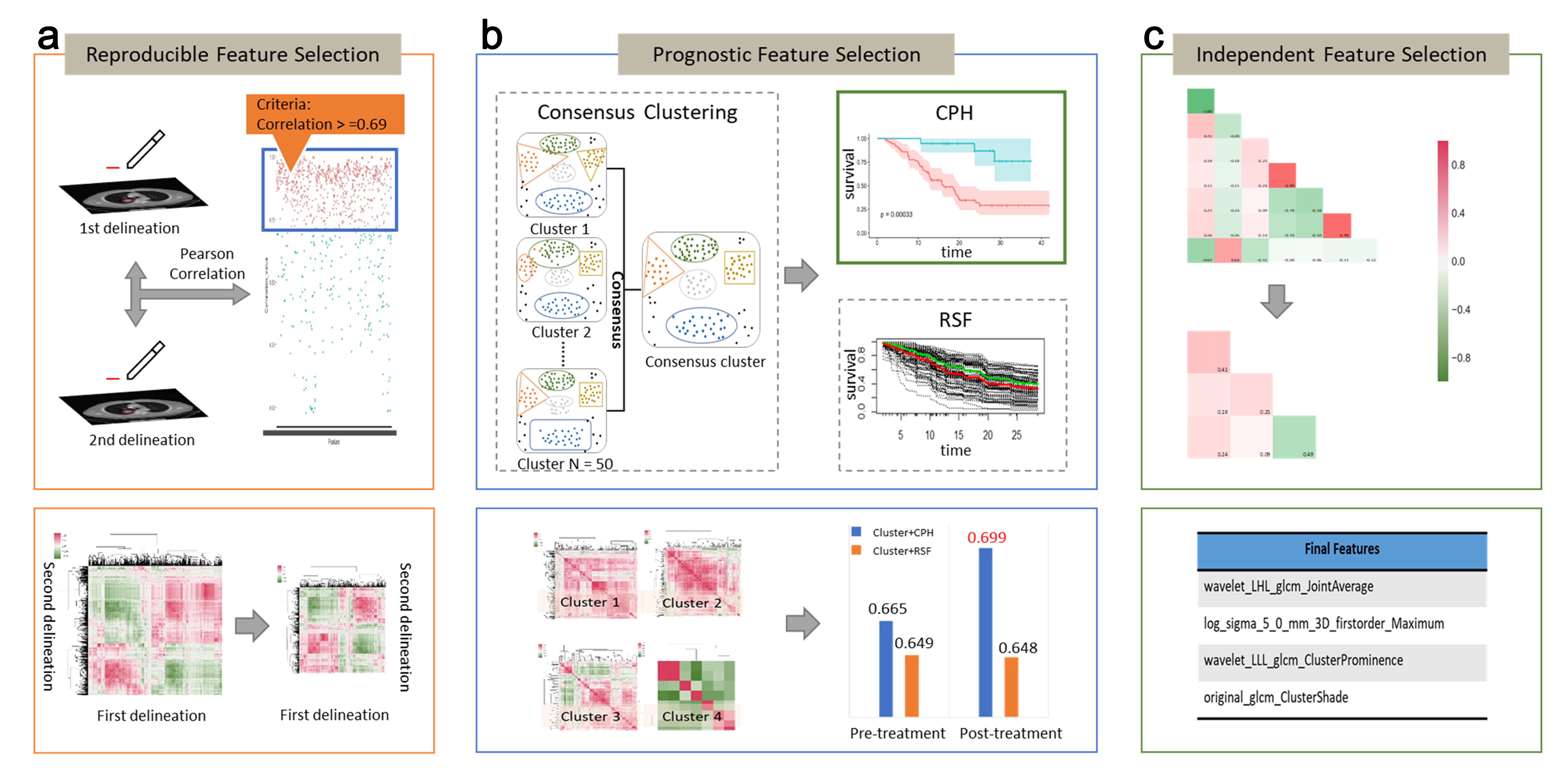
To address the challenge of optimally selecting informative, representative, and non-redundant features from the huge volume of data, we propose an integrative clustering and supervised (ICS) feature selection approach. In our framework, the unsupervised clutering contributes to reduce feature redundancy by exploring the correlation among features, while supervised learning selects informative and representative features by examining relavency between features and target outputs. The algorithm was implemented in R and validated on two datasets including CT image dataset and clinical factor dataset.
Xin, Bowen, et al. "Integrative Clustering and Supervised Feature Selection for Clinical Applications." 2018 15th International Conference on Control, Automation, Robotics and Vision (ICARCV). IEEE, 2018.
Wang, Linlin, Taotao Dong, Bowen Xin, Chongrui Xu, Meiying Guo, Huaqi Zhang, Dagan Feng, Xiuying Wang, and Jinming Yu. "Integrative nomogram of CT imaging, clinical, and hematological features for survival prediction of patients with locally advanced non-small cell lung cancer." European radiology 29, no. 6 (2019): 2958-2967.
- R environment
- packages: dplyr, survival, randomForestSRC, stats, ConsensusClusterPlus
- Get stable features over repeated meaturements:
getStableCor_func(df1, df2, threshold=0.7, method="pearson") - Get prognostic features by rank (Cox):
getBestCox(dataset, nFeature=5, rankby="p.value", p.threshold = 0.05) - Get prognostic features by rank (RSF):
getBestRSF(dataset, nFeature, seed = 1000, ntree = 2000) - Get ICS features (Cox):
getBestCluster(dataset, nFeature = 5, maxK = 15, optK = NULL,rankby = "p.value") - Get ICS features (RSF):
getBestCluster2(dataset, nFeature = 5, maxK = 15, optK = NULL,rankby = "p.value") - Fit multivaraite model (Cox):
multi_cox(dataset, features) - Fit multivariate model (RSF):
multi_rsf(dataset, features)