Releases: derdoktor667/DShotRMT
0.9.0
Changelog
Added
- Centralized
DSHOT_BITS_PER_FRAMEdefinition indshot_definitions.h.
Changed
- Comment Style Refactoring: Converted Doxygen-style comments to simple English line comments across
src/DShotRMT.handsrc/DShotRMT.cppfor improved readability and adherence to project guidelines. - Constant Definition Modernization: Replaced all
#definedirectives withstatic constexprinsrc/dshot_definitions.hfor enhanced type safety and modern C++ practices. - API Consistency: Renamed
_get_result_code_strtoget_result_code_strinsrc/dshot_utils.hand updated its call sites for better API consistency. - Documentation:
- Updated
README.mdto reflect current API descriptions and removed outdated information. - Updated
GEMINI.mdto accurately describe the constant definition style andREADME.mdgeneration process.
- Updated
Fixed
- Resolved compilation errors related to conflicting constant declarations by centralizing definitions in
src/dshot_definitions.h. - Corrected
_on_rx_donescope error insrc/DShotRMT.hby properly declaring it as a static member function.
0.8.9 Hotfix Release
--- Fixing reboot loops, sorry ---
DShotRMT - ESP32 RMT DShot Driver
An Arduino IDElibrary for generating DShot signals on ESP32 microcontrollers using the modern ESP-IDF 5 RMT encoder API (rmt_tx.h / rmt_rx.h). This library specifically leverages the official rmt_bytes_encoder API for an efficient, hardware-timed, and maintainable implementation. It provides a simple way to control brushless motors in both Arduino and ESP-IDF projects.
The legacy version using the old rmt.h API is available in the oldAPI branch.
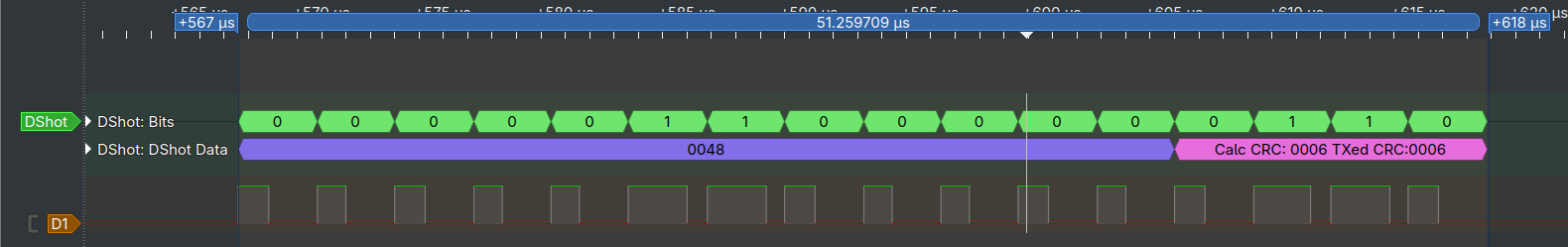
DShot300 Example Output
Here's an example of the output from the dshot300 example sketch:
🚀 Core Features
- Multiple DShot Modes: Supports DSHOT150, DSHOT300, DSHOT600, and DSHOT1200.
- Bidirectional DShot Support: Implemented, but note that official support is limited due to potential instability and external hardware requirements. Use with caution.
- Hardware-Timed Signals: Precise signal generation using the ESP32 RMT peripheral, ensuring stable and reliable motor control.
- Simple API: Easy-to-use C++ class with intuitive methods like
sendThrottlePercent(). - Error Handling: Provides detailed feedback on operation success or failure via
dshot_result_t. - Lightweight: The core library has no external dependencies.
- Arduino and ESP-IDF Compatible: Can be used in both Arduino and ESP-IDF projects.
⏱️ DShot Timing Information
The DShot protocol defines specific timing characteristics for each mode. The following table outlines the bit length, T1H (high time for a '1' bit), T0H (high time for a '0' bit), and frame length for the supported DShot modes:
| DShot Mode | Bit Length (µs) | T1H Length (µs) | T0H Length (µs) | Frame Length (µs) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DSHOT150 | 6.67 | 5.00 | 2.50 | 106.72 |
| DSHOT300 | 3.33 | 2.50 | 1.25 | 53.28 |
| DSHOT600 | 1.67 | 1.25 | 0.625 | 26.72 |
| DSHOT1200 | 0.83 | 0.67 | 0.335 | 13.28 |
📦 Installation
Arduino IDE
- Open the Arduino Library Manager (
Sketch>Include Library>Manage Libraries...). - Search for "DShotRMT" and click "Install".
- Alternatively, you can clone this repository or download it as a ZIP file and place it in your Arduino libraries folder (
~/Arduino/libraries/DShotRMT/).
⚡ Quick Start
Here's a basic example of how to use the DShotRMT library to control a motor. Please use example sketches for more detailes:
#include <Arduino.h>
#include <DShotRMT.h> // Include the DShotRMT library
// Define the GPIO pin connected to the motor ESC
const gpio_num_t MOTOR_PIN = GPIO_NUM_27;
// Create a DShotRMT instance for DSHOT300
DShotRMT motor(MOTOR_PIN, DSHOT300);
void setup() {
Serial.begin(115200);
// Initialize the DShot motor
motor.begin();
// Print CPU Info
printCpuInfo(Serial);
Serial.println("Motor initialized. Ramping up to 25% throttle...");
}
void loop() {
// Ramp up to 25% throttle over 2.5 seconds
for (int i = 0; i <= 25; i++) {
motor.sendThrottlePercent(i);
delay(100);
}
Serial.println("Stopping motor.");
motor.sendThrottlePercent(0);
// Print DShot Info
printDShotInfo(motor, Serial);
}🎮 Examples
The examples folder contains more advanced examples:
throttle_percent: A focused example showing how to control motor speed using percentage values (0-100) via the serial monitor.dshot300: A more advanced example demonstrating how to send raw DShot commands and receive telemetry via the serial monitor.web_control: A full-featured web application for controlling a motor from a web browser. It creates a WiFi access point and serves a web page with a throttle slider and arming switch.web_client: A variation of theweb_controlexample that connects to an existing WiFi network instead of creating its own access point.
Dependencies for Web Examples
The web_control and web_client examples require the following additional libraries:
📚 API Reference
The main class is DShotRMT. Here are the most important methods:
DShotRMT(gpio_num_t gpio, dshot_mode_t mode = DSHOT300, bool is_bidirectional = false, uint16_t magnet_count = DEFAULT_MOTOR_MAGNET_COUNT): Constructor to create a new DShotRMT instance.begin(): Initializes the DShot RMT channels and encoder.sendThrottlePercent(float percent): Sends a throttle value as a percentage (0.0-100.0) to the ESC.sendThrottle(uint16_t throttle): Sends a raw throttle value (48-2047) to the ESC. A value of 0 sends a motor stop command.sendCommand(uint16_t command): Sends a single DShot command (0-47) to the ESC.sendCommand(dshotCommands_e dshot_command, uint16_t repeat_count = DEFAULT_CMD_REPEAT_COUNT, uint16_t delay_us = DEFAULT_CMD_DELAY_US): Sends a DShot command multiple times with a delay between repetitions. This is a blocking function.getTelemetry(uint16_t magnet_count = 0): Retrieves telemetry data from the ESC. Ifmagnet_countis 0, uses the stored motor magnet count.getESCInfo(): Sends a command to the ESC to request ESC information.setMotorSpinDirection(bool reversed): Sets the motor spin direction.truefor reversed,falsefor normal.saveESCSettings(): Sends a command to the ESC to save its current settings. Use with caution as this writes to ESC's non-volatile memory.printDShotResult(dshot_result_t &result, Stream &output = Serial): Prints the result of a DShot operation to the specified output stream.printDShotInfo(const DShotRMT &dshot_rmt, Stream &output = Serial): Prints detailed DShot signal information for a given DShotRMT instance.printCpuInfo(Stream &output = Serial): Prints detailed CPU information.setMotorMagnetCount(uint16_t magnet_count): Sets the motor magnet count for RPM calculation.getMode(): Gets the current DShot mode.isBidirectional(): Checks if bidirectional DShot is enabled.getEncodedFrameValue(): Gets the last encoded DShot frame value.getThrottleValue(): Gets the last transmitted throttle value.
🤝 Contributing
Contributions are welcome! Please fork the repository, create a feature branch, and submit a pull request.
📄 License
This project is licensed under the MIT License. See the LICENSE file for details.
0.8.8
Changelog Version 0.8.8
✨ New Features & Improvements
- Simplified API for Helper Functions: The helper functions
printDShotInfo(),printCpuInfo(), andprintDShotResult()are now directly callable (e.g.,printCpuInfo(Serial)) instead of being static methods of theDShotRMTclass. This simplifies the API and improves readability. - Improved Readability of Results: A new function
getDShotMsg()has been added to get a textual description of the result code. - Simplified
dshot_mode_tUsage: Thedshot_mode_tenum is now a standardenum, so modes can be used directly (e.g.,DSHOT300instead ofdshot_mode_t::DSHOT300).
Refactoring
- Extraction of Helper Functions: All helper functions have been moved to a new, dedicated file
src/dshot_utils.hto structure the codebase and focus theDShotRMTclass on its core functionality. - Code Modernization: The code has been modernized by using C++11 features such as direct initialization of member variables in the header and improved
constcorrectness. This increases code quality and safety.
📚 Documentation
DShotRMT - ESP32 RMT DShot Driver
An Arduino IDElibrary for generating DShot signals on ESP32 microcontrollers using the modern ESP-IDF 5 RMT encoder API (rmt_tx.h / rmt_rx.h). This library specifically leverages the official rmt_bytes_encoder API for an efficient, hardware-timed, and maintainable implementation. It provides a simple way to control brushless motors in both Arduino and ESP-IDF projects.
The legacy version using the old rmt.h API is available in the oldAPI branch.
DShot300 Example Output
Here's an example of the output from the dshot300 example sketch:
🚀 Core Features
- Multiple DShot Modes: Supports DSHOT150, DSHOT300, DSHOT600, and DSHOT1200.
- Bidirectional DShot Support: Implemented, but note that official support is limited due to potential instability and external hardware requirements. Use with caution.
- Hardware-Timed Signals: Precise signal generation using the ESP32 RMT peripheral, ensuring stable and reliable motor control.
- Simple API: Easy-to-use C++ class with intuitive methods like
sendThrottlePercent(). - Error Handling: Provides detailed feedback on operation success or failure via
dshot_result_t. - Lightweight: The core library has no external dependencies.
- Arduino and ESP-IDF Compatible: Can be used in both Arduino and ESP-IDF projects.
⏱️ DShot Timing Information
The DShot protocol defines specific timing characteristics for each mode. The following table outlines the bit length, T1H (high time for a '1' bit), T0H (high time for a '0' bit), and frame length for the supported DShot modes:
| DShot Mode | Bit Length (µs) | T1H Length (µs) | T0H Length (µs) | Frame Length (µs) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DSHOT150 | 6.67 | 5.00 | 2.50 | 106.72 |
| DSHOT300 | 3.33 | 2.50 | 1.25 | 53.28 |
| DSHOT600 | 1.67 | 1.25 | 0.625 | 26.72 |
| DSHOT1200 | 0.83 | 0.67 | 0.335 | 13.28 |
📦 Installation
Arduino IDE
- Open the Arduino Library Manager (
Sketch>Include Library>Manage Libraries...). - Search for "DShotRMT" and click "Install".
- Alternatively, you can clone this repository or download it as a ZIP file and place it in your Arduino libraries folder (
~/Arduino/libraries/DShotRMT/).
⚡ Quick Start
Here's a basic example of how to use the DShotRMT library to control a motor. Please use example sketches for more detailes:
#include <Arduino.h>
#include <DShotRMT.h> // Include the DShotRMT library
// Define the GPIO pin connected to the motor ESC
const gpio_num_t MOTOR_PIN = GPIO_NUM_27;
// Create a DShotRMT instance for DSHOT300
DShotRMT motor(MOTOR_PIN, DSHOT300);
void setup() {
Serial.begin(115200);
// Initialize the DShot motor
motor.begin();
// Print CPU Info
printCpuInfo(Serial);
Serial.println("Motor initialized. Ramping up to 25% throttle...");
}
void loop() {
// Ramp up to 25% throttle over 2.5 seconds
for (int i = 0; i <= 25; i++) {
motor.sendThrottlePercent(i);
delay(100);
}
Serial.println("Stopping motor.");
motor.sendThrottlePercent(0);
// Print DShot Info
printDShotInfo(motor, Serial);
}🎮 Examples
The examples folder contains more advanced examples:
throttle_percent: A focused example showing how to control motor speed using percentage values (0-100) via the serial monitor.dshot300: A more advanced example demonstrating how to send raw DShot commands and receive telemetry via the serial monitor.web_control: A full-featured web application for controlling a motor from a web browser. It creates a WiFi access point and serves a web page with a throttle slider and arming switch.web_client: A variation of theweb_controlexample that connects to an existing WiFi network instead of creating its own access point.
Dependencies for Web Examples
The web_control and web_client examples require the following additional libraries:
📚 API Reference
The main class is DShotRMT. Here are the most important methods:
DShotRMT(gpio_num_t gpio, dshot_mode_t mode = DSHOT300, bool is_bidirectional = false, uint16_t magnet_count = DEFAULT_MOTOR_MAGNET_COUNT): Constructor to create a new DShotRMT instance.begin(): Initializes the DShot RMT channels and encoder.sendThrottlePercent(float percent): Sends a throttle value as a percentage (0.0-100.0) to the ESC.sendThrottle(uint16_t throttle): Sends a raw throttle value (48-2047) to the ESC. A value of 0 sends a motor stop command.sendCommand(uint16_t command): Sends a single DShot command (0-47) to the ESC.sendCommand(dshotCommands_e dshot_command, uint16_t repeat_count = DEFAULT_CMD_REPEAT_COUNT, uint16_t delay_us = DEFAULT_CMD_DELAY_US): Sends a DShot command multiple times with a delay between repetitions. This is a blocking function.getTelemetry(uint16_t magnet_count = 0): Retrieves telemetry data from the ESC. Ifmagnet_countis 0, uses the stored motor magnet count.getESCInfo(): Sends a command to the ESC to request ESC information.setMotorSpinDirection(bool reversed): Sets the motor spin direction.truefor reversed,falsefor normal.saveESCSettings(): Sends a command to the ESC to save its current settings. Use with caution as this writes to ESC's non-volatile memory.printDShotResult(dshot_result_t &result, Stream &output = Serial): Prints the result of a DShot operation to the specified output stream.printDShotInfo(const DShotRMT &dshot_rmt, Stream &output = Serial): Prints detailed DShot signal information for a given DShotRMT instance.printCpuInfo(Stream &output = Serial): Prints detailed CPU information.setMotorMagnetCount(uint16_t magnet_count): Sets the motor magnet count for RPM calculation.getMode(): Gets the current DShot mode.isBidirectional(): Checks if bidirectional DShot is enabled.getEncodedFrameValue(): Gets the last encoded DShot frame value.getThrottleValue(): Gets the last transmitted throttle value.
🤝 Contributing
Contributions are welcome! Please fork the repository, create a feature branch, and submit a pull request.
📄 License
This project is licensed under the MIT License. See the LICENSE file for details.
0.8.7
DShotRMT - ESP32 RMT DShot Driver
An Arduino IDElibrary for generating DShot signals on ESP32 microcontrollers using the modern ESP-IDF 5 RMT encoder API (rmt_tx.h / rmt_rx.h). This library specifically leverages the official rmt_bytes_encoder API for an efficient, hardware-timed, and maintainable implementation. It provides a simple way to control brushless motors in both Arduino and ESP-IDF projects.
The legacy version using the old rmt.h API is available in the oldAPI branch.
DShot300 Example Output
Here's an example of the output from the dshot300 example sketch:
🚀 Core Features
- Multiple DShot Modes: Supports DSHOT150, DSHOT300, DSHOT600, and DSHOT1200.
- Bidirectional DShot Support: Implemented, but note that official support is limited due to potential instability and external hardware requirements. Use with caution.
- Hardware-Timed Signals: Precise signal generation using the ESP32 RMT peripheral, ensuring stable and reliable motor control.
- Simple API: Easy-to-use C++ class with intuitive methods like
sendThrottlePercent(). - Error Handling: Provides detailed feedback on operation success or failure via
dshot_result_t. - Lightweight: The core library has no external dependencies.
- Arduino and ESP-IDF Compatible: Can be used in both Arduino and ESP-IDF projects.
⏱️ DShot Timing Information
The DShot protocol defines specific timing characteristics for each mode. The following table outlines the bit length, T1H (high time for a '1' bit), T0H (high time for a '0' bit), and frame length for the supported DShot modes:
| DShot Mode | Bit Length (µs) | T1H Length (µs) | T0H Length (µs) | Frame Length (µs) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DSHOT150 | 6.67 | 5.00 | 2.50 | 106.72 |
| DSHOT300 | 3.33 | 2.50 | 1.25 | 53.28 |
| DSHOT600 | 1.67 | 1.25 | 0.625 | 26.72 |
| DSHOT1200 | 0.83 | 0.67 | 0.335 | 13.28 |
📦 Installation
Arduino IDE
- Open the Arduino Library Manager (
Sketch>Include Library>Manage Libraries...). - Search for "DShotRMT" and click "Install".
- Alternatively, you can clone this repository or download it as a ZIP file and place it in your Arduino libraries folder (
~/Arduino/libraries/DShotRMT/).
⚡ Quick Start
Here's a basic example of how to use the DShotRMT library to control a motor. Please use example sketches for more detailes:
#include <Arduino.h>
#include <DShotRMT.h> // Include the DShotRMT library
// Define the GPIO pin connected to the motor ESC
const gpio_num_t MOTOR_PIN = GPIO_NUM_27;
// Create a DShotRMT instance for DSHOT300
DShotRMT motor(MOTOR_PIN, DSHOT300);
void setup() {
Serial.begin(115200);
// Initialize the DShot motor
motor.begin();
// Print CPU Info
DShotRMT::printCpuInfo(Serial);
Serial.println("Motor initialized. Ramping up to 25% throttle...");
}
void loop() {
// Ramp up to 25% throttle over 2.5 seconds
for (int i = 0; i <= 25; i++) {
motor.sendThrottlePercent(i);
delay(100);
}
Serial.println("Stopping motor.");
motor.sendThrottlePercent(0);
// Print DShot Info
DShotRMT::printDShotInfo(motor, Serial);
}🎮 Examples
The examples folder contains more advanced examples:
throttle_percent: A focused example showing how to control motor speed using percentage values (0-100) via the serial monitor.dshot300: A more advanced example demonstrating how to send raw DShot commands and receive telemetry via the serial monitor.web_control: A full-featured web application for controlling a motor from a web browser. It creates a WiFi access point and serves a web page with a throttle slider and arming switch.web_client: A variation of theweb_controlexample that connects to an existing WiFi network instead of creating its own access point.
Dependencies for Web Examples
The web_control and web_client examples require the following additional libraries:
You can install these libraries using the Arduino Library Manager or by adding them to your platformio.ini file:
lib_deps =
https://github.com/derdoktor667/DShotRMT.git
https://github.com/bblanchon/ArduinoJson
https://github.com/ESP32Async/ESPAsyncWebServer
https://github.com/ESP32Async/AsyncTCP📚 API Reference
The main class is DShotRMT. Here are the most important methods:
DShotRMT(gpio_num_t gpio, dshot_mode_t mode, bool is_bidirectional = false, uint16_t magnet_count = DEFAULT_MOTOR_MAGNET_COUNT): Constructor to create a new DShotRMT instance.begin(): Initializes the DShot RMT channels and encoder.sendThrottlePercent(float percent): Sends a throttle value as a percentage (0.0-100.0) to the ESC.sendThrottle(uint16_t throttle): Sends a raw throttle value (48-2047) to the ESC. A value of 0 sends a motor stop command.sendCommand(uint16_t command): Sends a single DShot command (0-47) to the ESC.sendCommand(dshotCommands_e dshot_command, uint16_t repeat_count = DEFAULT_CMD_REPEAT_COUNT, uint16_t delay_us = DEFAULT_CMD_DELAY_US): Sends a DShot command multiple times with a delay between repetitions. This is a blocking function.getTelemetry(uint16_t magnet_count = 0): Retrieves telemetry data from the ESC. Ifmagnet_countis 0, uses the stored motor magnet count.getESCInfo(): Sends a command to the ESC to request ESC information.setMotorSpinDirection(bool reversed): Sets the motor spin direction.truefor reversed,falsefor normal.saveESCSettings(): Sends a command to the ESC to save its current settings. Use with caution as this writes to ESC's non-volatile memory.printDShotResult(dshot_result_t &result, Stream &output = Serial): Prints the result of a DShot operation to the specified output stream.DShotRMT::printDShotInfo(const DShotRMT &dshot_rmt, Stream &output = Serial): Prints detailed DShot signal information for a given DShotRMT instance.DShotRMT::printCpuInfo(Stream &output = Serial): Prints detailed CPU information.setMotorMagnetCount(uint16_t magnet_count): Sets the motor magnet count for RPM calculation.getMode(): Gets the current DShot mode.isBidirectional(): Checks if bidirectional DShot is enabled.getEncodedFrameValue(): Gets the last encoded DShot frame value.getThrottleValue(): Gets the last transmitted throttle value.
🤝 Contributing
Contributions are welcome! Please fork the repository, create a feature branch, and submit a pull request.
📄 License
This project is licensed under the MIT License. See the LICENSE file for details.
0.8.6
DShotRMT - ESP32 RMT DShot Driver
A C++ library for generating DShot signals on ESP32 microcontrollers using the modern ESP-IDF 5 RMT encoder API (rmt_tx.h / rmt_rx.h). This library specifically leverages the official rmt_bytes_encoder API for an efficient, hardware-timed, and maintainable implementation. It provides a simple way to control brushless motors in both Arduino and ESP-IDF projects. The legacy version using the old rmt.h API is available in the oldAPI branch.
DShot300 Example Output
Here's an example of the output from the dshot300 example sketch:
🚀 Core Features
- Multiple DShot Modes: Supports DSHOT150, DSHOT300, DSHOT600, and DSHOT1200.
- Bidirectional DShot Support: Implemented, but note that official support is limited due to potential instability and external hardware requirements. Use with caution.
- Hardware-Timed Signals: Precise signal generation using the ESP32 RMT peripheral, ensuring stable and reliable motor control.
- Simple API: Easy-to-use C++ class with intuitive methods like
sendThrottlePercent(). - Robust Error Handling: Provides detailed feedback on operation success or failure via
dshot_result_t. - Efficient and Lightweight: The core library has no external dependencies.
- Arduino and ESP-IDF Compatible: Can be used in both Arduino and ESP-IDF projects.
⏱️ DShot Timing Information
The DShot protocol defines specific timing characteristics for each mode. The following table outlines the bit length, T1H (high time for a '1' bit), T0H (high time for a '0' bit), and frame length for the supported DShot modes:
| DShot Mode | Bit Length (µs) | T1H Length (µs) | T0H Length (µs) | Frame Length (µs) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DSHOT150 | 6.67 | 5.00 | 2.50 | 106.72 |
| DSHOT300 | 3.33 | 2.50 | 1.25 | 53.28 |
| DSHOT600 | 1.67 | 1.25 | 0.625 | 26.72 |
| DSHOT1200 | 0.83 | 0.67 | 0.335 | 13.28 |
📦 Installation
Arduino IDE
- Open the Arduino Library Manager (
Sketch>Include Library>Manage Libraries...). - Search for "DShotRMT" and click "Install".
- Alternatively, you can clone this repository or download it as a ZIP file and place it in your Arduino libraries folder (
~/Arduino/libraries/DShotRMT/).
PlatformIO
Add the following to your platformio.ini file:
lib_deps =
https://github.com/derdoktor667/DShotRMT.git⚡ Quick Start
Here's a basic example of how to use the DShotRMT library to control a motor:
#include <Arduino.h>
#include <DShotRMT.h> // Include the DShotRMT library
// Define the GPIO pin connected to the motor ESC
const gpio_num_t MOTOR_PIN = GPIO_NUM_27;
// Create a DShotRMT instance for DSHOT300
DShotRMT motor(MOTOR_PIN, DSHOT300);
void setup() {
Serial.begin(115200);
// Initialize the DShot motor
motor.begin();
// Print CPU Info
DShotRMT::printCpuInfo(Serial);
Serial.println("Motor initialized. Ramping up to 25% throttle...");
// Ramp up to 25% throttle over 2.5 seconds
for (int i = 0; i <= 25; i++) {
motor.sendThrottlePercent(i);
delay(100);
}
Serial.println("Stopping motor.");
motor.sendThrottlePercent(0);
// Print DShot Info
DShotRMT::printDShotInfo(motor, Serial);
}
void loop() {
// Your main code here
}🎮 Examples
The examples folder contains more advanced examples:
throttle_percent: A focused example showing how to control motor speed using percentage values (0-100) via the serial monitor.dshot300: A more advanced example demonstrating how to send raw DShot commands and receive telemetry via the serial monitor.web_control: A full-featured web application for controlling a motor from a web browser. It creates a WiFi access point and serves a web page with a throttle slider and arming switch.web_client: A variation of theweb_controlexample that connects to an existing WiFi network instead of creating its own access point.
Dependencies for Web Examples
The web_control and web_client examples require the following additional libraries:
You can install these libraries using the Arduino Library Manager or by adding them to your platformio.ini file:
lib_deps =
https://github.com/derdoktor667/DShotRMT.git
https://github.com/bblanchon/ArduinoJson
https://github.com/ESP32Async/ESPAsyncWebServer
https://github.com/ESP32Async/AsyncTCP📚 API Reference
The main class is DShotRMT. Here are the most important methods:
DShotRMT(gpio_num_t gpio, dshot_mode_t mode, bool is_bidirectional = false, uint16_t magnet_count = DEFAULT_MOTOR_MAGNET_COUNT): Constructor to create a new DShotRMT instance.begin(): Initializes the DShot RMT channels and encoder.sendThrottlePercent(float percent): Sends a throttle value as a percentage (0.0-100.0) to the ESC.sendThrottle(uint16_t throttle): Sends a raw throttle value (48-2047) to the ESC. A value of 0 sends a motor stop command.sendCommand(uint16_t command): Sends a single DShot command (0-47) to the ESC.sendCommand(dshotCommands_e dshot_command, uint16_t repeat_count = DEFAULT_CMD_REPEAT_COUNT, uint16_t delay_us = DEFAULT_CMD_DELAY_US): Sends a DShot command multiple times with a delay between repetitions. This is a blocking function.getTelemetry(uint16_t magnet_count = 0): Retrieves telemetry data from the ESC. Ifmagnet_countis 0, uses the stored motor magnet count.getESCInfo(): Sends a command to the ESC to request ESC information.setMotorSpinDirection(bool reversed): Sets the motor spin direction.truefor reversed,falsefor normal.saveESCSettings(): Sends a command to the ESC to save its current settings. Use with caution as this writes to ESC's non-volatile memory.printDShotResult(dshot_result_t &result, Stream &output = Serial): Prints the result of a DShot operation to the specified output stream.DShotRMT::printDShotInfo(const DShotRMT &dshot_rmt, Stream &output = Serial): Prints detailed DShot signal information for a given DShotRMT instance.DShotRMT::printCpuInfo(Stream &output = Serial): Prints detailed CPU information.setMotorMagnetCount(uint16_t magnet_count): Sets the motor magnet count for RPM calculation.getMode(): Gets the current DShot mode.isBidirectional(): Checks if bidirectional DShot is enabled.getEncodedFrameValue(): Gets the last encoded DShot frame value.getThrottleValue(): Gets the last transmitted throttle value.
🤝 Contributing
Contributions are welcome! Please fork the repository, create a feature branch, and submit a pull request.
📄 License
This project is licensed under the MIT License. See the LICENSE file for details.
0.8.3
DShotRMT - ESP32 RMT DShot Driver
A C++ library for generating DShot signals on ESP32 microcontrollers using the RMT (Remote Control) peripheral. It's designed for both Arduino and ESP-IDF projects, providing a simple and efficient way to control brushless motors.
This library is a rewrite using the modern ESP-IDF 5 RMT encoder API (rmt_tx.h / rmt_rx.h) for improved performance and flexibility. The legacy version using the old rmt.h API is available in the oldAPI branch.
🚀 Core Features
- Multiple DShot Modes: Supports DSHOT150, DSHOT300, DSHOT600, and DSHOT1200.
- Bidirectional DShot: Implemented, but currently not officially supported due to instability and external hardware requirements.
- Hardware-Timed Signals: Precise signal generation using the ESP32 RMT peripheral, ensuring stable and reliable motor control.
- Simple API: Easy-to-use C++ class with intuitive methods like
sendThrottlePercent(). - Efficient and Lightweight: The core library has no external dependencies.
- Arduino and ESP-IDF Compatible: Can be used in both Arduino and ESP-IDF projects.
📦 Installation
Arduino IDE
- Open the Arduino Library Manager (
Sketch>Include Library>Manage Libraries...). - Search for "DShotRMT" and click "Install".
- Alternatively, you can clone this repository or download it as a ZIP file and place it in your Arduino libraries folder (
~/Arduino/libraries/DShotRMT/).
PlatformIO
Add the following to your platformio.ini file:
lib_deps =
https://github.com/derdoktor667/DShotRMT.git⚡ Quick Start
Here's a basic example of how to use the DShotRMT library to control a motor:
#include <Arduino.h>
#include <DShotRMT.h>
// Define the GPIO pin connected to the motor ESC
const gpio_num_t MOTOR_PIN = GPIO_NUM_27;
// Create a DShotRMT instance for DSHOT300
DShotRMT motor(MOTOR_PIN, DSHOT300);
void setup() {
Serial.begin(115200);
// Initialize the DShot motor
motor.begin();
Serial.println("Motor initialized. Ramping up to 25% throttle...");
// Ramp up to 25% throttle over 2.5 seconds
for (int i = 0; i <= 25; i++) {
motor.sendThrottlePercent(i);
delay(100);
}
Serial.println("Stopping motor.");
motor.sendThrottlePercent(0);
}
void loop() {
// Your main code here
}🎮 Examples
The examples folder contains more advanced examples:
throttle_percent: A focused example showing how to control motor speed using percentage values (0-100) via the serial monitor.dshot300: A more advanced example demonstrating how to send raw DShot commands and receive telemetry via the serial monitor.web_control: A full-featured web application for controlling a motor from a web browser. It creates a WiFi access point and serves a web page with a throttle slider and arming switch.web_client: A variation of theweb_controlexample that connects to an existing WiFi network instead of creating its own access point.
Dependencies for Web Examples
The web_control and web_client examples require the following additional libraries:
You can install these libraries using the Arduino Library Manager or by adding them to your platformio.ini file:
lib_deps =
https://github.com/derdoktor667/DShotRMT.git
https://github.com/bblanchon/ArduinoJson
https://github.com/ESP32Async/ESPAsyncWebServer
https://github.com/ESP32Async/AsyncTCP📚 API Reference
The main class is DShotRMT. Here are the most important methods:
DShotRMT(gpio_num_t gpio, dshot_mode_t mode, bool is_bidirectional = false): Constructor to create a new DShotRMT instance. (Note: Bidirectional DShot is currently not officially supported.)begin(): Initializes the RMT peripheral and the DShot encoder.sendThrottlePercent(float percent): Sends a throttle value as a percentage (0.0-100.0).sendThrottle(uint16_t throttle): Sends a raw throttle value (48-2047) to the motor.sendCommand(uint16_t command): Sends a DShot command (0-47) to the motor.getTelemetry(uint16_t magnet_count): Receives and parses telemetry data from the motor (for bidirectional DShot, which is currently not officially supported).
⚡ Changes
Library Refactoring: The "DShotCommandManager" class and its associated examples have been removed, simplifying the library's API and reducing its footprint.
Enhanced Web Examples: The web examples ("web_client", "web_control") now include Over-The-Air (OTA) update functionality, allowing for convenient firmware updates directly through the web interface.
Improved Throttle Control: A new "sendThrottlePercent()" method has been added to the "DShotRMT" class, providing a more intuitive way to control motor speed using percentage values.
Updated Documentation: The "README.md" has been thoroughly revised to reflect the API changes, clarify the status of bidirectional DShot support, and provide updated quick start guides and examples.
Internal RMT Optimizations: The core "DShotRMT" class has undergone internal optimizations, including refined RMT channel initialization, improved GCR decoding for telemetry, and pre-calculation of bit positions for better performance.
0.8.0
DShotRMT - ESP32 Library (Rewrite for ESP-IDF 5)
A modern, robust C++ library for generating DShot signals on the ESP32 using the new ESP-IDF 5 RMT encoder API (rmt_tx.h / rmt_rx.h).
Supports all standard DShot modes (150, 300, 600, 1200) and features continuous frame transmission with configurable timing.
Now with BiDirectional DShot support, advanced command management, and modern web control interface!
The legacy version (using the old
rmt.hAPI) is still available in theoldAPIbranch.
🚀 Features
- All DShot Modes: DSHOT150, DSHOT300 (default), DSHOT600, DSHOT1200
- BiDirectional DShot: Full support for RPM telemetry feedback
- Web Control Interface: Modern responsive web UI with WiFi access point
- Advanced Command Manager: High-level API for ESC configuration and control
- Safety Features: Arming/disarming system with motor lockout protection
- Dual Control Options: Web interface and serial console control
- Real-time Telemetry: Live RPM monitoring and data display
- Hardware-Timed Signals: Independent, precise signal generation using ESP32 RMT peripheral
- Configurable Timing: Ensures ESCs can reliably detect frame boundaries
- Error Handling: Comprehensive result reporting with success/failure status
- Simple API: Easy integration into your Arduino or ESP-IDF project
📦 Installation
Arduino IDE
- Search "Arduino Library Manager" for "DShotRMT"
or
- Clone this repository or download as ZIP
- Place in your Arduino libraries folder (
~/Arduino/libraries/DShotRMT/) - Restart Arduino IDE
PlatformIO
Add to your platformio.ini:
lib_deps =
https://github.com/derdoktor667/DShotRMT.gitManual Installation
git clone https://github.com/derdoktor667/DShotRMT.gitDependencies
The library requires these additional libraries for full functionality:
Core DShotRMT (always required):
- ESP32 Arduino Core
Web Interface Example (web_control.ino / web_client.ino):
lib_deps =
https://github.com/derdoktor667/DShotRMT
https://github.com/bblanchon/ArduinoJson
https://github.com/ESP32Async/ESPAsyncWebServer
https://github.com/ESP32Async/AsyncTCPCommand Manager Example:
- No additional dependencies required
⚡ Quick Start
Basic Usage (DShotRMT)
#include <DShotRMT.h>
// Create motor instance (GPIO 17, DSHOT300, non-bidirectional)
DShotRMT motor(17, DSHOT300, false);
void setup() {
Serial.begin(115200);
// Initialize the motor
dshot_result_t result = motor.begin();
if (result.success) {
Serial.println("Motor initialized successfully");
} else {
Serial.printf("Motor init failed: %s\n", result.msg);
}
}
void loop() {
// Send throttle value (48-2047)
dshot_result_t result = motor.sendThrottle(1000);
if (!result.success) {
Serial.printf("Throttle command failed: %s\n", result.msg);
}
}🌐 Web Control Interface
The DShotRMT library now includes a modern web interface for wireless motor control:
Features
- Responsive Design: Works on mobile phones, tablets, and desktop computers
- WiFi Access Point: Creates hotspot "DShotRMT Control" (Password: 12345678)
- Safety System: Arming/disarming switch prevents accidental motor activation
- Real-time Control: Instant throttle response via WebSocket communication
- Live Telemetry: Real-time RPM display (bidirectional mode only)
- Auto-reconnect: Automatically reconnects on connection loss
Web Interface Access
- Connect to WiFi network: "DShotRMT Control"
- Password: 12345678
- Open browser and navigate to: http://10.10.10.1
Safety Features
- Motor control is disabled by default (disarmed state)
- Toggle the ARMING SWITCH to enable motor control
- Throttle slider is locked when disarmed
- Emergency stop resets all values to safe state
Technical Implementation
- AsyncWebServer for HTTP requests
- WebSocket communication for real-time data
- JSON message format for data exchange
- WiFi SoftAP mode for standalone operation
- Automatic client cleanup prevents memory leaks
⚠️ Known Issus
Make sure you are using these libraries for ESPAsyncWebServer and AsyncTCP to use "web_control.ino" example sketch.
📚 Examples
The library includes comprehensive examples:
1. Basic DShot Control with Web Interface (web_control.ino)
- Web Control Interface: Modern responsive web UI accessible at
http://10.10.10.1 - WiFi Access Point: Creates hotspot "DShotRMT Control" for wireless control
- Safety Features: Arming/disarming system with motor safety lockout
- Real-time Data: Live RPM telemetry display (bidirectional mode)
- Dual Control: Both web interface and serial console control
- WebSocket Communication: Real-time bidirectional data exchange
Web Interface Features:
- Responsive design optimized for mobile and desktop
- Visual arming switch with safety lockout
- Smooth throttle slider with real-time feedback
- Live RPM monitoring display
- Automatic reconnection on connection loss
2. Advanced Command Management (command_manager.ino)
Interactive ESC control with full menu system:
=== DShot Command Manager Menu ===
1 - Stop Motor
2 - Activate Beacon 1
3 - Set Normal Spin Direction
4 - Set Reversed Spin Direction
5 - Get ESC Info
6 - Turn LED 0 ON
7 - Turn LED 0 OFF
0 - Emergency Stop
Advanced Commands:
cmd <number> - Send DShot command (0 - 47)
throttle <value> - Set throttle (48 - 2047)
repeat cmd <num> count <count> - Repeat command
🔧 Hardware Configuration
Supported DShot Modes
| DSHOT | Bitrate | TH1 | TH0 | Bit Time (µs) | Frame Time (µs) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 150 | 150 kbit/s | 5.00 | 2.50 | 6.67 | ~106.72 |
| 300 | 300 kbit/s | 2.50 | 1.25 | 3.33 | ~53.28 |
| 600 | 600 kbit/s | 1.25 | 0.625 | 1.67 | ~26.72 |
For DShot, T1H length is always double T0H length.
GPIO Configuration
// Using GPIO number
DShotRMT motor(17, DSHOT300);
// Using GPIO enum
DShotRMT motor(GPIO_NUM_17, DSHOT300);
// With bidirectional support
DShotRMT motor(17, DSHOT300, true);🎯 DShot Commands
| Command | Value | Description | Usage |
|---|---|---|---|
| MOTOR_STOP | 0 | Stop motor | Always available |
| BEACON 1 - 5 | 1 - 5 | Motor beeping | Motor identification |
| ESC_INFO | 6 | Request ESC info | Get ESC version/settings |
| SPIN_DIRECTION_1/2 | 7 - 8 | Set spin direction | Motor configuration |
| 3D_MODE_OFF/ON | 9 - 10 | 3D mode control | Bidirectional flight |
| SAVE_SETTINGS | 12 | Save to EEPROM | Permanent configuration |
| EXTENDED_TELEMETRY_ENABLE/DISABLE | 13 - 14 | Telemetry control | Data transmission |
| SPIN_DIRECTION_NORMAL/REVERSED | 20 - 21 | Spin direction | Alias commands |
| LED 0-3_ON/OFF | 22 - 29 | LED control | BLHeli32 only |
| AUDIO_STREAM_MODE | 30 | Audio mode toggle | KISS ESCs |
| SILENT_MODE | 31 | Silent mode toggle | KISS ESCs |
📚 DShot Protocol Details
Packet Structure
Each DShot frame consists of 16 bits:
- 11 bits: Throttle/command value (0-2047)
- 1 bit: Telemetry request flag
- 4 bits: CRC checksum
Checksum Calculation
// Standard DShot CRC
uint16_t crc = (data ^ (data >> 4) ^ (data >> 8)) & 0x0F;
// Bidirectional DShot (inverted CRC)
uint16_t crc = (~(data ^ (data >> 4) ^ (data >> 8))) & 0x0F;Bidirectional DShot
- Inverted Logic: High/low levels are inverted
- GCR Encoding: Telemetry uses Group Code Recording
- 21-bit Response: 1 start + 16 data + 4 CRC bits
- eRPM Data: Electrical RPM transmitted back to controller
🛠️ ESP32 RMT Peripheral
The library utilizes the ESP32's RMT (Remote Control) peripheral for precise signal generation:
Advantages
- Hardware Timing: No CPU intervention during transmission
- Concurrent Operation: Multiple channels can run simultaneously
- DMA Support: Efficient, automatic memory-to-peripheral transfers
📖 References & Documentation
DShot Protocol
ESP32 Documentation
🤝 Contributing
We welcome contributions! Please:
- Fork the repository
- Create a feature branch
- Make your changes with tests
- Submit a pull request
Development Guidelines
- Follow existing code style
- Add documentation for new features
- Include examples where appropriate
- Test with real hardware when possible
Reporting Issues
When reporting issues, please include:
- ESP32 board...
0.7.6
DShotRMT - ESP32 Library (Rewrite for ESP-IDF 5)
A modern, robust C++ library for generating DShot signals on the ESP32 using the new ESP-IDF 5 RMT encoder API (rmt_tx.h / rmt_rx.h).
Supports all standard DShot modes (150, 300, 600, 1200) and features continuous frame transmission with configurable timing.
Now with BiDirectional DShot support, advanced command management, and modern web control interface!
The legacy version (using the old
rmt.hAPI) is still available in theoldAPIbranch.
🚀 Features
- All DShot Modes: DSHOT150, DSHOT300 (default), DSHOT600, DSHOT1200
- BiDirectional DShot: Full support for RPM telemetry feedback
- Web Control Interface: Modern responsive web UI with WiFi access point
- Advanced Command Manager: High-level API for ESC configuration and control
- Safety Features: Arming/disarming system with motor lockout protection
- Dual Control Options: Web interface and serial console control
- Real-time Telemetry: Live RPM monitoring and data display
- Hardware-Timed Signals: Independent, precise signal generation using ESP32 RMT peripheral
- Configurable Timing: Ensures ESCs can reliably detect frame boundaries
- Error Handling: Comprehensive result reporting with success/failure status
- Simple API: Easy integration into your Arduino or ESP-IDF project
📦 Installation
Arduino IDE
- Search "Arduino Library Manager" for "DShotRMT"
or
- Clone this repository or download as ZIP
- Place in your Arduino libraries folder (
~/Arduino/libraries/DShotRMT/) - Restart Arduino IDE
PlatformIO
Add to your platformio.ini:
lib_deps =
https://github.com/derdoktor667/DShotRMT.gitManual Installation
git clone https://github.com/derdoktor667/DShotRMT.gitDependencies
The library requires these additional libraries for full functionality:
Core DShotRMT (always required):
- ESP32 Arduino Core
Web Interface Example (dshot300.ino):
lib_deps =
https://github.com/derdoktor667/DShotRMT
https://github.com/bblanchon/ArduinoJson
https://github.com/ESP32Async/ESPAsyncWebServer
https://github.com/ESP32Async/AsyncTCPCommand Manager Example:
- No additional dependencies required
⚡ Quick Start
Basic Usage (DShotRMT)
#include <DShotRMT.h>
// Create motor instance (GPIO 17, DSHOT300, non-bidirectional)
DShotRMT motor(17, DSHOT300, false);
void setup() {
Serial.begin(115200);
// Initialize the motor
dshot_result_t result = motor.begin();
if (result.success) {
Serial.println("Motor initialized successfully");
} else {
Serial.printf("Motor init failed: %s\n", result.msg);
}
}
void loop() {
// Send throttle value (48-2047)
dshot_result_t result = motor.sendThrottle(1000);
if (!result.success) {
Serial.printf("Throttle command failed: %s\n", result.msg);
}
}Web Control Interface
#include <DShotRMT.h>
#include <WiFi.h>
#include <ESPAsyncWebServer.h>
DShotRMT motor(17, DSHOT300, false);
AsyncWebServer server(80);
AsyncWebSocket ws("/ws");
void setup() {
// Initialize motor
motor.begin();
// Create WiFi Access Point
WiFi.softAP("DShotRMT Control", "12345678");
// Setup web interface
ws.onEvent(onWsEvent);
server.addHandler(&ws);
server.on("/", HTTP_GET, [](AsyncWebServerRequest *request) {
request->send_P(200, "text/html", index_html);
});
server.begin();
// Access at http://10.10.10.1
}
void loop() {
// Handle WebSocket communication and motor control
ws.cleanupClients();
}Advanced Command Management
#include <DShotRMT.h>
#include <DShotCommandManager.h>
DShotRMT motor(17, DSHOT300, false);
DShotCommandManager cmdManager(motor);
void setup() {
motor.begin();
cmdManager.begin();
}
void loop() {
// High-level ESC control
cmdManager.stopMotor();
cmdManager.activateBeacon(1);
cmdManager.setSpinDirection(false);
cmdManager.executeInitSequence();
}Bidirectional DShot (RPM Telemetry)
#include <DShotRMT.h>
// Enable bidirectional mode for telemetry
DShotRMT motor(17, DSHOT300, true);
void setup() {
Serial.begin(115200);
motor.begin();
}
void loop() {
// Send throttle
motor.sendThrottle(1000);
// Get telemetry data
dshot_telemetry_result_t telemetry = motor.getTelemetry(14); // 14 magnets
if (telemetry.success) {
Serial.printf("eRPM: %u, Motor RPM: %u\n",
telemetry.erpm,
telemetry.motor_rpm);
}
}🌐 Web Control Interface
The DShotRMT library now includes a modern web interface for wireless motor control:
Features
- Responsive Design: Works on mobile phones, tablets, and desktop computers
- WiFi Access Point: Creates hotspot "DShotRMT Control" (Password: 12345678)
- Safety System: Arming/disarming switch prevents accidental motor activation
- Real-time Control: Instant throttle response via WebSocket communication
- Live Telemetry: Real-time RPM display (bidirectional mode only)
- Auto-reconnect: Automatically reconnects on connection loss
Web Interface Access
- Connect to WiFi network: "DShotRMT Control"
- Password: 12345678
- Open browser and navigate to: http://10.10.10.1
Safety Features
- Motor control is disabled by default (disarmed state)
- Toggle the ARMING SWITCH to enable motor control
- Throttle slider is locked when disarmed
- Emergency stop resets all values to safe state
Technical Implementation
- AsyncWebServer for HTTP requests
- WebSocket communication for real-time data
- JSON message format for data exchange
- WiFi SoftAP mode for standalone operation
- Automatic client cleanup prevents memory leaks
⚠️ Known Issus
Make sure you are using these libraries for ESPAsyncWebServer and AsyncTCP to use "web_control.ino" example sketch.
📚 Examples
The library includes comprehensive examples:
1. Basic DShot Control with Web Interface (dshot300.ino)
- Web Control Interface: Modern responsive web UI accessible at
http://10.10.10.1 - WiFi Access Point: Creates hotspot "DShotRMT Control" for wireless control
- Safety Features: Arming/disarming system with motor safety lockout
- Real-time Data: Live RPM telemetry display (bidirectional mode)
- Dual Control: Both web interface and serial console control
- WebSocket Communication: Real-time bidirectional data exchange
Web Interface Features:
- Responsive design optimized for mobile and desktop
- Visual arming switch with safety lockout
- Smooth throttle slider with real-time feedback
- Live RPM monitoring display
- Automatic reconnection on connection loss
2. Advanced Command Management (command_manager.ino)
Interactive ESC control with full menu system:
=== DShot Command Manager Menu ===
1 - Stop Motor
2 - Activate Beacon 1
3 - Set Normal Spin Direction
4 - Set Reversed Spin Direction
5 - Get ESC Info
6 - Turn LED 0 ON
7 - Turn LED 0 OFF
0 - Emergency Stop
Advanced Commands:
cmd <number> - Send DShot command (0-47)
throttle <value> - Set throttle (48-2047)
repeat cmd <num> count <count> - Repeat command
🔧 Hardware Configuration
Supported DShot Modes
| DSHOT | Bitrate | TH1 | TH0 | Bit Time (µs) | Frame Time (µs) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 150 | 150 kbit/s | 5.00 | 2.50 | 6.67 | ~106.72 |
| 300 | 300 kbit/s | 2.50 | 1.25 | 3.33 | ~53.28 |
| 600 | 600 kbit/s | 1.25 | 0.625 | 1.67 | ~26.72 |
GPIO Configuration
// Using GPIO number
DShotRMT motor(17, DSHOT300);
// Using GPIO enum
DShotRMT motor(GPIO_NUM_17, DSHOT300);
// With bidirectional support
DShotRMT motor(17, DSHOT300, true);🎯 DShot Commands
| Command | Value | Description | Usage |
|---|---|---|---|
| MOTOR_STOP | 0 | Stop motor | Always available |
| BEACON1 - 5 | 1 - 5 | Motor beeping | Motor identification |
| ESC_INFO | 6 | Request ESC info | Get ESC version/settings |
| SPIN_DIRECTION_1/2 | 7 - 8 | Set spin direction | Motor configuration |
| 3D_MODE_OFF/ON | 9 - 10 | 3D mode control | Bidirectional flight |
| SAVE_SETTINGS | 12 | Save to EEPROM | Permanent configuration |
| EXTENDED_TELEMETRY_ENABLE/DISABLE | 13 - 14 | Telemetry control | Data transmission |
| SPIN_DIRECTION_NORMAL/REVERSED | 20 - 21 | Spin direction | Alias commands |
| LED0-3_ON/OFF | 22 - 29 | LED control | BLHeli32 only |
| AUDIO_STREAM_MODE | 30 | Audio mode toggle | KISS ESCs |
| SILENT_MODE | 31 | Silent mode toggle | KISS ESCs |
📚 DShot Protocol Details
Packet Structure
Each DShot frame consists of 16 bits:
- 11 bits: Throttle/command value (0-2047)
- 1 bit: Telemetry request flag
- 4 bits: CRC checksum
Checksum Calculation
// Standard DShot CRC
uint16_t crc = (data ^ (data >> 4) ^ (data >> 8)) & 0x0F;
// Bidirectional DShot (inverted CRC)
uint16_t crc = (~(data ^ (data >> 4) ^ (data >> 8))) & 0x0F;Bidirectional DShot
- **In...
0.7.5
DShotRMT - ESP32 Library (Rewrite for ESP-IDF 5)
A modern, robust C++ library for generating DShot signals on the ESP32 using the new ESP-IDF 5 RMT encoder API (rmt_tx.h / rmt_rx.h).
Supports all standard DShot modes (150, 300, 600, 1200) and features continuous frame transmission with configurable timing.
Now with BiDirectional DShot support, advanced command management, and modern web control interface!
The legacy version (using the old
rmt.hAPI) is still available in theoldAPIbranch.
🚀 Features
- All DShot Modes: DSHOT150, DSHOT300 (default), DSHOT600, DSHOT1200
- BiDirectional DShot: Full support for RPM telemetry feedback
- Web Control Interface: Modern responsive web UI with WiFi access point
- Advanced Command Manager: High-level API for ESC configuration and control
- Safety Features: Arming/disarming system with motor lockout protection
- Dual Control Options: Web interface and serial console control
- Real-time Telemetry: Live RPM monitoring and data display
- Hardware-Timed Signals: Independent, precise signal generation using ESP32 RMT peripheral
- Configurable Timing: Ensures ESCs can reliably detect frame boundaries
- Error Handling: Comprehensive result reporting with success/failure status
- Simple API: Easy integration into your Arduino or ESP-IDF project
📦 Installation
Arduino IDE
- Search "Arduino Library Manager" for "DShotRMT"
or
- Clone this repository or download as ZIP
- Place in your Arduino libraries folder (
~/Arduino/libraries/DShotRMT/) - Restart Arduino IDE
PlatformIO
Add to your platformio.ini:
lib_deps =
https://github.com/derdoktor667/DShotRMT.gitManual Installation
git clone https://github.com/derdoktor667/DShotRMT.gitDependencies
The library requires these additional libraries for full functionality:
Core DShotRMT (always required):
- ESP32 Arduino Core
Web Interface Example (dshot300.ino):
lib_deps =
https://github.com/derdoktor667/DShotRMT
bblanchon/ArduinoJson
https://github.com/ESP32Async/ESPAsyncWebServer
https://github.com/ESP32Async/AsyncTCP ~/Arduino/libraries/AsyncTCPCommand Manager Example:
- No additional dependencies required
⚡ Quick Start
Basic Usage (DShotRMT)
#include <DShotRMT.h>
// Create motor instance (GPIO 17, DSHOT300, non-bidirectional)
DShotRMT motor(17, DSHOT300, false);
void setup() {
Serial.begin(115200);
// Initialize the motor
dshot_result_t result = motor.begin();
if (result.success) {
Serial.println("Motor initialized successfully");
} else {
Serial.printf("Motor init failed: %s\n", result.msg);
}
}
void loop() {
// Send throttle value (48-2047)
dshot_result_t result = motor.sendThrottle(1000);
if (!result.success) {
Serial.printf("Throttle command failed: %s\n", result.msg);
}
}Web Control Interface
#include <DShotRMT.h>
#include <WiFi.h>
#include <ESPAsyncWebServer.h>
DShotRMT motor(17, DSHOT300, false);
AsyncWebServer server(80);
AsyncWebSocket ws("/ws");
void setup() {
// Initialize motor
motor.begin();
// Create WiFi Access Point
WiFi.softAP("DShotRMT Control", "12345678");
// Setup web interface
ws.onEvent(onWsEvent);
server.addHandler(&ws);
server.on("/", HTTP_GET, [](AsyncWebServerRequest *request) {
request->send_P(200, "text/html", index_html);
});
server.begin();
// Access at http://10.10.10.1
}
void loop() {
// Handle WebSocket communication and motor control
ws.cleanupClients();
}Advanced Command Management
#include <DShotRMT.h>
#include <DShotCommandManager.h>
DShotRMT motor(17, DSHOT300, false);
DShotCommandManager cmdManager(motor);
void setup() {
motor.begin();
cmdManager.begin();
}
void loop() {
// High-level ESC control
cmdManager.stopMotor();
cmdManager.activateBeacon(1);
cmdManager.setSpinDirection(false);
cmdManager.executeInitSequence();
}Bidirectional DShot (RPM Telemetry)
#include <DShotRMT.h>
// Enable bidirectional mode for telemetry
DShotRMT motor(17, DSHOT300, true);
void setup() {
Serial.begin(115200);
motor.begin();
}
void loop() {
// Send throttle
motor.sendThrottle(1000);
// Get telemetry data
dshot_telemetry_result_t telemetry = motor.getTelemetry(14); // 14 magnets
if (telemetry.success) {
Serial.printf("eRPM: %u, Motor RPM: %u\n",
telemetry.erpm,
telemetry.motor_rpm);
}
}🌐 Web Control Interface
The DShotRMT library now includes a modern web interface for wireless motor control:
Features
- Responsive Design: Works on mobile phones, tablets, and desktop computers
- WiFi Access Point: Creates hotspot "DShotRMT Control" (Password: 12345678)
- Safety System: Arming/disarming switch prevents accidental motor activation
- Real-time Control: Instant throttle response via WebSocket communication
- Live Telemetry: Real-time RPM display (bidirectional mode only)
- Auto-reconnect: Automatically reconnects on connection loss
Web Interface Access
- Connect to WiFi network: "DShotRMT Control"
- Password: 12345678
- Open browser and navigate to: http://10.10.10.1
Safety Features
- Motor control is disabled by default (disarmed state)
- Toggle the ARMING SWITCH to enable motor control
- Throttle slider is locked when disarmed
- Emergency stop resets all values to safe state
Technical Implementation
- AsyncWebServer for HTTP requests
- WebSocket communication for real-time data
- JSON message format for data exchange
- WiFi SoftAP mode for standalone operation
- Automatic client cleanup prevents memory leaks
⚠️ Known Issus
Make sure you are using these libraries for ESPAsyncWebServer and AsyncTCP to use "web_control.ino" example sketch.
📚 Examples
The library includes comprehensive examples:
1. Basic DShot Control with Web Interface (dshot300.ino)
- Web Control Interface: Modern responsive web UI accessible at
http://10.10.10.1 - WiFi Access Point: Creates hotspot "DShotRMT Control" for wireless control
- Safety Features: Arming/disarming system with motor safety lockout
- Real-time Data: Live RPM telemetry display (bidirectional mode)
- Dual Control: Both web interface and serial console control
- WebSocket Communication: Real-time bidirectional data exchange
Web Interface Features:
- Responsive design optimized for mobile and desktop
- Visual arming switch with safety lockout
- Smooth throttle slider with real-time feedback
- Live RPM monitoring display
- Automatic reconnection on connection loss
2. Advanced Command Management (command_manager.ino)
Interactive ESC control with full menu system:
=== DShot Command Manager Menu ===
1 - Stop Motor
2 - Activate Beacon 1
3 - Set Normal Spin Direction
4 - Set Reversed Spin Direction
5 - Get ESC Info
6 - Turn LED 0 ON
7 - Turn LED 0 OFF
0 - Emergency Stop
Advanced Commands:
cmd <number> - Send DShot command (0-47)
throttle <value> - Set throttle (48-2047)
repeat cmd <num> count <count> - Repeat command
🔧 Hardware Configuration
Supported DShot Modes
| DSHOT | Bitrate | TH1 | TH0 | Bit Time (µs) | Frame Time (µs) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 150 | 150 kbit/s | 5.00 | 2.50 | 6.67 | ~106.72 |
| 300 | 300 kbit/s | 2.50 | 1.25 | 3.33 | ~53.28 |
| 600 | 600 kbit/s | 1.25 | 0.625 | 1.67 | ~26.72 |
GPIO Configuration
// Using GPIO number
DShotRMT motor(17, DSHOT300);
// Using GPIO enum
DShotRMT motor(GPIO_NUM_17, DSHOT300);
// With bidirectional support
DShotRMT motor(17, DSHOT300, true);🎯 DShot Commands
| Command | Value | Description | Usage |
|---|---|---|---|
| MOTOR_STOP | 0 | Stop motor | Always available |
| BEACON1 - 5 | 1 - 5 | Motor beeping | Motor identification |
| ESC_INFO | 6 | Request ESC info | Get ESC version/settings |
| SPIN_DIRECTION_1/2 | 7 - 8 | Set spin direction | Motor configuration |
| 3D_MODE_OFF/ON | 9 - 10 | 3D mode control | Bidirectional flight |
| SAVE_SETTINGS | 12 | Save to EEPROM | Permanent configuration |
| EXTENDED_TELEMETRY_ENABLE/DISABLE | 13 - 14 | Telemetry control | Data transmission |
| SPIN_DIRECTION_NORMAL/REVERSED | 20 - 21 | Spin direction | Alias commands |
| LED0-3_ON/OFF | 22 - 29 | LED control | BLHeli32 only |
| AUDIO_STREAM_MODE | 30 | Audio mode toggle | KISS ESCs |
| SILENT_MODE | 31 | Silent mode toggle | KISS ESCs |
📚 DShot Protocol Details
Packet Structure
Each DShot frame consists of 16 bits:
- 11 bits: Throttle/command value (0-2047)
- 1 bit: Telemetry request flag
- 4 bits: CRC checksum
Checksum Calculation
// Standard DShot CRC
uint16_t crc = (data ^ (data >> 4) ^ (data >> 8)) & 0x0F;
// Bidirectional DShot (inverted CRC)
uint16_t crc = (~(data ^ (data >> 4) ^ (data >> 8))) & 0x0F;Bidirectional DSh...
0.7.2
DShotRMT - ESP32 Library (Rewrite for ESP-IDF 5)
A modern, robust C++ library for generating DShot signals on the ESP32 using the new ESP-IDF 5 RMT encoder API (rmt_tx.h / rmt_rx.h).
Supports all standard DShot modes (150, 300, 600, 1200) and features continuous frame transmission with configurable timing.
Now with BiDirectional DShot support and advanced command management!
The legacy version (using the old
rmt.hAPI) is still available in theoldAPIbranch.
🚀 Features
- All DShot Modes: DSHOT150, DSHOT300 (default), DSHOT600, DSHOT1200
- BiDirectional DShot: Full support for RPM telemetry feedback
- Advanced Command Manager: High-level API for ESC configuration and control
- Command Sequences: Predefined initialization and calibration sequences
- Hardware-Timed Signals: Independent, precise signal generation using ESP32 RMT peripheral
- Configurable Timing: Ensures ESCs can reliably detect frame boundaries
- Error Handling: Comprehensive result reporting with success/failure status
- Simple API: Easy integration into your Arduino or ESP-IDF project
📦 Installation
Arduino IDE
- Search "Arduino Library Manager" for "DShotRMT"
or
- Clone this repository or download as ZIP
- Place in your Arduino libraries folder (
~/Arduino/libraries/DShotRMT/) - Restart Arduino IDE
PlatformIO
Add to your platformio.ini:
lib_deps =
https://github.com/derdoktor667/DShotRMT.gitManual Installation
git clone https://github.com/derdoktor667/DShotRMT.git⚡ Quick Start
Basic Usage (DShotRMT)
#include <DShotRMT.h>
// Create motor instance (GPIO 17, DSHOT300, non-bidirectional)
DShotRMT motor(17, DSHOT300, false);
void setup() {
Serial.begin(115200);
// Initialize the motor
dshot_result_t result = motor.begin();
if (result.success) {
Serial.println("Motor initialized successfully");
} else {
Serial.printf("Motor init failed: %s\n", result.msg);
}
}
void loop() {
// Send throttle value (48-2047)
dshot_result_t result = motor.sendThrottle(1000);
if (!result.success) {
Serial.printf("Throttle command failed: %s\n", result.msg);
}
}Bidirectional DShot (RPM Telemetry)
#include <DShotRMT.h>
// Enable bidirectional mode for telemetry
DShotRMT motor(17, DSHOT300, true);
void setup() {
Serial.begin(115200);
motor.begin();
}
void loop() {
// Send throttle
motor.sendThrottle(1000);
// Get telemetry data
dshot_telemetry_result_t telemetry = motor.getTelemetry(14); // 14 magnets
if (telemetry.success) {
Serial.printf("eRPM: %u, Motor RPM: %u\n",
telemetry.erpm,
telemetry.motor_rpm);
}
}📚 Examples
The library includes comprehensive examples:
1. Basic DShot Control (dshot300.ino)
- Simple throttle control
- Command execution
- Serial interface for testing
- Telemetry reading (if bidirectional enabled)
2. Advanced Command Management (command_manager.ino)
Interactive ESC control with full menu system:
=== DShot Command Manager Menu ===
1 - Stop Motor
2 - Activate Beacon 1
3 - Set Normal Spin Direction
4 - Set Reversed Spin Direction
5 - Get ESC Info
6 - Turn LED 0 ON
7 - Turn LED 0 OFF
0 - Emergency Stop
Advanced Commands:
cmd <number> - Send DShot command (0-47)
throttle <value> - Set throttle (48-2047)
repeat cmd <num> count <count> - Repeat command
🔧 Hardware Configuration
Supported DShot Modes
| Mode | Bitrate | Bit Time | Frame Time | Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DSHOT150 | 150 kbit/s | 6.67 µs | ~107 µs | Long wires, EMI-prone |
| DSHOT300 | 300 kbit/s | 3.33 µs | ~53 µs | Standard (recommended) |
| DSHOT600 | 600 kbit/s | 1.67 µs | ~27 µs | High performance |
| DSHOT1200 | 1200 kbit/s | 0.83 µs | ~13 µs | Racing applications |
GPIO Configuration
// Using GPIO number
DShotRMT motor(17, DSHOT300);
// Using GPIO enum
DShotRMT motor(GPIO_NUM_17, DSHOT300);
// With bidirectional support
DShotRMT motor(17, DSHOT300, true);🎯 DShot Commands
| Command | Value | Description | Usage |
|---|---|---|---|
| MOTOR_STOP | 0 | Stop motor | Always available |
| BEACON1 - 5 | 1 - 5 | Motor beeping | Motor identification |
| ESC_INFO | 6 | Request ESC info | Get ESC version/settings |
| SPIN_DIRECTION_1/2 | 7 - 8 | Set spin direction | Motor configuration |
| 3D_MODE_OFF/ON | 9 - 10 | 3D mode control | Bidirectional flight |
| SAVE_SETTINGS | 12 | Save to EEPROM | Permanent configuration |
| EXTENDED_TELEMETRY_ENABLE/DISABLE | 13 - 14 | Telemetry control | Data transmission |
| SPIN_DIRECTION_NORMAL/REVERSED | 20 - 21 | Spin direction | Alias commands |
| LED0-3_ON/OFF | 22 - 29 | LED control | BLHeli32 only |
| AUDIO_STREAM_MODE | 30 | Audio mode toggle | KISS ESCs |
| SILENT_MODE | 31 | Silent mode toggle | KISS ESCs |
📚 DShot Protocol Details
Packet Structure
Each DShot frame consists of 16 bits:
- 11 bits: Throttle/command value (0-2047)
- 1 bit: Telemetry request flag
- 4 bits: CRC checksum
Checksum Calculation
// Standard DShot CRC
uint16_t crc = (data ^ (data >> 4) ^ (data >> 8)) & 0x0F;
// Bidirectional DShot (inverted CRC)
uint16_t crc = (~(data ^ (data >> 4) ^ (data >> 8))) & 0x0F;Bidirectional DShot
- Inverted Logic: High/low levels are inverted
- GCR Encoding: Telemetry uses Group Code Recording
- 21-bit Response: 1 start + 16 data + 4 CRC bits
- eRPM Data: Electrical RPM transmitted back to controller
🛠️ ESP32 RMT Peripheral
The library utilizes the ESP32's RMT (Remote Control) peripheral for precise signal generation:
Advantages
- Hardware Timing: No CPU intervention during transmission
- Concurrent Operation: Multiple channels can run simultaneously
- DMA Support: Efficient memory-to-peripheral transfers
📖 References & Documentation
DShot Protocol
ESP32 Documentation
🤝 Contributing
We welcome contributions! Please:
- Fork the repository
- Create a feature branch
- Make your changes with tests
- Submit a pull request
Development Guidelines
- Follow existing code style
- Add documentation for new features
- Include examples where appropriate
- Test with real hardware when possible
Reporting Issues
When reporting issues, please include:
- ESP32 board type and version
- Arduino/ESP-IDF version
- ESC type and firmware
- Complete error messages
- Minimal reproduction code
📄 License
MIT License – see LICENSE
👤 Author
Wastl Kraus
- GitHub: @derdoktor667
- Website: wir-sind-die-matrix.de