ngsF-HMM is a program to estimate per-individual inbreeding tracts using a two-state Hidden Markov Model (HMM). Furthermore, instead of using called genotypes, it uses a probabilistic framework that takes the uncertainty of genotype's assignation into account; making it specially suited for low-quality or low-coverage datasets.
ngsF-HMM was published in 2016 at Bioinformatics, so please cite it if you use it in your work:
Vieira FG, Albrechtsen A and Nielsen R
Estimating IBD tracts from low coverage NGS data
Bioinformatics (2016) 32: 2096-2102
ngsF-HMM can be easily installed but has some external dependencies:
- Mandatory:
gcc: >= 4.9.2 tested on Debian 7.8 (wheezy)zlib: v1.2.7 tested on Debian 7.8 (wheezy)gsl: v1.15 tested on Debian 7.8 (wheezy)
- Optional (only needed for testing or auxilliary scripts):
md5sumPerlpackages:Getopt::Long, andIO::ZlibRpackages:optparse, andplyr
To install the entire package just download the source code:
% git clone https://github.com/fgvieira/ngsF-HMM.git
and run:
% cd ngsF-HMM
% make
To run the tests (only if installed through ngsTools):
% make test
Executables are built into the main directory. If you wish to clean all binaries and intermediate files:
% make clean
% ./ngsF-HMM [options] --n_ind INT --n_sites INT --glf glf/in/file --out output/file
--geno FILE: input file with genotypes, genotype likelihoods or genotype posterior probabilities.--posFILE: input file with site coordinates (one per line), where the 1st column stands for the chromosome/contig and the 2nd for the position (bp); remaining columns are ignored.--lkl: input are genotype likelihoods (BEAGLE format).--loglkl: input are genotype log-likelihoods.--n_ind INT: sample size (number of individuals).--n_sites INT: total number of sites.--call_geno: call genotypes before running analyses.--freq DOUBLE or CHAR: initial frequency values. Can be defined by user as a DOUBLE, (r)andom, (e)stimated or read from a FILE.--freq_est INT: allele frequency estimation method: 0) fixed (no optimizatopn); 1) assuming independence of sites; and 2) through haplotype frequency.--indF DOUBLE-DOUBLE or CHAR: initial inbreeding and transition parameter values. Can be defined by user as a DOUBLE-DOUBLE, (r)andom, or read from a FILE.--indF_fixed: inbreeding parameter values are fixed (will not be optimized).--alpha_fixed: transition parameter values are fixed (will not be optimized).--out CHAR: prefix for output files.--log INT: dump LOG file each INT iterations. [0]--log_bin: dump LOG file in binary.--min_iters INT: minimum number of EM iterations. [10]--max_iters INT: maximum number of EM iterations. [100]--min_epsilon FLOAT: maximum RMSD between iterations to assume convergence. [1e-5]--n_threads INT: number of threads to use. [1]--verbose INT: selects verbosity level. [1]--seed INT: seed for random number generator.
As input, ngsF-HMM accepts both genotypes, genotype likelihoods (GP) or genotype posterior probabilities (GP). Genotypes must be input as gziped TSV with one row per site and one column per individual 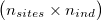
ngsF-HMM accepts both gzipd TSV and binary formats, but with 3 columns per individual 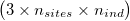
An issue on iterative algorithms is the stopping criteria. ngsF-HMM implements a dual condition threshold: relative difference in log-likelihood and estimates RMSD (F and freq). As for which threshold to use, simulations show that 1e-5 seems to be a reasonable value. However, if you're dealing with low coverage data (2x-3x), it might be worth to use lower thresholds (between 1e-6 and 1e-9).
To avoid convergence to local maxima, ngsF-HMM should be run several times from different starting points. To make this task easier, a script (ngsF-HMM.sh) is provided that can be called with the exact same parameters as ngsF-HMM.
ngsF-HMM will output several files, some depending on input options:
.indF: file similar to ngsF output format, where the first line stands for the final log-likelihood, followed by per individual (one per line) inbreeding coefficients (1st column) and transition rate parameters (2nd column) and, finally, the per-site minor allele frequency..ibd: file storing IBD tracts results, where the first line stores per-individual log-likelihoods. The following lines (one per individual) contain the most-probable inbreeding tracts coded as an INT per site (0: position is not IBD; 1: position is IBD), followed by the IBD posterior probabilities coded as a FLOAT per site (one line per individual)..geno: binary file with genotype posterior probabilities (similar to ANGSD-doGeno 32)..log.gz: if option-log INTis specified, a gziped log file similar to.ibdis printed everyINTiterations..pdf: optionally, thescripts/ngsF-HMMplot.Rscript can be used to plot the IBD tracts.
The thread pool implementation was adapted from Mathias Brossard's and is freely available from: https://github.com/mbrossard/threadpool