A simple code challenge in Python applied to a Machine Learning problem
The challenge requests to create Machine Learning model, according to dataset provided (file dataset.csv) which contains a list of ships and related features. The model should be able to predict 'crew' when receives input values. dataset.csv file has the fields below:
- Ship_name
- Cruise_line
- Age
- Tonnage
- passengers
- length
- cabins
- passenger_density
- crew
The solution is a Regression Analysis Model (Linear Regression, Polynomial Regression, Random Forests, etc.) because of continuous variables. We build the solutions on three steps:
- data analysis focusing on find features correlated to target variable
- build the simplest model (es. Linear Regression) and evaluate it, if the result is not so good
- build more complex model (es. Random Forests) and evaluate it
For this step we can use:
- scatterplot matrix, to select correlated variables
- covariance matrix, to evaluate the best correlated variable (for a first linear regression model)
Running covariance_matrix.py python code we can plot the two images below:
looking on the first image we see that we have to investigate “Tonnage” and “passengers” variables;
while looking on the second image we see that we have to investigate “cabins” and “length” variables too: the four variable seems to be correlated to crew (target variable).
Using covariance matrix:
we see that passengers variable is the candidate to evaluate a Linear Regression Model.
Linear Regression Model is the simplest one and it is very similar to Adaptive Linear Neuron Model. We can use the implementation in Scikit-Learn library which has an optimized implementation (file sklearn.linear.py).
For evaluation we use two measures:
- mean squared error
- coefficient of determination
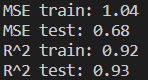
below the results:
0.93 for test dataset is already a good result.
We investigated also Random Forests. This model is based on decision tree (random_forest.py).
below the resutls:
0.98 for train dataset and 0.95 for test dataset is the best results.
The source code is taken from:
preferred-citation: type: book authors: "Raschka Sebastian" website: "https://sebastianraschka.com/news/2019-news/"