Elena Dreyer [email protected] |

Giorgio Coppola [email protected] |

Nadine Daum [email protected] |

Nicolas Reichardt [email protected] |
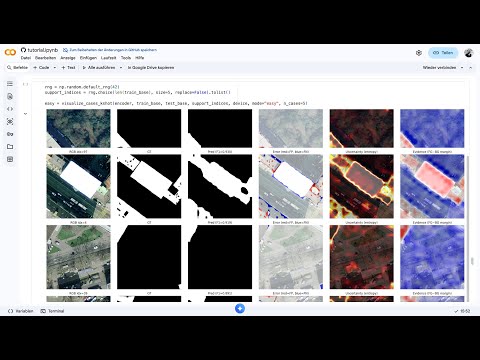
This tutorial introduces few-shot learning techniques for semantic segmentation in satellite imagery using high-resolution images from Geneva, Switzerland. We will demonstrate how Prototypical Networks can learn meaningful rooftop representations from only a few labeled examples and generalize to new geographic areas with minimal annotation effort.
By the end of the tutorial, you will be able to:
- Understand the core concepts behind Few-Shot Learning and Few-Shot Semantic Segmentation
- Work with satellite imagery, geographic splits, and pixel-level segmentation masks
- Implement Prototypical Networks with episodic training for segmentation tasks
- Evaluate model performance using metrics such as IoU and interpret FSL model behavior
- Reflect on policy-relevant applications such as rooftop solar assessment and data-scarce mapping tasks
- Intermediate Python programming
- Familiarity with PyTorch
- Basics of Machine and Deep Learning
- Understanding of convolutional neural networks
The dataset being used for the demonstration of this tutorial consists of:
- Satellite Images: High-resolution RGB satellite images of Geneva, Switzerland
- Segmentation Labels: Binary masks indicating rooftop locations
Either start by watching the video tutorial or jump straight into running the tutorial notebook.
Click the image above to watch the tutorial video
To run the tutorial, you can either use Google Colab or set up a local environment.
-
Install prerequisites:
- Docker
- VS Code with the Dev Containers Extension
-
Clone the repository:
git clone https://github.com/hertie-data-science-lab/tutorial-new-tutorial-group-1.git cd tutorial-new-tutorial-group-1 -
Open in VS Code:
code . -
Reopen in Container (when prompted by VS Code). This will set up all dependencies automatically in the devcontainer environment.
-
Clone the repository:
git clone https://github.com/hertie-data-science-lab/tutorial-new-tutorial-group-1.git cd tutorial-new-tutorial-group-1 -
Set up a virtual environment:
python3.11 -m venv .venv source .venv/bin/activate -
Install dependencies: Using
pyproject.toml:pip install .Or, using
requirements.txt:pip install -r requirements.txt
-
Run the tutorial notebook:
pip install jupyter jupyter notebook
Open
tutorial.ipynband start coding!
Tips:
- For Jupyter support, ensure
ipykernelandnbformatare installed.
-
Alsentzer, E., Li, M. M., Kobren, S. N., Noori, A., Undiagnosed Diseases Network, Kohane, I. S., & Zitnik, M. (2025). Few shot learning for phenotype-driven diagnosis of patients with rare genetic diseases. npj Digital Medicine, 8(1), 380. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41746-025-01749-1
-
Castello, R., Walch, A., Attias, R., Cadei, R., Jiang, S., & Scartezzini, J.-L. (2021). Quantification of the suitable rooftop area for solar panel installation from overhead imagery using convolutional neural networks. Journal of Physics: Conference Series, 2042(1), 012002. https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/2042/1/012002
-
Chen, Y., Wei, C., Wang, D., Ji, C., & Li, B. (2022). Semi-supervised contrastive learning for few-shot segmentation of remote sensing images. Remote Sensing, 14(17), 4254. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14174254
-
Ding, H., Zhang, H., & Jiang, X. (2022). Self-regularized prototypical network for few-shot semantic segmentation. Pattern Recognition, 132, 109018. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patcog.2022.109018
-
Finn, C., Abbeel, P., & Levine, S. (2017). Model-agnostic meta-learning for fast adaptation of deep networks. In International Conference on Machine Learning (pp. 1126–1135). PMLR. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.1703.03400
-
Ge, Z., Fan, X., Zhang, J., & Jin, S. (2025). SegPPD-FS: Segmenting plant pests and diseases in the wild using few-shot learning. Plant Phenomics, 100121. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphe.2025.100121
-
Hu, Y., Liu, C., Li, Z., Xu, J., Han, Z., & Guo, J. (2022). Few-shot building footprint shape classification with relation network. ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information, 11(5), 311. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi11050311
-
Jadon, S. (2021, February). COVID-19 detection from scarce chest x-ray image data using few-shot deep learning approach. In Medical Imaging 2021: Imaging Informatics for Healthcare, Research, and Applications (Vol. 11601, pp. 161–170). SPIE. https://doi.org/10.1117/12.2581496
-
Lee, G. Y., Dam, T., Ferdaus, M. M., Poenar, D. P., & Duong, V. (2025). Enhancing Few-Shot Classification of Benchmark and Disaster Imagery with ATTBHFA-Net. arXiv preprint arXiv:2510.18326. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2510.18326
-
Li, X., He, Z., Zhang, L., Guo, S., Hu, B., & Guo, K. (2025). CDCNet: Cross-domain few-shot learning with adaptive representation enhancement. Pattern Recognition, 162, 111382. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patcog.2025.111382
-
Puthumanaillam, G., & Verma, U. (2023). Texture based prototypical network for few-shot semantic segmentation of forest cover: Generalizing for different geographical regions. Neurocomputing, 538, 126201. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2023.03.062
-
Shaban, A., Bansal, S., Liu, Z., Essa, I., & Boots, B. (2017). One-shot learning for semantic segmentation. BMVC. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.1709.03410
-
Snell, J., Swersky, K., & Zemel, R. (2017). Prototypical networks for few-shot learning. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS 2017), Vol. 30. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.1703.05175
-
Sung, F., Yang, Y., Zhang, L., Xiang, T., Torr, P. H., & Hospedales, T. M. (2018). Learning to compare: Relation network for few-shot learning. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (pp. 1199–1208). https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2018.00131
-
Tian, Z., Zhao, H., Shu, M., Yang, Z., Li, R., & Jia, J. (2020). Prior guided feature enrichment network for few-shot segmentation. IEEE TPAMI, 44(2), 1050–1065. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2020.3013717
-
Wang, K., Liew, J. H., Zou, Y., Zhou, D., & Feng, J. (2019). PANet: Few-shot image semantic segmentation with prototype alignment. ICCV. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.1908.06391