NetFL is a framework that extends Fogbed by integrating Flower, enabling simulation of Federated Learning experiments within Fog/Edge computing environments. It supports the modeling of heterogeneous and resource-constrained edge scenarios, incorporating factors such as computational disparities among devices and dynamic network conditions, including bandwidth limitations, latency variations, and packet loss. This facilitates realistic evaluations of FL systems under non-ideal, real-world conditions.
Requirements: Ubuntu 22.04 LTS or later, Python 3.9.
Refer to the Containernet documentation for further details.
Install Ansible:
sudo apt-get install ansible
Clone the Containernet repository:
git clone https://github.com/containernet/containernet.git
Run the installation playbook:
sudo ansible-playbook -i "localhost," -c local containernet/ansible/install.yml
Create and activate a virtual environment:
python3 -m venv venv
source venv/bin/activate
Note: The virtual environment must be activated before installing or using any Python packages, including Containernet and NetFL.
Install Containernet into the active virtual environment:
pip install containernet/.
While the virtual environment is still active, run:
pip install netfl
Follow the steps below to set up and run an experiment using NetFL. This is an example using the MNIST dataset. You can find more examples in the examples folder:
import tensorflow as tf
from keras import models, optimizers
from flwr.server.strategy import FedAvg
from netfl.core.task import Task, Dataset, DatasetInfo, DatasetPartitioner, TrainConfigs
from netfl.core.models import cnn3
from netfl.core.partitioners import IidPartitioner
class MNIST(Task):
def dataset_info(self) -> DatasetInfo:
return DatasetInfo(
huggingface_path="ylecun/mnist",
input_key="image",
label_key="label",
input_dtype=tf.float32,
label_dtype=tf.int32
)
def dataset_partitioner(self) -> DatasetPartitioner:
return IidPartitioner()
def normalized_dataset(self, raw_dataset: Dataset) -> Dataset:
return Dataset(
x=tf.cast(raw_dataset.x, tf.float32) / 255.0,
y=raw_dataset.y
)
def model(self) -> models.Model:
return cnn3(
input_shape=(28, 28, 1),
output_classes=10,
optimizer=optimizers.SGD(learning_rate=0.01)
)
def aggregation_strategy(self) -> type[FedAvg]:
return FedAvg
def train_configs(self) -> TrainConfigs:
return TrainConfigs(
batch_size=16,
epochs=2,
num_clients=4,
num_partitions=4,
num_rounds=10,
seed_data=42,
shuffle_data=True
)
class MainTask(MNIST):
passfrom fogbed import HardwareResources, CloudResourceModel, EdgeResourceModel
from netfl.core.experiment import NetflExperiment
from netfl.utils.resources import LinkResources
from task import MainTask
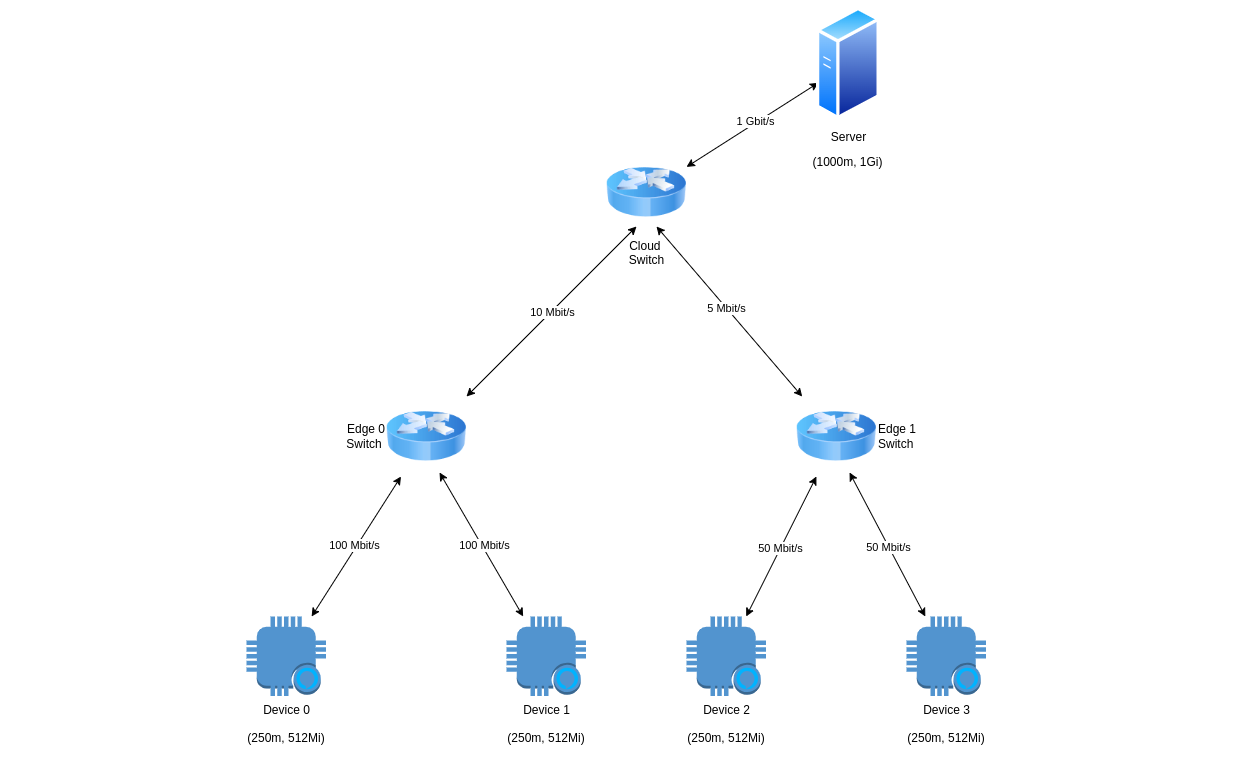
exp = NetflExperiment(name="mnist-exp", task=MainTask(), max_cu=2.0, max_mu=3072)
cloud_resources = CloudResourceModel(max_cu=1.0, max_mu=1024)
edge_0_resources = EdgeResourceModel(max_cu=0.5, max_mu=1024)
edge_1_resources = EdgeResourceModel(max_cu=0.5, max_mu=1024)
server_resources = HardwareResources(cu=1.0, mu=1024)
server_link = LinkResources(bw=1000)
edge_0_total_devices = 2
edge_0_device_resources = HardwareResources(cu=0.25, mu=512)
edge_0_device_link = LinkResources(bw=100)
edge_1_total_devices = 2
edge_1_device_resources = HardwareResources(cu=0.25, mu=512)
edge_1_device_link = LinkResources(bw=50)
cloud_edge_0_link = LinkResources(bw=10)
cloud_edge_1_link = LinkResources(bw=5)
cloud = exp.add_virtual_instance("cloud", cloud_resources)
edge_0 = exp.add_virtual_instance("edge_0", edge_0_resources)
edge_1 = exp.add_virtual_instance("edge_1", edge_1_resources)
server = exp.create_server("server", server_resources, server_link)
edge_0_devices = exp.create_devices(
"edge_0_device", edge_0_device_resources, edge_0_device_link, edge_0_total_devices
)
edge_1_devices = exp.create_devices(
"edge_1_device", edge_1_device_resources, edge_1_device_link, edge_1_total_devices
)
exp.add_docker(server, cloud)
for device in edge_0_devices: exp.add_docker(device, edge_0)
for device in edge_1_devices: exp.add_docker(device, edge_1)
worker = exp.add_worker("127.0.0.1", port=5000)
worker.add(cloud)
worker.add(edge_0)
worker.add(edge_1)
worker.add_link(cloud, edge_0, **cloud_edge_0_link.params)
worker.add_link(cloud, edge_1, **cloud_edge_1_link.params)
try:
exp.start()
except Exception as ex:
print(ex)
finally:
exp.stop()RunWorker -p=5000
python3 experiment.py
Refer to the Fogbed documentation for detailed instructions on starting workers.
https://github.com/larsid/netfl.git
In the project root directory, create or modify a NetFL Task and name the file task.py. Refer to the examples in the examples folder for guidance on task creation.
Use Docker Compose to set up the infrastructure, including the server and clients:
docker compose up -d
To check the server logs, run:
docker logs server
Training logs are also stored in the logs folder within the project root directory.
To stop and remove all running containers, use the following command:
docker compose down