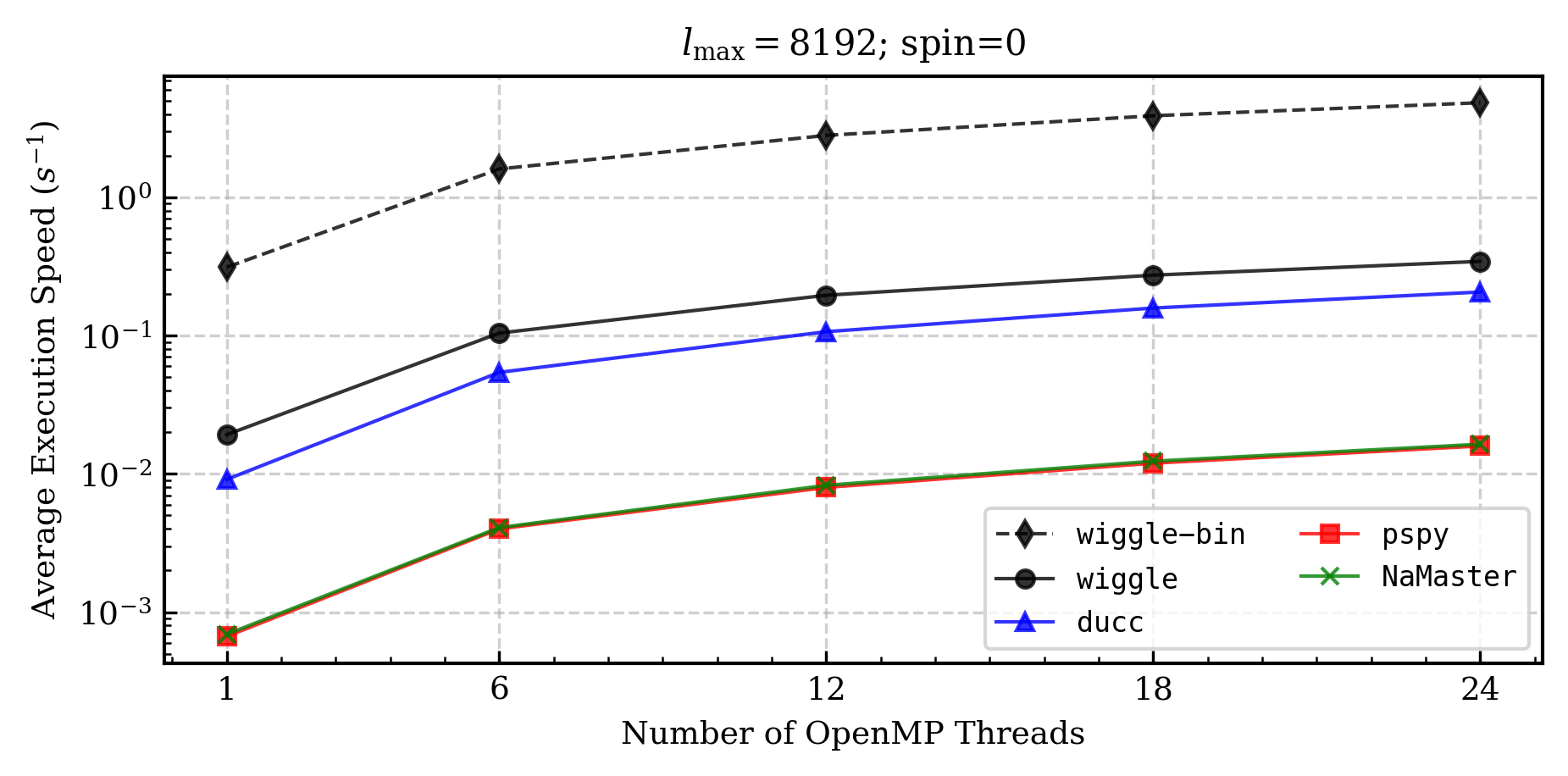
wiggle stands for the WIGner Gauss-Legendre Estimator. This Python package provides a fast implementation of unbiased angular power spectrum estimation of spin-0 and spin-2 fields on the sphere, most commonly encountered in the context of cosmological data analysis. With an efficient and exact algorithm, this code performs mode-decoupling very fast; in the case of binned spectra, wiggle can be orders of magnitude faster than other approaches (often around one second of compute-time at most).
- Free software: BSD license
- Documentation: https://wiggle.readthedocs.io.
Make sure your pip tool is up-to-date. To install wiggle, run:
$ pip install pywiggle --userThis will install a pre-compiled binary suitable for your system (only Linux and Mac OS X with Python>=3.9 are supported). After installation, make sure to run a test with:
$ pytest --pyargs pywiggle.testsIf you require more control over your installation, e.g. using Intel compilers, please see the section below on compiling from source.
The easiest way to install from source is to use the pip tool,
with the --no-binary flag. This will download the source distribution
and compile it for you. Don't forget to make sure you have CXX set
if you have any problems.
For all other cases, below are general instructions.
First, download the source distribution or git clone this repository. You
can work from master or checkout one of the released version tags (see the
Releases section on Github). Then change into the cloned/source directory.
Once downloaded, you can install using pip install . inside the project
directory. We use the meson build system, which should be understood by
pip (it will build in an isolated environment).
We suggest you then test the installation by running the unit tests. You
can do this by running pytest.
To run an editable install, you will need to do so in a way that does not have build isolation (as the backend build system, meson and ninja, actually perform micro-builds on usage in this case):
$ pip install --upgrade pip meson ninja meson-python cython numpy pybind11
$ pip install --no-build-isolation --editable .After installation, make sure to run a test with:
$ pytestAccurate power spectrum estimation requires you to first convert a pixelated and masked map to its spherical harmonic coefficients. wiggle does not provide tools for SHTs and expects you to have the alm coefficients both for the masked fields and the mask itself already in hand. These can be obtained using a code like healpy in the case of HEALPix maps or a code like pixell in the case of rectangular pixelization maps.
If you are interested in accurate power spectra out to some maximum multipole lmax, we recommend you evaluate SHTs out to lmax for the masked fields, but out to 2 lmax for the mask itself. With these in hand, you can obtain unbiased power spectra as follows, in the case of a spin-0 field for example:
> import pywiggle
> import numpy as np
> import healpy as hp # or use pixell for rectangular pixel maps
> lmax = 4000 # Max multipole out to which you want reliable answers
> bin_edges = np.arange(40,lmax,40) # Choose bin edges
> alms1 = hp.map2alm(map1 * mask, lmax=lmax) # or get these from your favorite way of getting an SHT of masked maps
> alms2 = hp.map2alm(map2 * mask, lmax=lmax) # same as above
> mask_alm = hp.map2alm(map2 * mask, lmax=2*lmax) # Notice that mask alms are needed out to 2*lmax
> ret = pywiggle.get_powers(alms1,alms2, mask_alm1, return_theory_filter=True,lmax=lmax,bin_edges=bin_edges)
> bcls = ret['TT']['Cls'] # The debiased power spectrum for spin-0
> th_filt = ret['TT']['Th'] # Optional binning matrix for precision theory comparisonsThe interface to get_powers is flexible enough to allow all auto- and cross- spectra of spin-0 and spin-2 fields. If the input spherical harmonics are (1,nalm) or (nalm,) dimensional, where nalm is the number of spherical harmonic a_lm elements, the field is assumed to be spin-0 and only the TT-like spectrum is returned in the dictionary. If the input spherical harmonics are (2,nalm) dimensional, then the inputs are assumed to be E/B decompositions of a spin-2 field, and EE, EB, BE and BB are returned. If the input spherical harmonics are (3,nalm) dimensional, then the inputs are assumed to be a scalar field along with E/B decompositions of a spin-2 field, and TT, TE, ET, EE, EB, BE and BB are returned.
Here bcls is the mode-decoupled unbiased power spectrum and th_filt is a matrix that can be dotted with a theory spectrum to obtain the binned theory to compare the power spectrum to (e.g. for inference):
> chisquare = get_chisquare(bcls,th_filt @ theory_cls,cinv)If you have write access to this repository, please:
- create a new branch
- push your changes to that branch
- merge or rebase to get in sync with master
- submit a pull request on github
If you do not have write access, create a fork of this repository and proceed as described above.