To develop an algorithm to find the route from the source to the destination point using breadth-first search.
To implement Breadth-First_Search ( BFS ) algorithm to find the route between an initial state to a final state.
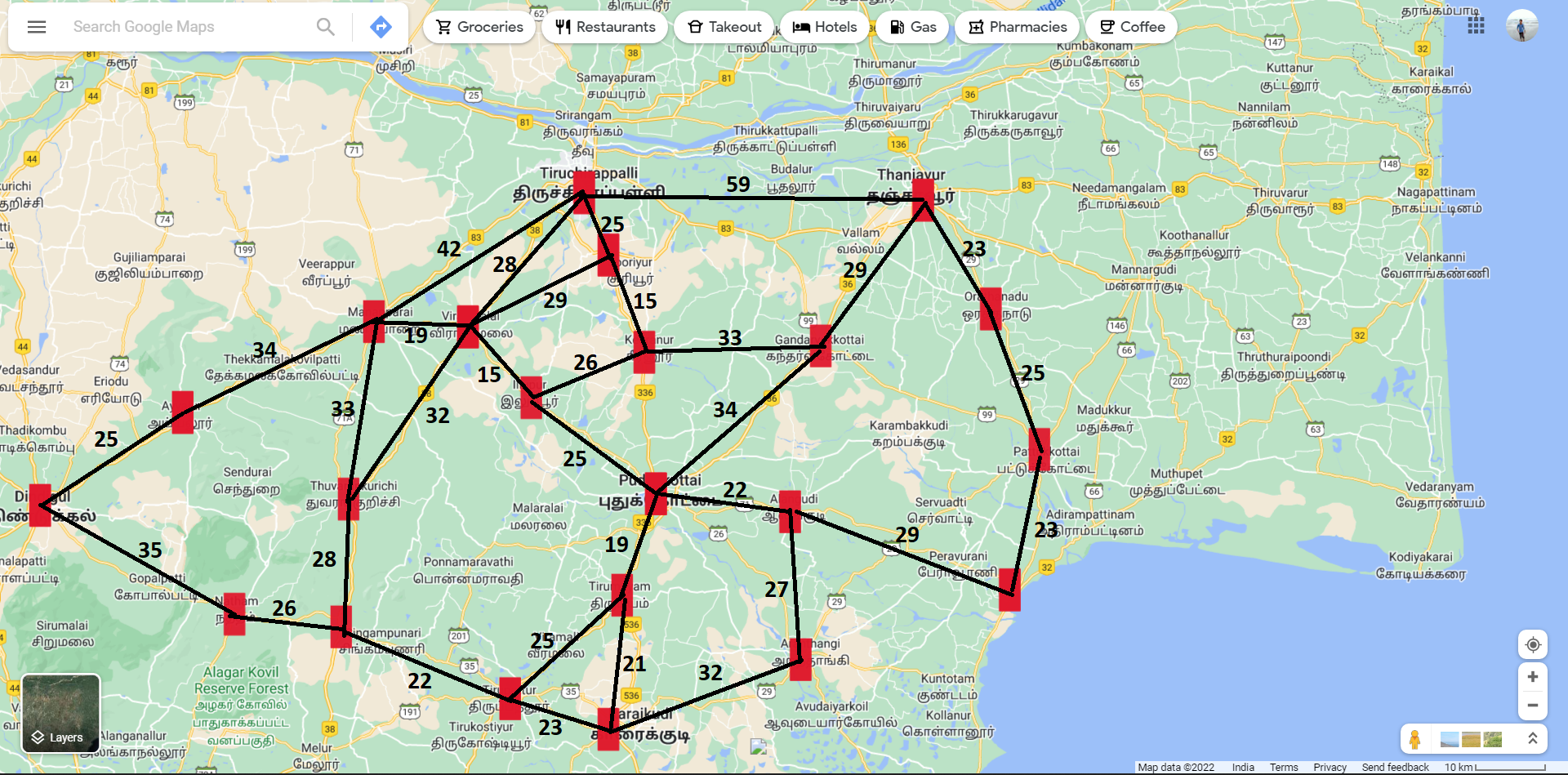
Something like google maps. We create a dictionary to act as the dataset for the search alogrithm, containing all the distances between all the nodes ( Places ).
Identify a location in the google map:
Select a specific number of nodes with distance
Create a dictionary with all the node pairs (keys) and their respective distances as the values
Implement the search algorithm by passing any two nodes/places to find a possible route.
Display the route sequence.
Developed by: Vijayaragavan ARR
Register No: 212220230059
%matplotlib inline
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import random
import math
import sys
from collections import defaultdict, deque, Counter
from itertools import combinations
class Problem(object):
"""The abstract class for a formal problem. A new domain subclasses this,
overriding `actions` and `results`, and perhaps other methods.
The default heuristic is 0 and the default action cost is 1 for all states.
When yiou create an instance of a subclass, specify `initial`, and `goal` states
(or give an `is_goal` method) and perhaps other keyword args for the subclass."""
def __init__(self, initial=None, goal=None, **kwds):
self.__dict__.update(initial=initial, goal=goal, **kwds)
def actions(self, state):
raise NotImplementedError
def result(self, state, action):
raise NotImplementedError
def is_goal(self, state):
return state == self.goal
def action_cost(self, s, a, s1):
return 1
def __str__(self):
return '{0}({1}, {2})'.format(
type(self).__name__, self.initial, self.goal)class Node:
"A Node in a search tree."
def __init__(self, state, parent=None, action=None, path_cost=0):
self.__dict__.update(state=state, parent=parent, action=action, path_cost=path_cost)
def __str__(self):
return '<{0}>'.format(self.state)
def __len__(self):
return 0 if self.parent is None else (1 + len(self.parent))
def __lt__(self, other):
return self.path_cost < other.path_cost
failure = Node('failure', path_cost=math.inf) # Indicates an algorithm couldn't find a solution.
cutoff = Node('cutoff', path_cost=math.inf) # Indicates iterative deepening search was cut off.
def expand(problem, node):
"Expand a node, generating the children nodes."
s = node.state
for action in problem.actions(s):
s1 = problem.result(s, action)
cost = node.path_cost + problem.action_cost(s, action, s1)
yield Node(s1, node, action, cost)
def path_actions(node):
"The sequence of actions to get to this node."
if node.parent is None:
return []
return path_actions(node.parent) + [node.action]
def path_states(node):
"The sequence of states to get to this node."
if node in (cutoff, failure, None):
return []
return path_states(node.parent) + [node.state]
FIFOQueue = deque
def breadth_first_search(problem):
"Search shallowest nodes in the search tree first."
node = Node(problem.initial)
if problem.is_goal(problem.initial):
return node
# Remove the following comments to initialize the data structure
frontier = FIFOQueue([node])
reached = {problem.initial}
while frontier:
node = frontier.pop()
for child in expand(problem, node):
s = child.state
if problem.is_goal(s):
return child
if s not in reached:
reached.add(s)
frontier.appendleft(child)
return failure
class RouteProblem(Problem):
"""A problem to find a route between locations on a `Map`.
Create a problem with RouteProblem(start, goal, map=Map(...)}).
States are the vertexes in the Map graph; actions are destination states."""
def actions(self, state):
"""The places neighboring `state`."""
return self.map.neighbors[state]
def result(self, state, action):
"""Go to the `action` place, if the map says that is possible."""
return action if action in self.map.neighbors[state] else state
def action_cost(self, s, action, s1):
"""The distance (cost) to go from s to s1."""
return self.map.distances[s, s1]
def h(self, node):
"Straight-line distance between state and the goal."
locs = self.map.locations
return straight_line_distance(locs[node.state], locs[self.goal])
class Map:
"""A map of places in a 2D world: a graph with vertexes and links between them.
In `Map(links, locations)`, `links` can be either [(v1, v2)...] pairs,
or a {(v1, v2): distance...} dict. Optional `locations` can be {v1: (x, y)}
If `directed=False` then for every (v1, v2) link, we add a (v2, v1) link."""
def __init__(self, links, locations=None, directed=False):
if not hasattr(links, 'items'): # Distances are 1 by default
links = {link: 1 for link in links}
if not directed:
for (v1, v2) in list(links):
links[v2, v1] = links[v1, v2]
self.distances = links
self.neighbors = multimap(links)
self.locations = locations or defaultdict(lambda: (0, 0))
def multimap(pairs) -> dict:
"Given (key, val) pairs, make a dict of {key: [val,...]}."
result = defaultdict(list)
for key, val in pairs:
result[key].append(val)
return result
# Create your own map and define the nodes
locations = Map(
{('dindigul','ayyalur'):25,
('ayyalur','manapaarai'):34,
('manapaarai','trichy'):42,
('trichy','tanjore'):59,
('tanjore','orathanaadu'):23,
('orathanaadu','pattukottai'):25,
('pattukottai','peravurani'):23,
('peravurani','alangudi'):29,
('alangudi','aranthangi'):27,
('aranthangi','karaikudi'):32,
('karaikudi','thirupattur'):23,
('thirupattur','singampunari'):22,
('singampunari','natham'):26,
('natham','dindigul'):35,
('manapaarai','thuvarangurichi'):33,
('thuvarangurichi','singampunari'):28,
('manapaarai','viralimalai'):19,
('viralimalai','thuvarangurichi'):32,
('viralimalai','trichy'):28,
('viralimalai','sooriyur'):29,
('trichy','sooriyur'):25,
('sooriyur','keeranur'):15,
('keeranur','gandarvakottai'):33,
('gandarvakottai','tanjore'):29,
('keeranur','ilupur'):26,
('ilupur','viralimalai'):15,
('pudukottai','gandarvakottai'):34,
('pudukottai','ilupur'):25,
('pudukottai','alangudi'):22,
('pudukottai','thirumayam'):19,
('thirumayam','thirupattur'):25,
('thirumayam','karaikudi'):21})
r0 = RouteProblem('dindigul', 'pudukottai', map=locations)
# r1 = RouteProblem('pudukottai', 'trichy', map=locations)
# r2 = RouteProblem('tanjore', 'pudukottai', map=locations)
# r3 = RouteProblem('trichy', 'alangudi', map=locations)
# r4 = RouteProblem('tanjore', 'peravurani', map=locations)
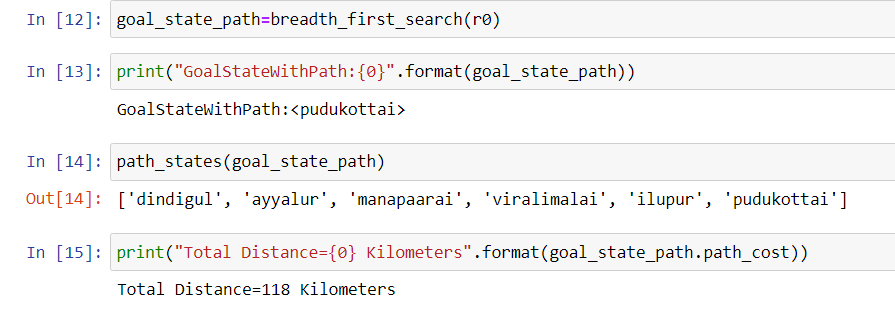
goal_state_path=breadth_first_search(r0)
print("GoalStateWithPath:{0}".format(goal_state_path))
path_states(goal_state_path)
print("Total Distance={0} Kilometers".format(goal_state_path.path_cost))The Algorithm searches all the nodes for the most eligible node, and then it goes into the deep, to find the next eligible node to reach the desired destination.
Hence, Breadth-First-Search Algorithm was implemented for a route finding problem.