- 🌟 Overview
- 🚧 Disclaimer
- ⚙️ Notable Features
- 📋 Requirements
- Installation
- 🤝 Contributing
- 🛠️ Hardware
- 🏗️ Architecture
- 📦 Notable dependencies
- 🗺️ Roadmap
- 🔒 License
Ubo App is a Python application that provides a unified interface and tools for developing and running hardware-integrated apps.
It offers a minimalistic, yet intuitive UI for end-users to install and interact with developer apps. It is optimized for Raspberry Pi (4 & 5) devices.
Hardware specific capabilities such as infrared send/receive, sensing, LED ring, etc. are supported by Ubo Pod hardware.
It is also possible to DIY your own hardware, see the hardware DIY section below.
The design is centered around the following goals:
- Making hardware-integarted app development easier
- Offer no-code/no-terminal UI/UX optionsto both developers and end-users of their apps
- Give developers tools to build apps with multi-modal UX
- Leverage tight hardware and software co-development to unlock new potentials
- Let users focus on their app logic while Ubo app handles the rest (hardware abstractions, UI, etc.)
- Hot-pluggable services
- Modular and friendly to AI tool-calling
- Remote API access (gRPC)
If you are willing to supporting other SBCs or operating systems, please consider contributing to the project.
Example GUI screenshots
Be aware that at the moment, Ubo app sends crash reports to Sentry. Soon we will limit this to beta versions only.
- Easy WiFi on-boarding with QR code or hotspot
- Headless (no monitor/keyboard) remote access setup
- SSH
- VS Code tunnel
- Raspberry Pi Connect
- Install and run Dockerized apps headlessly
- One-click install for pre-configured apps
- Access and control basic Linux utilities and settings
- User management
- Network management
- File system operations
- Natural language interactions for tool calling (voice AI) (experimental)
- Web UI
- Infrared remote control (send/receive)
- gRPC API for remote control - find sample clients here
Check roadmap section below for upcoming features.
At minimum you need a Raspberry Pi 4 or 5 to run Ubo App.
To run LLM models locally, we recommend a Raspberry Pi 5 with at least 8GB of RAM.
For features that require add-on hardware that is not natively supported by Raspberry Pi (such as audio, infrared rx/tx, sensors, etc), you can:
- Purchase an Ubo Pod Development Kit
- DIY the hardware
- Use only subset of hardware features emulated in the browser
For more details check out the hardware section below.
🙏 Please consider supporting this project by pre-ordering an Ubo Pod Dev Edition on Kickstarter.
The sales proceeds from the hardware will be used to support continued development and maintenance of Ubo App and its open source dependencies.
Note : The app still functions even if some special hardware elements (audio, infrared rx/tx, sensors, etc) are not provided. The features that rely on these hardware components just won't function. For example, WiFi onboarding with QR code requires a camera onboard.
Ubo Pod ships with a pre-flashed MicroSD card that has the app installed on it by default.
If you don't have it, or you just want to set up a fresh device, then:
- Download one of the images from the release section
- Use Raspberry Pi Images and choose
custom imageto provide the download image file. - Write to the image
- Use the image to boot your Ubo Pod or Raspberry Pi
This is the fastest, easiest, and recommended way to get started with Ubo App.
🙋♂️If this is the first time you are flashing an image for Raspberry Pi, I recommend following the more detailed steps here.
To run the app on bare Raspberry Pi, you can watch this short demo video.
If you want to install the image on an existing operating system, then read on. Otherwise, skip this section.
To install ubo, run this command in a terminal shell:
curl -sSL https://raw.githubusercontent.com/ubopod/ubo-app/main/ubo_app/system/scripts/install.sh | sudo bashIf you don't want to install docker service you can set the WITH_DOCKER environment variable to false:
curl -sSL https://raw.githubusercontent.com/ubopod/ubo-app/main/ubo_app/system/scripts/install.sh | sudo WITHOUT_DOCKER=true bashTo install a specific version of ubo, you can set the TARGET_VERSION environment variable to the desired version:
curl -sSL https://raw.githubusercontent.com/ubopod/ubo-app/main/ubo_app/system/scripts/install.sh | sudo TARGET_VERSION=0.0.1 bashNote that as part of the installation process, these debian packages are installed:
- accountsservice
- dhcpcd
- dnsmasq
- git
- hostapd
- i2c-tools
- ir-keytable
- libasound2-dev
- libcap-dev
- libegl1
- libgl1
- libmtdev1
- libzbar0
- python3-alsaaudio
- python3-apt
- python3-dev
- python3-gpiozero
- python3-libcamera
- python3-picamera2
- python3-pip
- python3-virtualenv
- rpi-lgpio
Also be aware that ubo-app only installs in /opt/ubo and it is not customizable
at the moment.
Contributions following Python best practices are welcome.
- Use
UBO_prefix for environment variables. - Use
ubo:prefix for notification ids used in ubo core and<service_name>:prefix for notification ids used in services. - Use
ubo:prefix for icon ids used in ubo core and<service_name>:prefix for icon ids used in services.
To set up the development environment, you need to have uv installed.
First, clone the repository (you need to have git-lfs installed):
git clone https://github.com/ubopod/ubo_app.git
git lfs install
git lfs pullIn environments where some python packages are installed system-wide, like Raspberry Pi OS, you need to run the following command to create a virtual environment with system site packages enabled:
uv venv --system-site-packagesThen, navigate to the project directory and install the dependencies:
uv sync --devNow you can run the app with:
HEADLESS_KIVY_DEBUG=true uv run uboAdd ubo-development-pod host in your ssh config at ~/.ssh/config:
Host ubo-development-pod
HostName <ubopod IP here>
User pi
~/.ssh/authorized_keys) so that you don't need to enter the password each time you ssh into the device. If you decide to use password instead, you need to reset the password for Pi user first using the GUI on the device by going to Hamburger Menu -> Settings -> System -> Users and select pi user
Before you deploy the code onto the pod, you have to run the following command to generate the protobuf files and compile the web application.
Please make sure you have buf library installed locally. If you are developing on a Mac or Linux, you can install it using Homebrew:
brew install bufbuild/buf/bufThen, run the following command to generate the protobuf files whenever an action or
uv run poe protoThis is a shortcut for running the following commands:
uv run poe proto:generate # generate the protobuf files based on the actions/events defined in python files
uv run poe proto:compile # compile the protobuf files to python filesIf you are running it for the firt time, you first need to install the dependencies for the web application:
cd ubo_app/services/090-web-ui/web-app
npm install # Only needed the first time or when dependencies changeThen, you need to compile the protobuf files and build the web application:
cd ubo_app/services/090-web-ui/web-app
npm run proto:compile
npm run buildIf you are modifying web-app typescript files, run npm run build:watch and let it stay running in a terminal. This way, whenever you modify web-app files, it will automatically update the built files in dist directory as long as it’s running.
If you ever add, modify or remove an action or an event you need to run poe proto and npm run proto:compile again manually.
Then you need to run this command once to set up the pod for development:
uv run poe device:deploy:completeAfter that, you can deploy the app to the device with:
uv run poe device:deployTo run the app on the device, you can use either of these commands:
uv run poe device:deploy:restart # gracefully restart the app with systemctl
uv run poe device:deploy:kill # kill the process, which will be restarted by systemd if the service is not stoppedEasiest way to run tests is to use the provided Dockerfiles. To run the tests in a container, you first need to create the development images by running:
uv run poe build-docker-imagesThen you can run the tests with:
docker run --rm -it --name ubo-app-test -v .:/ubo-app -v ubo-app-dev-uv-cache:/root/.cache/uv ubo-app-testYou can add arguments to the pytest command to run specific tests like this:
docker run --rm -it --name ubo-app-test -v .:/ubo-app -v ubo-app-dev-uv-cache:/root/.cache/uv ubo-app-test -- <pytest-args>For example, to run only the tests in the tests/integration/test_core.py file, you can run:
docker run --rm -it -v .:/ubo-app -v ubo-app-dev-uv-cache:/root/.cache/uv -v uvo-app-dev-uv-local:/root/.local/share/uv -v ubo-app-dev-uv-venv:/ubo-app/.venv ubo-app-testTo pass it command line options add a double-dash before the options:
docker run --rm -it -v .:/ubo-app -v ubo-app-dev-uv-cache:/root/.cache/uv -v uvo-app-dev-uv-local:/root/.local/share/uv -v ubo-app-dev-uv-venv:/ubo-app/.venv ubo-app-test -- -svv --make-screenshots --override-store-snapshots --override-window-snapshotsYou can also run the tests in your local environment by running:
uv run poe testYou need to install dependencies with following commands once:
uv run poe device:test:copy
uv run poe device:test:depsThen you can use the following command each time you want to run the tests:
uv run poe device:testTo run the linter run the following command:
uv run poe lintTo automatically fix the linting issues run:
uv run poe lint --fixTo run the type checker run the following command on the pod:
uv run poe typecheckIf you prefer to run typecheck on the local machine, clone stubs repository (which includes typing stubs for third-party packages) and place the files under typings directory. Then run poe typecheck command.
It is not documented at the moment, but you can see examples in ubo_app/services directory.
create_task function imported from ubo_app.utils.async_ to create a new task. Using await inside async functions is always fine and doesn't need any special attention.
create_task imported from ubo_app.utils.async_ is alright.
In development environment, the camera is probably not working, as it is relying on picamera2, so it may become challenging to test the flows relying on QR code input.
To address this, the camera module, in not-RPi environments, will try reading from /tmp/qrcode_input.txt and /tmp/qrcode_input.png too. So, whenever you encounter a QR code input, you can write the content of the QR code in the text file path or put the qrcode image itself in the image file path and the application will read it from there and continue the flow.
Alternatively you may be able to provide the input in the web-ui (needs refresh at the moment) or provide it by InputProvideAction in grpc channel.
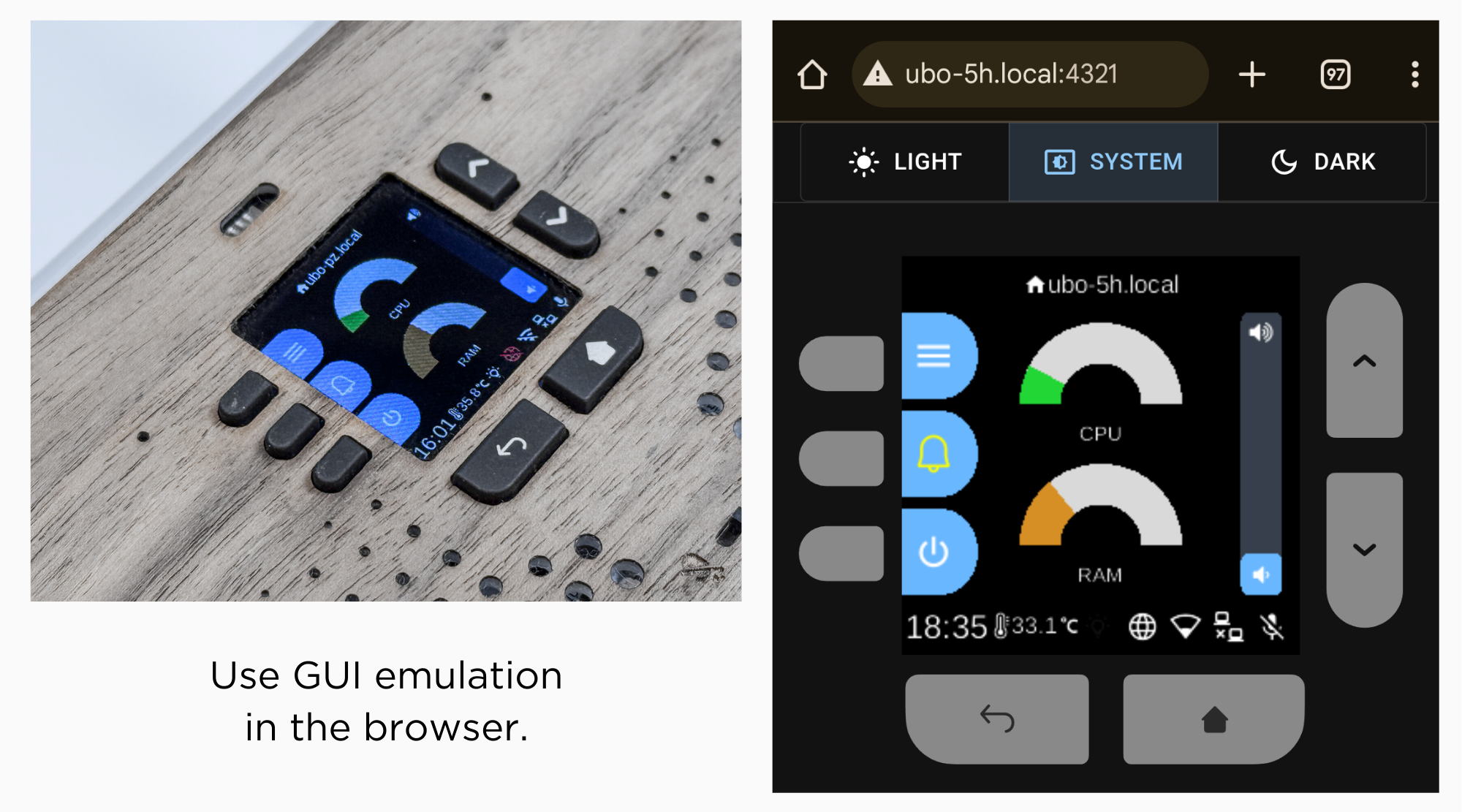
This section presents different hardware or emulation options that you can use with Ubo app.
To remove barriers to adoption as much as possible and allow developers use Ubo app without hardware depenencies, we are currently emulating the physical GUI in the browser.
The audio playback is also streamed through the broswer.
We plan to emulate camera and microphone with WebRTC in the future.
However, other specialized hardware components (sensors, infrared rx/tx, etc) cannot be emulated.
Ubo pod is an open hardware that includes the following additional hardware capabilities that is supported by Ubo app out of the box:
- A built-in minimal GUI (color LCD display and keypad)
- Stereo microphone and speakers (2W)
- Camera (5MP)
- LED ring (27 addressable RGB LEDs)
- Sensors
- Ambient light sensor
- Temperature sensor
- STEMMA QT / Qwiic connector for additional sensors
- Infrared
- Receiver (wideband)
- Transmitter (4 high power LEDs)
- 2 full HDMI ports
- Power/reset button
- NVMe storage (Pi 5 only)
For more information on hardware spec, see the website getubo.com.
This is an open hardware. You can access mechanical design files here and electrical design files here.
You can also buy different HATs from different vendors to DIY the hardware. Future plans include supporting USB microphone, speakers, cameras as well with headless setup.
This however involves having to purchase multiple HATs from different vendors and the process may not be the easiest and most frictionless. You may have to dig into the code and make some small changes to certain setups and configurations.
I made the table below that shows options for audio, cameras, and other sub-components:
| Function | Options |
|---|---|
| Audio | Respeaker 2-Mic Audio HAT, Adafruit Voice Bonnet, Waveshare WM8960 Hat, Adafruit BrainCraft HAT |
| Speakers | 1 or 2W, 8 Ohm |
| Camera | Raspberry Pi Camera Modules V1.3, V2, or V3 |
| LCD (also emulated in the browser) | 240x240 TFT Display, Adafruit BrainCraft HAT |
| Keypad | AW9523 GPIO Expander |
| LED ring | Neopixel LED ring |
| Ambient Light Sensor | VEML7700 Lux Sensor |
| Temperature Sensor | PCT2075 Temperature Sensor |
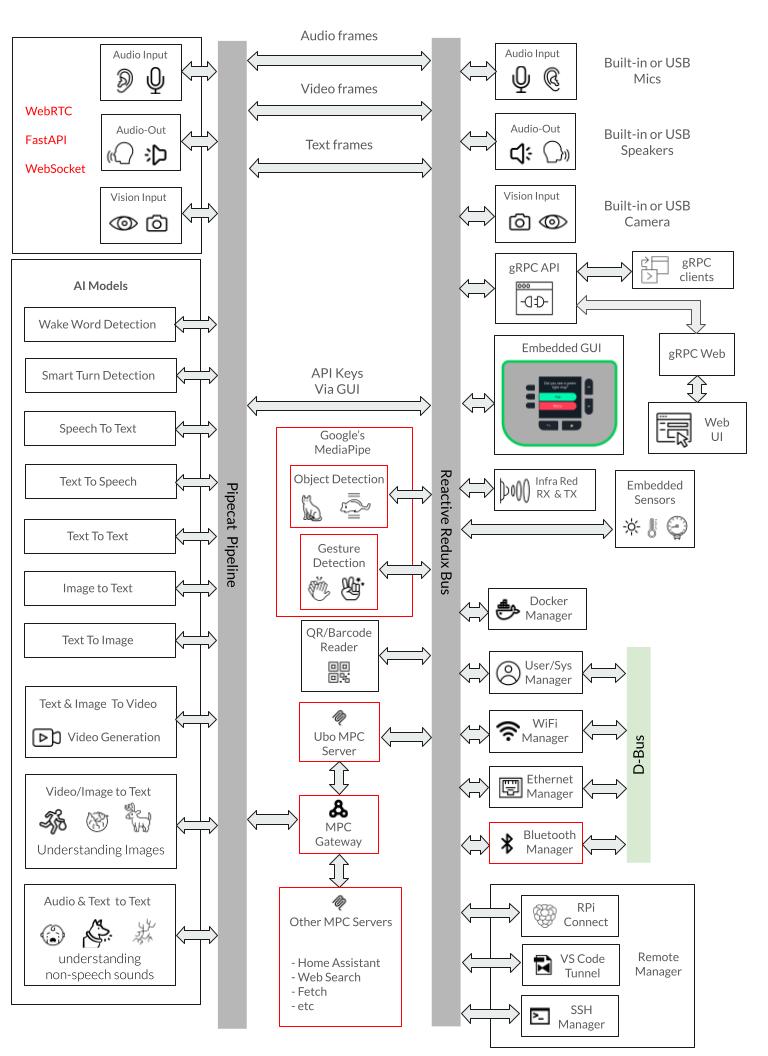
The architecture is fundamentally event-driven and reactive, built around a centralized Redux store that coordinates all system interactions through immutable state updates and event dispatching.
Services communicate exclusively through Redux actions and events rather than direct method calls, with each service running in its own isolated thread while subscribing to relevant state changes and events.
The system uses custom event handlers that automatically route events to the appropriate service threads, enabling reactive responses to state changes across hardware interfaces, user interactions, and system events.
This reactive architecture allows components like the web UI to subscribe to display render events and audio playback events in real-time, creating a responsive system where changes propagate automatically through the event stream without tight coupling between components.
The following is a summary of key architecture components.
-
Redux-Based State Management: Central
UboStoremanages all application state through immutable state trees, with each service contributing its own state slice (audio, camera, display, docker, wifi, etc.) and communicating via actions and events. -
Modular Service Architecture: 21+ core services run in isolated threads with dedicated event loops, organized by priority (
000-0xxfor hardware,030-0xxfor networking,080-0xxfor applications,090-0xxfor UI), each with their own setup.py, reducer.py, and ubo_handle.py files. -
Hardware Abstraction Layer: Comprehensive abstraction for Raspberry Pi components (ST7789 LCD, WM8960 audio, GPIO keypad, sensors, camera, RGB ring) with automatic environment detection and mock implementations for development on non-RPi systems.
-
Multi-Interface Access: Supports web browser access (port 4321), gRPC API (port 50051), SSH access, and direct hardware interaction, with a web UI service providing hotspot configuration and dashboard functionality.
-
System Integration: Integrates with
systemdandd-busfor service management, Docker for container runtime, andNetworkManagerfor network configuration, with a separate system manager process handling root-privilege operations via Unix sockets.
Notes:
The application follows a structured initialization sequence through ubo_app/main.py and uses the uv package manager for dependency management.
The architecture supports both production deployment on Raspberry Pi devices and development environments with comprehensive mocking systems, making it suitable for cross-platform development while maintaining hardware-specific capabilities.
DeepWiki pages you might want to explore:
Here are the key dependencies organized by category:
python-redux: Redux-based state management system for the entire appubo-gui: Custom GUI framework built on Kivy for the user interfaceheadless-kivy: Headless Kivy implementation for supporting LCD display over SPI
adafruit-circuitpython-rgb-display: ST7789 LCD display driveradafruit-circuitpython-neopixel: RGB LED ring controladafruit-circuitpython-aw9523: I2C GPIO expander for keypadadafruit-circuitpython-pct2075: Temperature sensor driveradafruit-circuitpython-veml7700: Light sensor driverrpi-lgpio: Low-level GPIO access for Raspberry Pigpiozero: GPIO abstraction layerrpi-ws281x: WS281x LED strip control librarypyalsaaudio: ALSA audio interface for Linux audio controlpulsectl: PulseAudio control for audio managementsimpleaudio: Simple audio playback functionality
piper-tts: Text-to-speech synthesis enginevosk: Speech recognition librarypvorca: Picovoice Text-to-speech synthesis enginepipecat-ai: framework for building real-time voice and multimodal conversational agents
aiohttp: Async HTTP client/server for web servicesquart: Async web framework for the web UI servicesdbus-networkmanager: NetworkManager D-Bus interface for WiFinetifaces: Network interface enumerationdocker: Docker API client for container management
pyzbar: QR code and barcode scanning library
psutil: System and process monitoring utilitiesplatformdirs: Platform-specific directory pathstenacity: Retry logic and error handlingfasteners: File locking and synchronization
python-fake: Mock hardware components for development
betterproto: Protocol buffer compiler and runtime
Notes:
The project uses platform-specific dependencies with markers like platform_machine=='aarch64' for Raspberry Pi-specific libraries and sys_platform=='linux' for Linux-only components. The python-fake library enables development on non-Raspberry Pi systems by providing mock implementations of hardware components.
This is a tentative roadmap for future features. It is subject to change.
- Emulation for camera and microphone inside browser (requires SSL certificate for browser permissions)
- Allow users to pick their soundcard for play and record via GUI (e.g. USB audio)
- Allow users to pick their camera for video via GUI (e.g. USB camera)
- Option to turn Ubo pod into a voice satellite with wyoming protocol with Home Assistant
- Make all on-board sensors and infrared discoverable and accessible by Home Assistant
- Let users record Infrared signals and assign them to trigger custom actions
- Expose
pipecat-aipreset pipeline configuration via GUI - Support for Debian Trixie (13)
If you have any suggestions or feature requests, please open a discussion here.
This project is released under the Apache-2.0 License. See the LICENSE file for more details.