-
-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 238
Protect
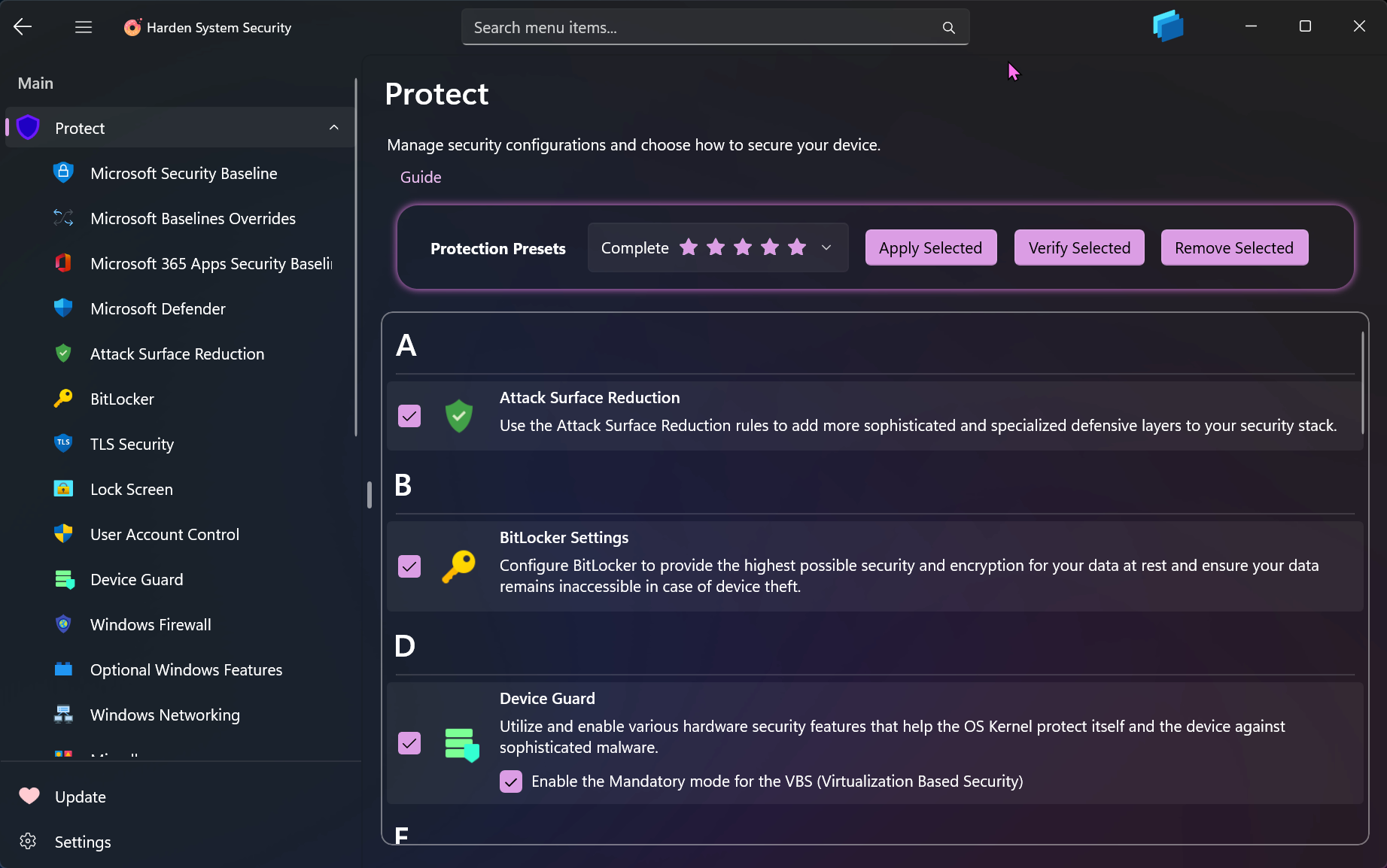
The Protect page in the Harden System Security App is a central hub for Applying, Verifying or Removing the security measures. It offers presets with optimal pre-selected categories and sub-categories to streamline the hardening process.
Each Security Measure category on this page has its own dedicated page where you can view and modify the specific settings related to that category in a more detailed manner. When you use the Apply, Verify or Remove buttons on this page, it is as if you are directly interacting with the button on that category's page.
Harden and secure your devices according to how you use them. Device Usage Intents work like the OS's Out-of-Box Experience (OOBE): during initial Windows setup you're asked how you'll use the device. Intents provide an easy, complementary way (in addition to the existing Presets) to configure your entire system. The currently available Device Usage Intents are:
-
Development: Built for writing and testing software. Uses secure defaults while allowing common developer tools and local builds without unnecessary restrictions.
-
Gaming: Tuned for performance and compatibility with games. Keeps essential protections while avoiding settings that can impact gameplay.
-
School: Suitable for students, keeps compatibility with learning apps, avoids heavy enterprise controls.
-
Business: Everyday corporate device with strong protections for work data and accounts. Balanced for productivity with sensible access, logging, and update behavior.
-
Specialized Access Workstation: The Specialized security user demands a more controlled environment while still being able to do activities such as email and web browsing in a simple-to-use experience.
-
Privileged Access Workstation: This is the highest security configuration designed for extremely sensitive roles that would have a significant or material impact on the organization if their account was compromised.
Each security measure in their own dedicated page is also annotated with device usage intent badges so you can easily tell which security measure belongs to which device usage intent.

Note
When the Microsoft Security Baselines or Microsoft 365 Security Baselines are selected in the Protect page, either via Presets or Device Intents, they will be applied first among the selected categories. Similarly, if the Overrides for Microsoft Security Baselines category is among the selected categories, it will be applied last. Any other categories that are selected will be applied between these priority groups. This type of prioritization ensures complete and proper application of the security measures.
The preview ListView lets you remove individual security measures before pressing Apply, giving you finer control over what gets applied. Items can be deleted in two ways:
-
Right-click (or Tap + Hold) a row and choose the delete option.
-
Swipe left on touch devices — a smooth animation and deletion motion will remove the item from the ListView.

- Create AppControl Policy
- Create Supplemental Policy
- System Information
- Configure Policy Rule Options
- Policy Editor
- Simulation
- Allow New Apps
- Build New Certificate
- Create Policy From Event Logs
- Create Policy From MDE Advanced Hunting
- Create Deny Policy
- Merge App Control Policies
- Deploy App Control Policy
- Get Code Integrity Hashes
- Get Secure Policy Settings
- Update
- Sidebar
- Validate Policies
- View File Certificates
- Microsoft Graph
- Protect
- Microsoft Security Baselines
- Microsoft Security Baselines Overrides
- Microsoft 365 Apps Security Baseline
- Microsoft Defender
- Attack Surface Reduction
- Bitlocker
- Device Guard
- TLS Security
- Lock Screen
- User Account Control
- Windows Firewall
- Optional Windows Features
- Windows Networking
- Miscellaneous Configurations
- Windows Update
- Edge Browser
- Certificate Checking
- Country IP Blocking
- Non Admin Measures
- Group Policy Editor
- Manage Installed Apps
- File Reputation
- Audit Policies
- Cryptographic Bill of Materials
- Introduction
- How To Generate Audit Logs via App Control Policies
- How To Create an App Control Supplemental Policy
- The Strength of Signed App Control Policies
- How To Upload App Control Policies To Intune Using AppControl Manager
- How To Create and Maintain Strict Kernel‐Mode App Control Policy
- How to Create an App Control Deny Policy
- App Control Notes
- How to use Windows Server to Create App Control Code Signing Certificate
- Fast and Automatic Microsoft Recommended Driver Block Rules updates
- App Control policy for BYOVD Kernel mode only protection
- EKUs in App Control for Business Policies
- App Control Rule Levels Comparison and Guide
- Script Enforcement and PowerShell Constrained Language Mode in App Control Policies
- How to Use Microsoft Defender for Endpoint Advanced Hunting With App Control
- App Control Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- System Integrity Policy Transformations | XML to CIP and Back
- About Code Integrity Policy Signing
- Create Bootable USB flash drive with no 3rd party tools
- Event Viewer
- Group Policy
- How to compact your OS and free up extra space
- Hyper V
- Git GitHub Desktop and Mandatory ASLR
- Signed and Verified commits with GitHub desktop
- About TLS, DNS, Encryption and OPSEC concepts
- Things to do when clean installing Windows
- Comparison of security benchmarks
- BitLocker, TPM and Pluton | What Are They and How Do They Work
- How to Detect Changes in User and Local Machine Certificate Stores in Real Time Using PowerShell
- Cloning Personal and Enterprise Repositories Using GitHub Desktop
- Only a Small Portion of The Windows OS Security Apparatus
- Rethinking Trust: Advanced Security Measures for High‐Stakes Systems
- Clean Source principle, Azure and Privileged Access Workstations
- How to Securely Connect to Azure VMs and Use RDP
- Basic PowerShell tricks and notes
- Basic PowerShell tricks and notes Part 2
- Basic PowerShell tricks and notes Part 3
- Basic PowerShell tricks and notes Part 4
- Basic PowerShell tricks and notes Part 5
- How To Access All Stream Outputs From Thread Jobs In PowerShell In Real Time
- PowerShell Best Practices To Follow When Coding
- How To Asynchronously Access All Stream Outputs From Background Jobs In PowerShell
- Powershell Dynamic Parameters and How to Add Them to the Get‐Help Syntax
- RunSpaces In PowerShell
- How To Use Reflection And Prevent Using Internal & Private C# Methods in PowerShell
