-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 4
Metagnomics background

Overview
Shotgun metagenomic sequencing allows researchers to comprehensively sample all DNA in all organisms present in a given complex samples such as humans or the environment. The method enables microbiologists to evaluate bacterial diversity and detect the abundance of microbes in various environments. Shotgun metagenomics also provides a means to study unculturable microorganisms that are otherwise difficult or impossible to analyze.
There are many different ways to analyze a shotgun metagenome though the quality and amount of data can be the deciding factor on which route to take. For larger, high quality datasets, de novo sequencing is often an option worth entertaining. For sparse and/or lower quality datasets assembly free methods such as binning or marker gene analysis are the preferred methods.
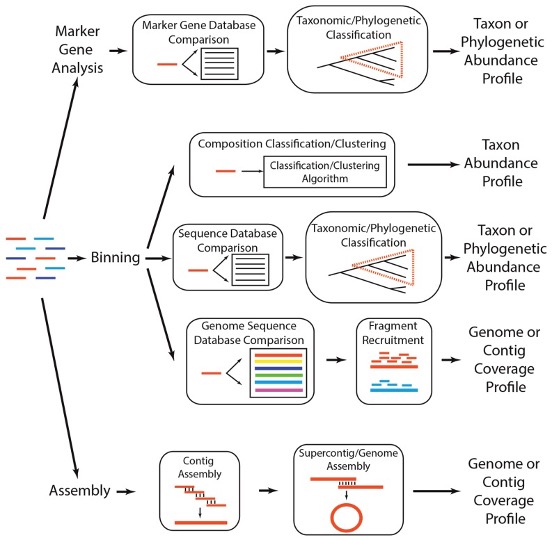
Sharpton TJ (2014) An introduction to analyzing shotgun metagenomic data. Front. Plant Sci. 5:209. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2014.00209
metagenomics VS amplicon sequencing
Amplicon sequencing targets sequences of a gene (or regions in a specific gene) called marker genes to identify organisms in certain samples. It involves using specific primers that can 'amplify' and produce multiple copies of sequences. Whereas shotgun metagenomic sequencing aims to sequence all the accessible DNA in mixed communities. Metagenomics provides not only taxonomic identification but also functional analysis of the sample as well.
Some people think that shotgun metagenomics is a much more powerful tool than amplicon sequencing since it provides higher resolution. However, each approach has its advantages and disadvantages.
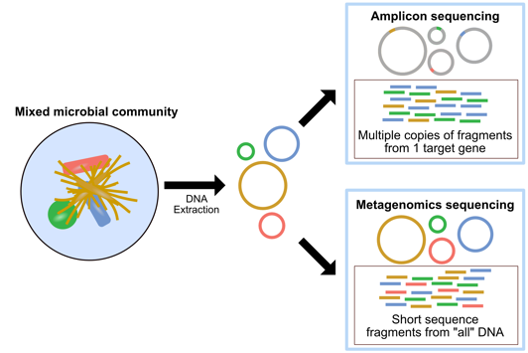
Advantages and disadvantages of each approaches
| Category | Amplicon sequencing | Metagnomics |
|---|---|---|
| Bacterial coverage | High | Limited |
| Host contamination | No | Yes |
| False positives | low | high |
| Taxonomy resolution | Genus or species | Species or strains |
| Functional profiling | limited | Yes |
- Home
- Basic resources
- Metagenomics workshop (In progress)