-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 497
Apache Kafka Clients: Usage & Best Practices
Apache Kafka has become a cornerstone technology for building real-time data pipelines and streaming applications. At the heart of any Kafka implementation are the client libraries that allow applications to interact with Kafka clusters. This comprehensive guide explores Kafka clients, their configuration, and best practices to ensure optimal performance, reliability, and security.
Kafka clients are software libraries that enable applications to communicate with Kafka clusters. They provide the necessary APIs to produce messages to topics and consume messages from topics, forming the foundation for building distributed applications and microservices.
The official Confluent-supported clients include:
-
Java : The original and most feature-complete client, supporting producer, consumer, Streams, and Connect APIs
-
C/C++ : Based on librdkafka, supporting admin, producer, and consumer APIs
-
Python : A Python wrapper around librdkafka
-
Go : A Go implementation built on librdkafka
-
.NET : For .NET applications
-
JavaScript : For Node.js and browser applications
These client libraries follow Confluent's release cycle, ensuring enterprise-level support for organizations using Confluent Platform[4].
Producers are responsible for publishing data to Kafka topics. Their performance and reliability directly impact the entire streaming pipeline.
Several configuration parameters significantly influence producer behavior:
-
Batch Size and Linger Time
-
Acknowledgments
-
acks: Determines the level of delivery guarantees -
acks=all: Provides strongest guarantee but impacts throughput -
acks=0: Offers maximum throughput but no delivery guarantees[15]
-
-
Retry Mechanism
-
retries: Number of retries before failing -
retry.backoff.ms: Time between retries -
delivery.timeout.ms: Upper bound for the total time between sending and acknowledgment[20]
-
-
Idempotence and Transactions
-
enable.idempotence=true: Prevents duplicate messages when retries occur -
Transaction APIs: Enable exactly-once semantics[1]
-
For optimal producer performance, consider these best practices:
-
Throughput Optimization
-
Balance batch size and linger time based on latency requirements
-
Implement compression to reduce data size and improve throughput
-
Use appropriate partitioning strategies for even data distribution[10]
-
-
Error Handling
-
Implement robust retry mechanisms with exponential backoff
-
Enable idempotence for exactly-once processing semantics
-
Use synchronous commits for critical data and asynchronous for higher throughput[1]
-
-
Resource Allocation
-
Monitor and adjust memory allocation based on performance metrics
-
Set appropriate buffer sizes based on message volume[3]
-
Consumers read messages from Kafka topics and process them. Proper consumer configuration ensures efficient data processing and prevents issues like consumer lag.
Important consumer configuration parameters include:
-
Group Management
-
group.id: Identifies the consumer group -
heartbeat.interval.ms: Frequency of heartbeats to the coordinator -
max.poll.interval.ms: Maximum time between poll calls before rebalancing[11]
-
-
Offset Management
-
enable.auto.commit: Controls automatic offset commits -
auto.offset.reset: Determines behavior when no offset is found ("earliest", "latest", "none") -
max.poll.records: Maximum records returned in a single poll call[11]
-
-
Performance Settings
For reliable and efficient consumers, implement these best practices:
-
Partition Management
-
Choose the right number of partitions based on throughput requirements
-
Maintain consumer count consistency relative to partitions
-
Use a replication factor greater than 2 for fault tolerance[18]
-
-
Offset Commit Strategy
-
Disable auto-commit (
enable.auto.commit=false) for critical applications -
Implement manual commit strategies after successful processing
-
Balance commit frequency to minimize reprocessing risk while maintaining performance[11]
-
-
Error Handling
-
Implement robust error handling for transient errors
-
Have a strategy for handling poison pill messages (messages that consistently fail processing)
-
Configure appropriate
retry.backoff.msvalues to prevent retry storms[16]
-
Security is paramount when implementing Kafka clients in production environments. Key security considerations include:
-
Authentication
-
Implement SASL (SCRAM, GSSAPI) or mTLS for client authentication
-
Configure SSL/TLS to encrypt data in transit
-
Use environment variables or secure vaults to manage credentials rather than hardcoding them[13]
-
-
Authorization
-
Implement ACLs (Access Control Lists) to control read/write access to topics
-
Follow the principle of least privilege when assigning permissions
-
Enable
zookeeper.set.aclin secure clusters to enforce access controls[13]
-
-
Secret Management
-
Avoid storing secrets as cleartext in configuration files
-
Consider using Confluent's Secret Protection or the Connect Secret Registry
-
Implement envelope encryption for protecting sensitive configuration values[13]
-
Achieving optimal performance requires careful monitoring and tuning of Kafka clients.
-
JVM Tuning (for Java clients)
-
Allocate sufficient heap space
-
Configure garbage collection appropriately
-
Consider using G1GC for large heaps[3]
-
-
Network Configuration
-
Optimize
socket.send.buffer.bytesandsocket.receive.buffer.bytes -
Adjust
connections.max.idle.msto manage connection lifecycle -
Configure appropriate timeouts based on network characteristics[2]
-
-
Compression Settings
-
Enable compression (
compression.type=snappyorgzip) for better network utilization -
Balance compression ratio against CPU usage[10]
-
Implement comprehensive monitoring for early detection of issues:
-
Key Metrics to Watch
-
Consumer lag: Difference between the latest produced offset and consumed offset
-
Produce/consume throughput: Messages processed per second
-
Request latency: Time taken for requests to complete
-
Error rates: Frequency of different error types[1]
-
-
Monitoring Tools
-
JMX metrics for Java applications
-
Prometheus and Grafana for visualization
-
Conduktor or other Kafka UI tools for comprehensive cluster monitoring[19]
-
-
Alerting
-
Set up alerts for critical metrics exceeding thresholds
-
Implement progressive alerting based on severity
-
Ensure alerts include actionable information[1]
-
Even with best practices in place, issues can arise. Here are common problems and their solutions:
-
Broker Not Available
-
Check if brokers are running
-
Verify network connectivity
-
Review firewall settings that might block connections[7]
-
-
Leader Not Available
-
Ensure broker that went down is restarted
-
Force a leader election if necessary
-
Check for network partitions[7]
-
-
Offset Out of Range
-
Verify retention policies
-
Reset consumer group offsets to a valid position
-
Adjust
auto.offset.resetconfiguration[7]
-
-
In-Sync Replica Alerts
-
Address under-replicated partitions promptly
-
Check for resource constraints on brokers
-
Consider adding more brokers or redistributing partitions[8]
-
-
Slow Production/Consumption
When developing applications that use Kafka clients, follow these best practices:
-
Version Compatibility
-
Use the latest supported client version for your Kafka cluster
-
Be aware of protocol compatibility between clients and brokers
-
Consider the impact of client upgrades on existing applications[4]
-
-
Connection Management
-
Implement connection pooling for better resource utilization
-
Handle reconnection logic gracefully
-
Properly close resources when they're no longer needed[2]
-
-
Error Handling
-
Design for fault tolerance with appropriate retry mechanisms
-
Implement dead letter queues for messages that repeatedly fail processing
-
Log detailed error information for troubleshooting[1]
-
-
Testing and Validation
-
Implement comprehensive testing of client applications
-
Include failure scenarios in test cases
-
Perform load testing to understand performance characteristics under stress[1]
-
Several web UI tools can simplify Kafka cluster management:
-
Conduktor
-
Offers intuitive user interface for managing Kafka
-
Provides monitoring, testing, and management capabilities
-
Features excellent UI/UX design[19]
-
-
Redpanda Console
-
Lightweight alternative with clean interface
-
Offers topic management and monitoring
-
Provides schema registry integration[19]
-
-
Apache Kafka Tools
-
Open-source options available
-
May require more setup and configuration
-
Often offer basic functionality for smaller deployments[19]
-
These tools can complement your client applications by providing visibility into cluster operations and simplifying management tasks.
Check more tools here: Top 12 Free Kafka GUI Tools
Kafka clients form the foundation of any successful Kafka implementation. By understanding their configuration options and following best practices, you can ensure reliable, secure, and high-performance data streaming applications.
Key takeaways include:
-
Select appropriate client libraries based on your programming language and requirements
-
Configure producers and consumers with careful attention to performance, reliability, and security parameters
-
Implement proper error handling and monitoring
-
Follow security best practices to protect data and access
-
Regularly test and validate client applications under various conditions
-
Use management tools to gain visibility and simplify operations
By adhering to these guidelines, you'll be well-positioned to leverage the full potential of Apache Kafka in your data streaming architecture.
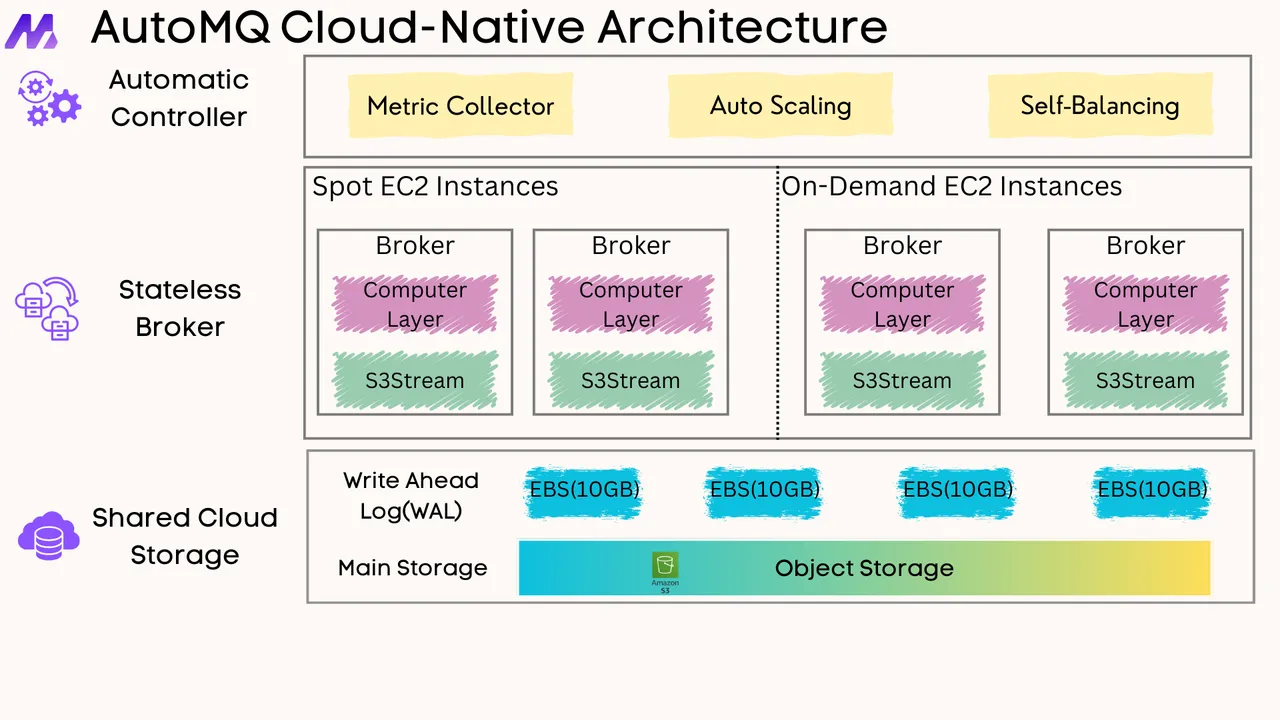
If you find this content helpful, you might also be interested in our product AutoMQ. AutoMQ is a cloud-native alternative to Kafka by decoupling durability to S3 and EBS. 10x Cost-Effective. No Cross-AZ Traffic Cost. Autoscale in seconds. Single-digit ms latency. AutoMQ now is source code available on github. Big Companies Worldwide are Using AutoMQ. Check the following case studies to learn more:
-
Grab: Driving Efficiency with AutoMQ in DataStreaming Platform
-
Palmpay Uses AutoMQ to Replace Kafka, Optimizing Costs by 50%+
-
How Asia’s Quora Zhihu uses AutoMQ to reduce Kafka cost and maintenance complexity
-
XPENG Motors Reduces Costs by 50%+ by Replacing Kafka with AutoMQ
-
Asia's GOAT, Poizon uses AutoMQ Kafka to build observability platform for massive data(30 GB/s)
-
AutoMQ Helps CaoCao Mobility Address Kafka Scalability During Holidays
- What is automq: Overview
- Difference with Apache Kafka
- Difference with WarpStream
- Difference with Tiered Storage
- Compatibility with Apache Kafka
- Licensing
- Deploy Locally
- Cluster Deployment on Linux
- Cluster Deployment on Kubernetes
- Example: Produce & Consume Message
- Example: Simple Benchmark
- Example: Partition Reassignment in Seconds
- Example: Self Balancing when Cluster Nodes Change
- Example: Continuous Data Self Balancing
- Architecture: Overview
- S3stream shared streaming storage
- Technical advantage
- Deployment: Overview
- Runs on Cloud
- Runs on CEPH
- Runs on CubeFS
- Runs on MinIO
- Runs on HDFS
- Configuration
- Data analysis
- Object storage
- Kafka ui
- Observability
- Data integration