-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 382
Apache Kafka vs. Confluent Platform
Apache Kafka and Confluent Platform represent two interconnected but distinct options for implementing event streaming architecture. While Apache Kafka provides the foundational open-source framework, Confluent Platform extends it with enterprise-grade features and tools. This report examines their key differences, capabilities, configuration approaches, and best practices to help organizations make informed decisions.
Apache Kafka is an open-source distributed event streaming platform developed by the Apache Software Foundation. Written in Scala and Java, it provides a unified, high-throughput, low-latency platform for handling real-time data feeds[6]. Kafka's core capabilities include fault-tolerant storage, processing streams of records, and performing real-time analysis.
Confluent Platform, on the other hand, is a commercial distribution built on top of Apache Kafka, developed by Confluent—a company founded by the original creators of Kafka. It extends Kafka's capabilities with additional enterprise-grade tools and services[1][9].
|
Feature |
Apache Kafka |
Confluent Platform |
|---|---|---|
|
Origin |
Open-source project primarily for stream processing |
Commercial offering built on Kafka with enhanced features[1] |
|
Feature Set |
Core features: publish-subscribe messaging, fault tolerance, high throughput |
All Kafka features plus schema registry, REST proxy, and various connectors[1] |
|
Ease of Use |
Requires manual setup and configuration |
More user-friendly with additional tools and pre-built connectors[1] |
|
Support |
Community support; professional support via third parties |
Professional support, training, and consultancy included[1] |
|
Pricing |
Free and open-source |
Free community version and paid enterprise options[1][17] |
|
Licensing |
Apache 2.0 License |
Confluent Community License (with restrictions) and Enterprise License[17] |
Kafka's architecture is distributed, fault-tolerant, and scalable[6]. The key components include:
-
Brokers : Kafka servers responsible for receiving, storing, and replicating data
-
Topics : Logical groupings of events
-
Partitions : Append-only, ordered log files holding subsets of topic data
-
Producers : Applications that publish data to topics
-
Consumers : Applications that subscribe to and process data from topics
-
Consumer Groups : Logical groupings of consumers sharing processing load
-
Zookeeper/KRaft : For coordination and configuration management[6]
Confluent extends Kafka with several enterprise components[2][15]:
-
Schema Registry : Enforces schemas for message consistency
-
ksqlDB : SQL-based stream processing
-
Kafka Connect : Pre-built connectors for integrating with external systems
-
Control Center : GUI for monitoring and managing clusters
-
Enhanced Security : LDAP integration, Role-Based Access Control (RBAC)
-
Cluster Linking : Simplifies replication between Kafka clusters[15]
Confluent claims significant performance advantages over Apache Kafka, particularly with their cloud-native Kafka engine called Kora.
According to Confluent's benchmarks:
-
Confluent Cloud is up to 10x faster than Apache Kafka[14]
-
End-to-end latency improvements of up to 12x at higher throughputs[14]
-
More consistent performance at tail latencies (p99), showing 16x better performance[14]
Redpanda, another streaming platform, also published comparisons showing performance differences with Kafka using KRaft[4], demonstrating the ongoing competition in the streaming platform space.
Several factors influence Kafka/Confluent performance:
-
Partitioning strategy : Proper partition design is crucial for parallelism and load balancing[13]
-
Compression : Using compression for producers reduces network bandwidth requirements[5]
-
Network and I/O threads : Tuning these parameters affects throughput and latency[5][14]
-
Replica fetchers : Increasing these can improve replication performance[14]
Top configuration parameters to tune for better performance include:
-
Partitioning : Increase partition numbers based on workload requirements[5]
-
Replica lag time : Tune
replica.lag.time.max.msfor optimal replication[5] -
Threading : Adjust
num.network.threadsandnum.io.threadsfor better concurrency[5][14] -
Compression : Enable compression for producers to reduce network bandwidth[5]
-
Batch size : Increase producer batch size for higher throughput at the cost of latency[12]
Confluent Platform offers additional configuration options:
-
Schema Validation : Enable with
confluent.value.schema.validation=truefor data quality[16] -
Quotas : Configure client quotas to prevent resource starvation[16]
-
Secret Protection : Use envelope encryption instead of plaintext configuration[16]
-
Structured Audit Logs : Enable for capturing security events[16]
Apache Kafka provides fundamental security features:
-
Authentication via SASL mechanisms
-
Authorization with ACLs
-
Encryption with SSL/TLS
-
Network segmentation[16]
Confluent Platform adds enterprise security capabilities:
-
Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) : More granular access control than Kafka ACLs
-
Secret Protection : Protects encrypted secrets through envelope encryption
-
Structured Audit Logs : Records authorization decisions in structured format
-
Connect Secret Registry : Manages secrets for Kafka Connect through REST API[16]
Apache Kafka :
-
Self-managed deployment requiring manual setup and configuration
-
Requires expertise in Kafka administration and operations[1]
Confluent Platform :
-
Self-managed Confluent Platform: Enhanced tools but still requires internal operations
-
Confluent Cloud: Fully-managed SaaS offering with minimal operational overhead[8]
Apache Kafka :
-
Requires third-party monitoring tools
-
Manual management of logging and metrics
-
Controller logs in
logs/controller.logand state change logs inlogs/state-change.log[10]
Confluent Platform :
-
Confluent Control Center for monitoring and management
-
Integrated metrics and alerting
-
Simplified cluster management[1][2]
Several common Kafka issues affect both platforms:
-
Broker Not Available : When producers/consumers can't connect to brokers
- Resolution: Check if broker is running, verify network connectivity[7]
-
Leader Not Available : When a partition leader is unavailable
- Resolution: Restart failed brokers or force leader election manually[7]
-
Offset Out of Range : When consumers request unavailable offsets
- Resolution: Adjust consumer configurations or reset offsets[7]
-
Authentication Errors : When security settings are misconfigured
- Resolution: Verify credentials and security protocols[7]
Confluent-specific tools can help troubleshoot these issues more efficiently but may introduce their own complexity.
-
Real-time analytics : Processing and analyzing data streams
-
Data integration : Connecting disparate systems
-
Event-driven architectures : Building reactive applications
-
Stream processing : Transforming data in motion[8]
Confluent Platform is particularly valuable when:
-
Enterprise-level support and SLAs are required
-
Pre-built connectors would accelerate development
-
Schema management is critical for data governance
-
Complex security requirements exist
-
Management tooling would reduce operational burden[11][15]
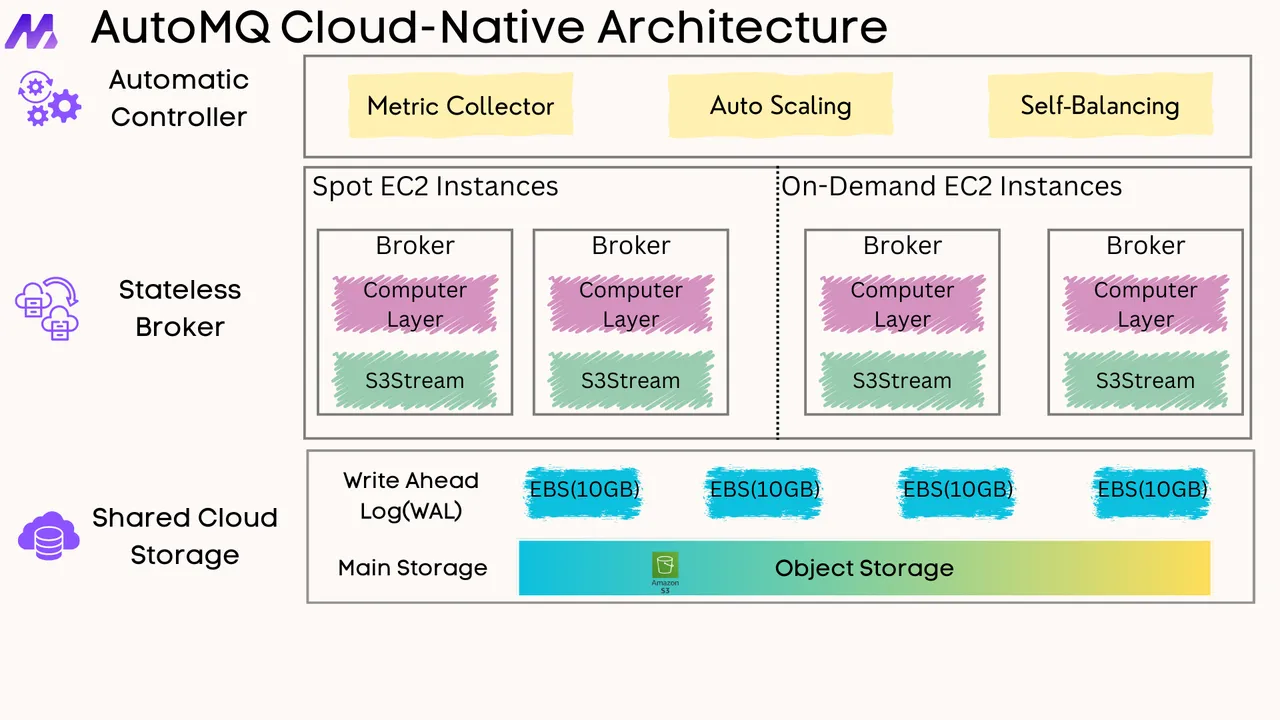
For organizations seeking alternatives to Confluent, several options are available, each offering unique advantages. One of the most promising alternatives is AutoMQ , a cloud-native solution designed to reimagine Kafka's architecture for cost efficiency and scalability.
AutoMQ is built as a replacement for Apache Kafka, leveraging shared storage like Amazon S3 and stateless brokers to significantly reduce operational costs. It offers 10x cost-effectiveness compared to traditional Kafka setups by eliminating data replication and utilizing Spot instances for compute resources[2][4]. AutoMQ's architecture ensures single-digit millisecond latency while maintaining high throughput, making it suitable for real-time data streaming applications[6]. It also provides 100% compatibility with Kafka protocols, allowing seamless integration with existing Kafka ecosystems[4].
-
Cost Efficiency : AutoMQ reduces costs by up to 90% compared to Apache Kafka and Confluent, primarily through optimized EC2 resource usage and shared storage[3][5].
-
Stateless Brokers : Enables elastic scaling and reduces operational complexity by eliminating the need for data replication across brokers[1][4].
-
Shared Storage : Utilizes object storage like S3, eliminating cross-AZ replication costs and improving scalability[5].
-
Latency Performance : Offers superior latency compared to other Kafka alternatives like WarpStream, with single-digit millisecond P99 latency[6].
-
Compatibility : Fully compatible with Kafka protocols, ensuring easy migration from existing Kafka environments[4].
The choice between Apache Kafka and Confluent Platform ultimately depends on organizational needs, resources, and priorities. Apache Kafka provides a robust open-source foundation for event streaming, suitable for organizations with the technical expertise to manage complex distributed systems. Confluent Platform enhances Kafka with enterprise features, management tools, and support services that can reduce operational burden and accelerate development.
For organizations just starting with event streaming or with limited Kafka expertise, Confluent's offerings—especially Confluent Cloud—can provide a more accessible entry point. For those with existing Kafka expertise and a desire for maximum control and customization, the open-source Apache Kafka may be sufficient.
When evaluating either option, organizations should consider performance requirements, operational capabilities, budget constraints, and specific use cases to determine the best fit for their event streaming needs.
If you find this content helpful, you might also be interested in our product AutoMQ. AutoMQ is a cloud-native alternative to Kafka by decoupling durability to S3 and EBS. 10x Cost-Effective. No Cross-AZ Traffic Cost. Autoscale in seconds. Single-digit ms latency. AutoMQ now is source code available on github. Big Companies Worldwide are Using AutoMQ. Check the following case studies to learn more:
-
Grab: Driving Efficiency with AutoMQ in DataStreaming Platform
-
Palmpay Uses AutoMQ to Replace Kafka, Optimizing Costs by 50%+
-
How Asia’s Quora Zhihu uses AutoMQ to reduce Kafka cost and maintenance complexity
-
XPENG Motors Reduces Costs by 50%+ by Replacing Kafka with AutoMQ
-
Asia's GOAT, Poizon uses AutoMQ Kafka to build observability platform for massive data(30 GB/s)
-
AutoMQ Helps CaoCao Mobility Address Kafka Scalability During Holidays
-
JD.com x AutoMQ x CubeFS: A Cost-Effective Journey at Trillion-Scale Kafka Messaging
- What is automq: Overview
- Difference with Apache Kafka
- Difference with WarpStream
- Difference with Tiered Storage
- Compatibility with Apache Kafka
- Licensing
- Deploy Locally
- Cluster Deployment on Linux
- Cluster Deployment on Kubernetes
- Example: Produce & Consume Message
- Example: Simple Benchmark
- Example: Partition Reassignment in Seconds
- Example: Self Balancing when Cluster Nodes Change
- Example: Continuous Data Self Balancing
-
S3stream shared streaming storage
-
Technical advantage
- Deployment: Overview
- Runs on Cloud
- Runs on CEPH
- Runs on CubeFS
- Runs on MinIO
- Runs on HDFS
- Configuration
-
Data analysis
-
Object storage
-
Kafka ui
-
Observability
-
Data integration